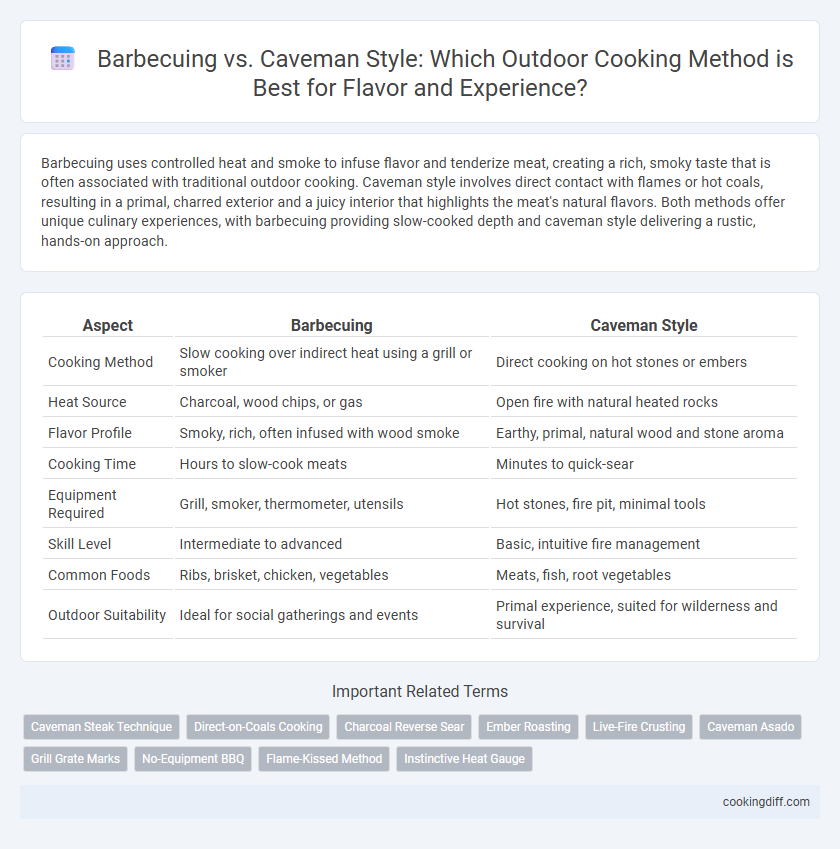
Barbecuing uses controlled heat and smoke to infuse flavor and tenderize meat, creating a rich, smoky taste that is often associated with traditional outdoor cooking. Caveman style involves direct contact with flames or hot coals, resulting in a primal, charred exterior and a juicy interior that highlights the meat's natural flavors. Both methods offer unique culinary experiences, with barbecuing providing slow-cooked depth and caveman style delivering a rustic, hands-on approach.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Barbecuing | Caveman Style |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Slow cooking over indirect heat using a grill or smoker | Direct cooking on hot stones or embers |
| Heat Source | Charcoal, wood chips, or gas | Open fire with natural heated rocks |
| Flavor Profile | Smoky, rich, often infused with wood smoke | Earthy, primal, natural wood and stone aroma |
| Cooking Time | Hours to slow-cook meats | Minutes to quick-sear |
| Equipment Required | Grill, smoker, thermometer, utensils | Hot stones, fire pit, minimal tools |
| Skill Level | Intermediate to advanced | Basic, intuitive fire management |
| Common Foods | Ribs, brisket, chicken, vegetables | Meats, fish, root vegetables |
| Outdoor Suitability | Ideal for social gatherings and events | Primal experience, suited for wilderness and survival |
Defining Barbecuing and Caveman Style Cooking
Barbecuing involves cooking food slowly over indirect heat using wood smoke to enhance flavor, while caveman style cooking directly exposes food to open flames or hot coals for a primal, high-heat experience. Both methods emphasize outdoor cooking but differ significantly in technique and flavor profiles.
- Barbecuing - Utilizes controlled, low-and-slow heat with smoke from wood or charcoal to tenderize and flavor meats.
- Caveman Style Cooking - Involves placing food directly on hot coals or stones for rapid cooking with a charred, smoky crust.
