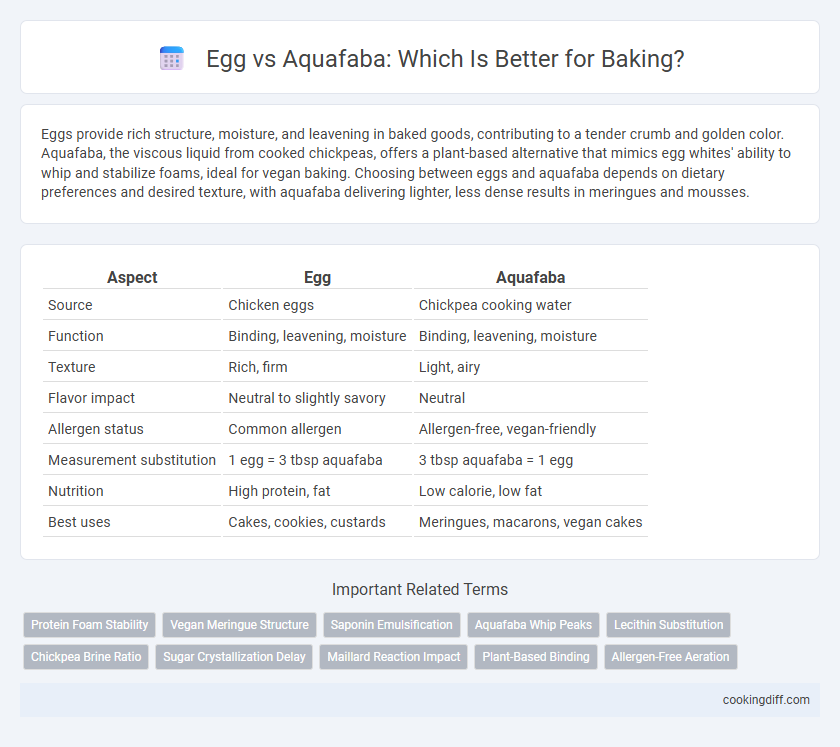
Eggs provide rich structure, moisture, and leavening in baked goods, contributing to a tender crumb and golden color. Aquafaba, the viscous liquid from cooked chickpeas, offers a plant-based alternative that mimics egg whites' ability to whip and stabilize foams, ideal for vegan baking. Choosing between eggs and aquafaba depends on dietary preferences and desired texture, with aquafaba delivering lighter, less dense results in meringues and mousses.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Egg | Aquafaba |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Chicken eggs | Chickpea cooking water |
| Function | Binding, leavening, moisture | Binding, leavening, moisture |
| Texture | Rich, firm | Light, airy |
| Flavor impact | Neutral to slightly savory | Neutral |
| Allergen status | Common allergen | Allergen-free, vegan-friendly |
| Measurement substitution | 1 egg = 3 tbsp aquafaba | 3 tbsp aquafaba = 1 egg |
| Nutrition | High protein, fat | Low calorie, low fat |
| Best uses | Cakes, cookies, custards | Meringues, macarons, vegan cakes |
Understanding Eggs and Aquafaba: Key Differences
What are the key differences between eggs and aquafaba in baking? Eggs provide structure, moisture, and leavening due to their protein and fat content, making them essential in many traditional recipes. Aquafaba, the viscous water from cooked chickpeas, offers a vegan-friendly alternative by mimicking egg whites' binding and emulsifying properties without adding fat or cholesterol.
Nutritional Comparison: Eggs vs Aquafaba
| Component | Egg | Aquafaba |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 68 kcal per large egg | 3 kcal per 3 tablespoons |
| Protein | 6 grams | Less than 0.5 grams |
| Fat | 5 grams, including 1.6 grams saturated fat | Negligible fat |
| Cholesterol | 186 mg | 0 mg |
| Carbohydrates | Less than 1 gram | About 1 gram |
| Vitamins & Minerals | Rich in B vitamins, selenium, and vitamin D | Minimal vitamins and trace minerals |
Functional Properties in Baking
Eggs provide superior emulsifying, binding, and leavening properties essential for traditional baking structures. Aquafaba serves as a versatile vegan alternative, mimicking egg whites' foaming ability but with less protein content.
- Emulsification - Eggs stabilize mixtures by combining fats and liquids, ensuring uniform texture and moisture retention.
- Binding - Egg proteins coagulate upon heating, creating structure and preventing crumbly textures.
- Leavening - Whipped aquafaba traps air effectively, contributing to volume and lightness in baked goods.
Texture and Flavor Impact
Eggs contribute a rich, creamy texture and enhance the flavor profile in baked goods, providing moisture and structure that help products rise and retain softness. The proteins in eggs create a firmer crumb with a slight richness that is difficult to replicate.
Aquafaba, the liquid from cooked chickpeas, offers a lighter and airier texture, making it ideal for vegan baking where a fluffy consistency is desired. Its subtle, neutral flavor allows other ingredients to shine, though it lacks the depth of taste imparted by eggs.
Whipping and Leavening Abilities
Eggs provide superior whipping and leavening properties due to their unique protein structure that stabilizes air bubbles effectively in baked goods. Aquafaba, the viscous liquid from cooked chickpeas, can mimic egg whites but generally produces lighter foams with less stability and rising power.
- Eggs create stable foams - Their albumin proteins coagulate and trap air, enhancing volume and texture.
- Aquafaba forms lighter foams - Its sugar and protein content helps incorporate air but results in softer peaks.
