Barbecue traditionally uses charcoal or wood as fuel, imparting a smoky, rich flavor to the food through direct or indirect heat. Pellet grilling relies on compressed wood pellets fed into an electric-powered heating element, offering precise temperature control and convenience. While barbecue fuel creates authentic smoke flavor, pellet grilling provides consistent heat and ease of use for longer cooking sessions.
Table of Comparison
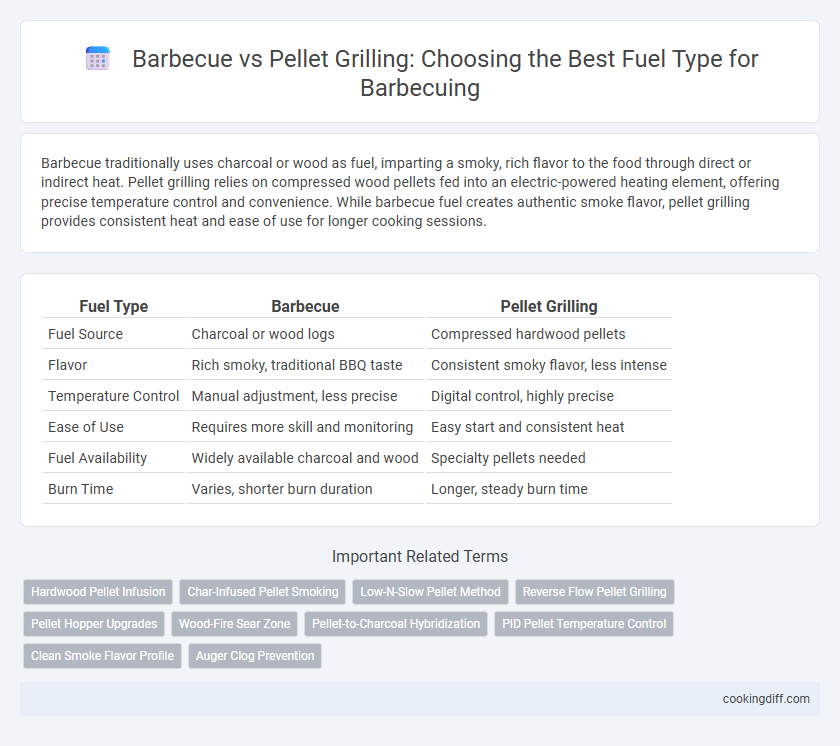
| Fuel Type | Barbecue | Pellet Grilling |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Source | Charcoal or wood logs | Compressed hardwood pellets |
| Flavor | Rich smoky, traditional BBQ taste | Consistent smoky flavor, less intense |
| Temperature Control | Manual adjustment, less precise | Digital control, highly precise |
| Ease of Use | Requires more skill and monitoring | Easy start and consistent heat |
| Fuel Availability | Widely available charcoal and wood | Specialty pellets needed |
| Burn Time | Varies, shorter burn duration | Longer, steady burn time |
Understanding Traditional Barbecue Fuel Types
Traditional barbecue relies heavily on charcoal and wood as primary fuel sources, imparting distinct smoky flavors essential to authentic grilling. Charcoal produces intense heat and a rich aroma, while wood offers a variety of flavor profiles depending on the tree species used, such as hickory or mesquite.
Pellet grilling, by contrast, uses compressed wood pellets made from sawdust, providing a more consistent temperature and easier fuel management. Although pellet grills generate less smoke compared to traditional charcoal or wood fires, they offer convenience and precise control for longer cooking sessions.
What Sets Pellet Grilling Apart?
What sets pellet grilling apart from traditional barbecue when it comes to fuel type? Pellet grills use compressed wood pellets that provide consistent heat and a smoky flavor, unlike traditional charcoal or wood that require manual monitoring and adjustment. This automated feed system allows for precise temperature control, making pellet grilling more convenient and efficient for prolonged cooking sessions.
Charcoal vs. Wood Pellets: Fuel Efficiency
Charcoal provides intense heat and a classic smoky flavor but typically burns faster, requiring frequent refueling during long cook sessions. Its high energy density means quick heat-up times but less consistent temperature control compared to pellets.
Wood pellets offer greater fuel efficiency with longer burn times and steady temperature regulation, making them ideal for low-and-slow cooking styles. The compressed hardwood pellets produce consistent smoke and heat, optimizing fuel use and enhancing flavor complexity.
Flavor Profiles: Smoke Intensity and Taste
Barbecue using traditional wood or charcoal imparts a rich, smoky flavor with intense smoke intensity that enhances the taste of meats. Pellet grilling offers a more controlled, milder smoke profile, delivering consistent flavor with subtle wood notes.
- Wood/Charcoal Smoke Intensity - Creates bold, robust smoky flavors by producing dense smoke during combustion.
- Pellet Grill Flavor Consistency - Uses compressed hardwood pellets to generate steady, moderate smoke for balanced taste.
- Impact on Meat Taste - Stronger smoke from charcoal often penetrates deeper, enriching the meat's natural flavors compared to pellets.
Temperature Control and Consistency
| Fuel Type | Barbecue grills typically use charcoal or wood, providing traditional smoky flavors but requiring manual adjustments for temperature control. Pellet grills utilize wood pellets and feature digital controllers for precise temperature regulation and consistent heat distribution. Pellet grills maintain steady cooking temperatures ranging from 180degF to 500degF, while charcoal grills may vary significantly, affecting cooking consistency. |
Convenience: Loading and Maintenance
Pellet grills use pre-made wooden pellets that are easy to load and require minimal refilling during cooking, offering a hassle-free experience. Traditional barbecues often rely on charcoal or wood, which demand more frequent monitoring and manual replenishment to maintain consistent heat.
