Regular butter provides a creamy texture and mild flavor that enhances cookie softness and richness, making it a classic choice for everyday recipes. Brown butter, created by gently cooking butter until it turns golden and develops a nutty aroma, adds depth and complexity, resulting in cookies with a caramelized, slightly toasty taste and crisp edges. Choosing between regular and brown butter impacts the cookie's flavor profile and texture, with brown butter elevating traditional recipes to gourmet levels.
Table of Comparison
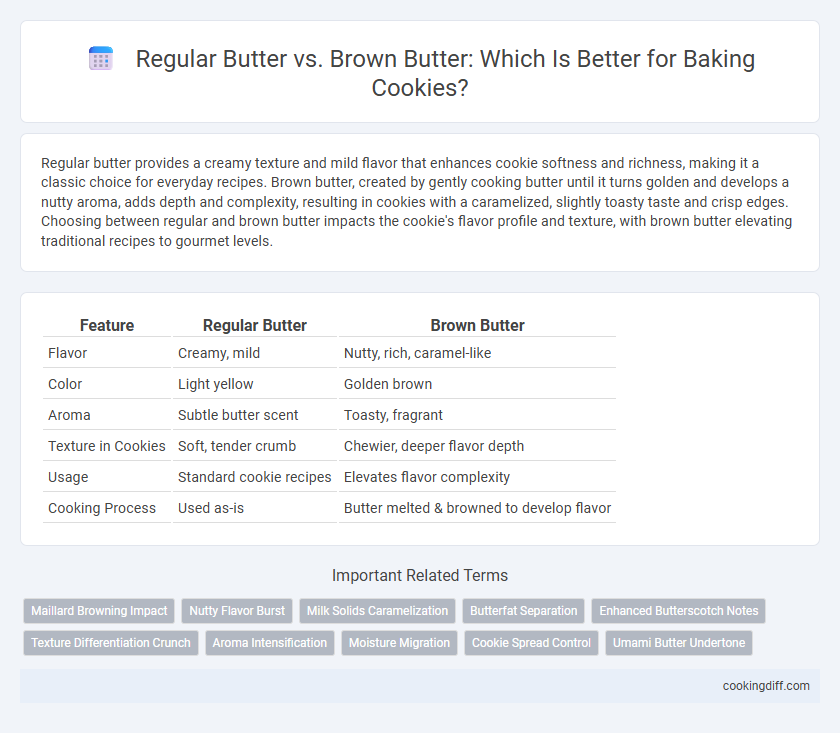
| Feature | Regular Butter | Brown Butter |
|---|---|---|
| Flavor | Creamy, mild | Nutty, rich, caramel-like |
| Color | Light yellow | Golden brown |
| Aroma | Subtle butter scent | Toasty, fragrant |
| Texture in Cookies | Soft, tender crumb | Chewier, deeper flavor depth |
| Usage | Standard cookie recipes | Elevates flavor complexity |
| Cooking Process | Used as-is | Butter melted & browned to develop flavor |
Understanding Regular Butter and Brown Butter
Regular butter contains about 80% fat and 20% water, providing a creamy texture and mild flavor essential for classic cookie recipes. Brown butter undergoes a cooking process where milk solids caramelize, creating a nutty aroma and deeper, richer taste that enhances cookie complexity. Understanding these differences allows bakers to choose between the smoothness of regular butter and the distinctive flavor profile of brown butter for optimal cookie results.
Flavor Profiles: Regular vs Brown Butter
Regular butter provides a creamy, rich flavor that enhances the traditional sweetness of cookies without overpowering other ingredients. Brown butter offers a nutty, caramelized depth that adds complexity and a slightly toasted aroma to baked goods.
- Regular Butter Flavor - Mild and creamy taste that maintains the classic cookie profile.
- Brown Butter Flavor - Intensified nutty and toasty notes from the Maillard reaction during browning.
- Flavor Impact on Cookies - Brown butter creates a richer, more complex cookie flavor compared to the straightforward richness of regular butter.
How Brown Butter Changes Cookie Texture
How does brown butter change the texture of cookies compared to regular butter? Brown butter enhances the cookie's texture by creating a chewier center and crispier edges due to its caramelized milk solids. This process intensifies nutty flavors and contributes to a more complex, richer mouthfeel that regular butter cannot achieve.
Nutritional Differences Between Regular and Brown Butter
Regular butter contains higher levels of moisture and retains most of its original fat content, while brown butter undergoes a Maillard reaction, altering its nutritional profile. The browning process slightly reduces moisture and concentrates milk solids, potentially increasing antioxidant compounds but also forming trace amounts of advanced glycation end products (AGEs).
- Fat Content - Regular butter typically has about 80% fat, whereas brown butter's fat content is marginally higher due to water evaporation during browning.
- Antioxidants - Brown butter contains increased antioxidant levels from caramelized milk solids, which may provide added health benefits compared to regular butter.
- AGEs Formation - The heating process in making brown butter generates small quantities of AGEs, compounds linked to oxidative stress and inflammation when consumed in large amounts.