- Eggs offer stronger leavening - Chemical and physical interactions during baking lead to better rise and structure.
While aquafaba is a valuable vegan alternative, eggs remain the gold standard for whipping and leavening efficiency in baking.
Allergy and Dietary Considerations
Eggs are a common allergen and unsuitable for vegan diets, while aquafaba offers a plant-based, allergen-friendly alternative derived from chickpea water. Aquafaba mimics egg whites in baking, making it ideal for individuals with egg allergies or those following vegan and low-cholesterol dietary plans.
- Egg allergies - Affect approximately 1-2% of adults and 6-8% of children worldwide, requiring substitution in recipes.
- Vegan suitability - Aquafaba is entirely plant-based, catering to ethical and dietary vegan choices.
- Cholesterol content - Eggs contain cholesterol, whereas aquafaba is cholesterol-free, supporting heart-healthy diets.
Vegan and Plant-Based Baking Benefits
Eggs provide structure, moisture, and leavening in traditional baking, but aquafaba, the liquid from cooked chickpeas, serves as an excellent vegan alternative that mimics these properties. Aquafaba enables plant-based bakers to create airy, fluffy textures without animal products, making it ideal for vegan cakes, meringues, and cookies.
Using aquafaba supports sustainable baking by reducing reliance on animal agriculture and lowering carbon footprints. Its versatility allows for emulsification and binding similar to eggs, enhancing recipes while keeping them allergen-friendly. Many plant-based bakers prefer aquafaba for its neutral flavor and ability to create stable foams in vegan desserts.
Substitution Ratios and Best Practices
When substituting eggs with aquafaba in baking, use 3 tablespoons of aquafaba to replace one whole egg for optimal texture and binding. Aquafaba works best in recipes where eggs serve as a binding agent rather than for leavening, so adjust baking times slightly for moisture retention. Whip aquafaba until it forms soft peaks to mimic egg whites, enhancing its effectiveness in cakes, meringues, and cookies.
Popular Recipes for Each Ingredient
Eggs are a staple in baking recipes such as classic pound cakes, souffles, and meringues due to their binding and leavening properties. Aquafaba, the liquid from cooked chickpeas, is popular in vegan baking, commonly used for making dairy-free macarons, mousses, and fluffy cakes. Both ingredients serve as effective emulsifiers and foaming agents, but aquafaba provides a plant-based alternative favored in allergy-friendly recipes.
Related Important Terms
Protein Foam Stability
Egg whites contain high-quality proteins such as ovalbumin that create a stable foam with excellent structure and volume, essential for meringues and souffles. Aquafaba, derived from chickpea brine, forms a less stable foam with lower protein content, resulting in softer textures and reduced hold in baked goods compared to egg proteins.
Vegan Meringue Structure
Egg-based meringue achieves a stable, glossy structure due to the high protein content and ability to trap air during whipping, while aquafaba, derived from chickpea water, mimics this functionality by forming a similar protein and carbohydrate foam network essential for vegan meringue stability. Although aquafaba requires longer whipping times and may yield a slightly softer texture, it provides a reliable egg-free alternative that maintains structure and moisture in vegan baking.
Saponin Emulsification
Aquafaba contains natural saponins that enhance emulsification in baking by stabilizing mixtures and improving texture, making it an effective egg substitute for vegan and allergy-friendly recipes. Eggs provide lecithin, a phospholipid that also supports emulsification but may lack the plant-based saponins found in aquafaba, which contribute to superior foam stability and moisture retention.
Aquafaba Whip Peaks
Aquafaba, the viscous water from cooked chickpeas, creates stable, airy whip peaks that closely mimic egg whites in baking, making it an ideal vegan substitute for meringues, macarons, and mousses. Its ability to trap air and maintain structure enhances the texture and rise of baked goods without altering flavor, providing an allergen-free alternative to eggs.
Lecithin Substitution
Eggs provide lecithin, a natural emulsifier critical for stable batter and moisture retention in baking, while aquafaba, derived from chickpea water, offers a plant-based lecithin substitute that mimics egg's emulsifying properties though with slightly less binding strength. Using aquafaba enhances vegan and allergen-free recipes by improving texture and rise without compromising the structural integrity normally supported by egg lecithin.
Chickpea Brine Ratio
Aquafaba, the chickpea brine substitute, typically requires a ratio of 3 tablespoons to replace one whole egg in baking recipes, providing comparable binding and moisture. Its unique composition of proteins and starches mimics egg properties, making it ideal for vegan cakes, meringues, and cookies without impacting flavor.
Sugar Crystallization Delay
Eggs in baking provide proteins that stabilize sugar crystals, effectively delaying sugar crystallization and improving texture by maintaining moisture balance. Aquafaba, a plant-based substitute, lacks the same protein structure but offers polysaccharides and saponins that moderately slow sugar crystallization, making it ideal for vegan recipes with slightly different textural outcomes.
Maillard Reaction Impact
Eggs contribute to the Maillard reaction in baking through the presence of proteins and sugars, enhancing browning, flavor, and texture. Aquafaba, lacking proteins but containing carbohydrates, results in less intense Maillard browning and a lighter crust color in baked goods.
Plant-Based Binding
Aquafaba, the viscous water from cooked chickpeas, serves as an effective plant-based binding agent in baking, mimicking the emulsifying and leavening properties of eggs. It provides moisture and structure in vegan recipes, allowing baked goods to achieve a similar texture and rise without animal products.
Egg vs Aquafaba for baking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com