Maintaining pellet grills involves cleaning the burn pot and ash tray periodically, which is straightforward due to their design. Barbecue smokers and grills necessitate removing ash and managing airflow through vents, requiring more hands-on attention. Pellet grills feature automated fuel feeding systems, reducing the effort needed to sustain temperature and making them more convenient for longer cooking sessions.
Environmental Impact: Carbon Footprint Comparison
Barbecue grilling primarily uses charcoal, which releases higher levels of carbon dioxide and particulate matter compared to pellet grills that use compressed wood pellets, resulting in a lower carbon footprint. Pellet grills offer more efficient combustion, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting a more sustainable grilling option.
- Charcoal grilling - Emits approximately 8.5 kg of CO2 per kilogram of fuel burned, contributing significantly to air pollution.
- Pellet grills - Use renewable wood pellets that produce less harmful emissions and have a carbon-neutral lifecycle.
- Efficiency - Pellet grills convert fuel to heat more efficiently, reducing the amount of fuel needed and overall emissions.
Choosing pellet grilling over traditional charcoal reduces environmental impact by lowering direct carbon emissions and promoting sustainable fuel sources.
Cost Analysis: Fuel Price and Value
Barbecue grilling typically uses charcoal or wood, which can vary widely in cost depending on quality and source, often ranging from $10 to $30 per bag. Pellet grilling relies on compressed wood pellets, generally priced around $20 to $25 per 40-pound bag, offering consistent fuel efficiency and longer burn times. When evaluating cost-effectiveness, pellet grills may provide greater value through fuel economy and ease of use, while traditional barbecue methods can be cheaper upfront but less consistent in fuel consumption.
Versatility: Cooking Styles and Capabilities
Barbecue using charcoal or wood offers traditional smoky flavors and higher heat variability, ideal for slow smoking and direct grilling. Pellet grilling provides precise temperature control with automated fuel feeding, supporting a wide range of cooking styles from smoking to baking. The versatility of pellet grills makes them suitable for users seeking convenience and consistency in their outdoor cooking experience.
Related Important Terms
Hardwood Pellet Infusion
Hardwood pellet grilling offers a consistent temperature and convenient fuel delivery, infusing meats with a rich, smoky flavor derived from compressed hardwood sawdust pellets like hickory, mesquite, or applewood. Traditional barbecue relies on charcoal or wood logs, providing intense heat and authentic smoke but requiring more attention to fuel management and temperature control.
Char-Infused Pellet Smoking
Char-infused pellet smoking utilizes hardwood pellets that provide a consistent heat source while imparting rich, smoky flavors, distinguishing it from traditional barbecue methods relying on charcoal or wood logs. This fuel type offers precise temperature control and minimal flare-ups, enhancing the efficiency and flavor complexity of smoked meats.
Low-N-Slow Pellet Method
Low-N-Slow pellet grilling uses compressed wood pellets as fuel, providing consistent heat and a clean burn that enhances smoky flavors without flare-ups common in traditional charcoal or wood barbecuing. This method excels in maintaining stable temperatures over extended periods, making it ideal for slow-cooked meats with tender, juicy results and rich smoke infusion.
Reverse Flow Pellet Grilling
Reverse flow pellet grilling uses compressed wood pellets as fuel, providing consistent heat and enhanced smoke flavor compared to traditional charcoal or gas barbecuing. This method improves fuel efficiency and temperature control, delivering tender, evenly cooked meats with a distinctive smoky aroma.
Pellet Hopper Upgrades
Pellet grilling offers precise temperature control and consistent heat output through automated pellet feeding, while traditional barbecue relies on manual fuel adjustments using charcoal or wood. Upgrading pellet hoppers increases fuel capacity and augments feeding mechanisms, enabling longer cook times and enhanced smoke flavor infusion critical for low-and-slow barbecuing.
Wood-Fire Sear Zone
Wood-fire sear zones in barbecue use hardwood charcoal or natural lump charcoal, providing intense, direct heat and rich smoky flavors essential for authentic grilling. Pellet grilling relies on compressed wood pellets, offering consistent temperature control and convenience but typically lacks the intense searing capability and smoky depth achieved by traditional wood-fired charcoal.
Pellet-to-Charcoal Hybridization
Pellet-to-charcoal hybridization combines the convenience and precise temperature control of pellet grilling with the traditional smoky flavor and high heat capabilities of charcoal barbecue, offering versatile fuel options for enhanced flavor profiles. This hybrid approach allows pitmasters to ignite charcoal with pellets for quick startup and consistent heat, optimizing both cooking efficiency and the rich, authentic taste of wood-fired barbecue.
PID Pellet Temperature Control
PID pellet temperature control enhances precision in pellet grilling by maintaining consistent heat through finely regulated fuel combustion of hardwood pellets, contrasting with traditional barbecue methods relying on charcoal or wood that often cause temperature fluctuations. This advanced technology allows pellet grills to deliver steady cooking temperatures, improving smoke flavor infusion and overall cooking efficiency compared to conventional fuel types.
Clean Smoke Flavor Profile
Barbecue using traditional fuels like charcoal or wood produces a rich, smoky flavor with complex, natural aromas that pellet grilling's compressed wood pellets may struggle to fully replicate. Pellet grills generate cleaner, more consistent smoke with less particulate matter, resulting in a milder, more subtle flavor profile ideal for those prioritizing convenience and reduced smoke intensity.
Barbecue vs Pellet Grilling for fuel type. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com