Step-by-Step Guide: Browning Butter for Cookies
Start by melting unsalted butter in a light-colored saucepan over medium heat to monitor the color change accurately. Stir frequently with a heat-resistant spatula to prevent burning and ensure even browning.
Once the butter turns a golden brown with a nutty aroma, immediately remove it from the heat to stop the cooking process. Cool slightly before incorporating into your cookie dough to enhance flavor and achieve chewy, caramelized cookies.
When to Use Regular Butter in Cookie Recipes
Regular butter is ideal for cookie recipes that require a softer texture and a classic buttery flavor. It provides consistent moisture and helps achieve a tender crumb without adding the nutty complexity that brown butter imparts.
- Flavor neutrality - Regular butter maintains the traditional sweetness of cookies without overpowering other ingredients.
- Texture control - It delivers a smooth, creamy texture that supports chewy or soft cookie varieties.
- Stability in baking - Regular butter has a higher moisture content, which contributes to even spreading and rise.
Use regular butter when you want predictable results and a familiar cookie taste with balanced softness.
Best Cookie Recipes for Brown Butter
Brown butter enhances cookie recipes by adding a rich, nutty flavor that regular butter lacks, intensifying the overall taste experience. Best cookie recipes for brown butter often include brown sugar and vanilla to complement its caramelized notes.
Popular brown butter cookie recipes feature ingredients like chocolate chips, nuts, and sea salt to balance sweetness and texture. Using browned butter in cookie dough creates a chewy exterior with a tender, flavorful center, making it a favorite for bakers seeking depth in classic cookies.
Shelf Life and Storage: Regular vs Brown Butter
| Type of Butter | Shelf Life | Storage Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Butter Cookies | Up to 1 week at room temperature | Store in an airtight container away from direct sunlight; refrigeration extends freshness up to 2 weeks |
| Brown Butter Cookies | Typically 4-5 days at room temperature due to higher oil content | Best kept in airtight containers in the refrigerator to prevent rancidity; can last up to 10 days |
Common Mistakes When Baking With Brown Butter
One common mistake when baking with brown butter is overheating it, which can cause a burnt, bitter flavor that ruins the cookie's taste. Another error is not allowing the brown butter to cool properly before mixing it with sugar and eggs, leading to uneven texture and spreading issues. Additionally, substituting regular butter with brown butter without adjusting baking times or moisture levels can result in cookies that are too crisp or dry.
Related Important Terms
Maillard Browning Impact
Regular butter provides a creamy texture to cookies, while brown butter enhances flavor through Maillard browning, producing complex nutty and caramelized notes. The Maillard reaction in brown butter intensifies cookie aroma and deepens color, creating a richer sensory experience compared to cookies made with regular butter.
Nutty Flavor Burst
Brown butter offers a richer, nutty flavor burst compared to regular butter due to the Maillard reaction that caramelizes milk solids during browning. This complex, toasted aroma enhances cookie recipes by adding depth and a warm, buttery taste that regular butter cannot achieve.
Milk Solids Caramelization
Milk solids caramelize more intensely in brown butter due to prolonged heating, creating a deeper, nuttier flavor and richer color in cookies. Regular butter contains uncooked milk solids, resulting in a milder, creamier taste and softer texture.
Butterfat Separation
Regular butter contains about 80-82% butterfat, which maintains a consistent texture in cookie dough, while brown butter undergoes gentle heating that separates the butterfat from milk solids, intensifying nutty flavors and enhancing cookie texture. This butterfat separation in brown butter promotes better caramelization during baking, resulting in richer, more complex cookies with a slightly crisp edge and chewy center.
Enhanced Butterscotch Notes
Brown butter intensifies cookies with rich, nutty, enhanced butterscotch notes due to the Maillard reaction during browning, creating deeper flavor complexity compared to regular butter. This transformation elevates cookie recipes by adding caramelized sweetness and a toasted aroma that regular butter lacks.
Texture Differentiation Crunch
Regular butter in cookies provides a tender, soft texture with slight crispness around the edges, while brown butter enhances crunch by caramelizing milk solids, creating a deeper, nutty flavor and a firmer, more textured bite. The Maillard reaction in brown butter intensifies crispness, offering a satisfying crunch contrast to the chewiness typical of regular butter cookies.
Aroma Intensification
Brown butter enhances cookie aroma by developing nutty, caramelized notes through the Maillard reaction, intensifying flavor complexity beyond regular butter's creamy profile. This deeper aroma profile creates a richer sensory experience, making cookies more fragrant and appetizing.
Moisture Migration
Regular butter contains about 80% fat and 16-18% water, which influences moisture migration in cookie dough, resulting in a softer texture with balanced spread. Brown butter, having reduced moisture due to evaporation during browning, concentrates milk solids and fat, leading to less moisture migration, crisper edges, and a more complex nutty flavor in cookies.
Cookie Spread Control
Regular butter contains more water and less fat, causing cookies to spread more during baking, while brown butter has reduced moisture and concentrated fat, resulting in thicker, more textured cookies with controlled spread. Using brown butter enhances flavor complexity without sacrificing cookie shape, making it ideal for precise cookie spread control.
Regular Butter vs Brown Butter for Cookies Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com