- Flavor and Technique Contrast - Barbecuing creates deep, smoky taste and tender texture, whereas caveman style delivers intense, seared exterior and primal simplicity.
Historical Origins of Fire-Based Outdoor Cooking
Barbecuing traces its roots to indigenous Caribbean cooking methods where meat was slowly cooked over an open fire on wooden structures called "barbacoa." Caveman-style cooking, dating back millions of years, involved roasting food directly over open flames or hot coals, highlighting humanity's earliest use of fire for survival. Both techniques showcase the evolution of fire-based outdoor cooking, blending cultural rituals with practical culinary innovation.
Tools and Equipment: Grill vs Open Fire
Barbecuing relies on specialized grills equipped with adjustable grates, temperature controls, and often built-in thermometers, allowing precise heat management and consistent cooking. In contrast, caveman style cooking uses open fires without tools, requiring skill to manage flames and heat directly from burning wood or charcoal.
Grills typically utilize metal construction, offering durability and features like vents to regulate airflow and smoke, essential for barbecue flavor. Open fires demand natural materials such as stones or logs to contain the fire, and cooks use basic implements or none at all. The equipment difference significantly impacts cooking control, safety, and flavor outcomes in outdoor cooking experiences.
Flavor Profiles: Wood Smoke vs Direct Flame
Barbecuing imparts rich, smoky flavors by cooking meat low and slow over wood smoke, allowing the natural sugars and fats to caramelize deeply. Caveman style relies on direct flame grilling, which sears meat quickly, creating a charred crust with a distinct, robust taste. The choice between wood smoke and direct flame dramatically influences the flavor profile, with barbecue offering complexity and caveman style delivering intense, primal heat.
Cooking Techniques and Methods Compared
How do barbecuing and caveman style differ in outdoor cooking techniques? Barbecuing relies on slow, indirect heat over smoldering wood or charcoal to infuse food with smoky flavor, while caveman style uses direct contact with open flames or hot embers, often wrapping ingredients in leaves or foil. These methods create distinct textures and taste profiles, with barbecuing emphasizing tenderness and caveman style delivering a roasted, charred exterior.
Heat Control: Precision Grilling vs Primal Cooking
Barbecuing offers precise heat control through adjustable grills and temperature gauges, allowing for consistent cooking and flavor development. This method enables chefs to maintain steady temperatures, essential for slow smoking and even cooking of meats.
Caveman style cooking relies on direct exposure to open flames or hot embers, resulting in a more primal, uneven heat distribution. The lack of precise control produces a unique char and smoky flavor, emphasizing natural cooking techniques over precision.
Food Selection: Ideal Meats and Ingredients
Barbecuing typically favors cuts like ribs, brisket, and pork shoulder, which benefit from slow cooking and smoke to develop rich flavors and tender textures. Ingredients such as hardwood chips, marinades, and dry rubs enhance the meat's taste and complement the smoky aroma.
Caveman style, or direct open-flame cooking, excels with thick steaks, whole vegetables, and bone-in cuts like lamb chops that cook quickly and retain juiciness. Simple seasonings like coarse salt, pepper, and fresh herbs highlight the natural flavors, requiring less preparation and focusing on primal cooking techniques.
Safety Considerations Outdoors
Barbecuing typically involves controlled heat sources like grills, reducing the risk of uncontrolled fires compared to caveman style cooking, which uses direct flames and open pits. Proper ventilation and distance from flammable materials are essential in both methods to ensure outdoor safety.
- Fire Management - Barbecuing offers better control of fire intensity, minimizing flare-ups and accidents.
- Smoke Exposure - Caveman style produces more smoke, requiring careful positioning to avoid inhalation hazards.
- Surface Stability - Grills provide stable surfaces unlike uneven ground fires in caveman style, lowering the risk of tipping and burns.
Time Commitment and Preparation Differences
Barbecuing requires careful preparation, including marinating and slow cooking over indirect heat, often lasting several hours. Caveman style cooking involves direct, high-heat grilling with minimal prep, making it a faster, more spontaneous outdoor cooking method.
- Barbecuing demands long cook times - It often takes 4 to 12 hours to achieve tender, flavorful results through slow smoking.
- Caveman style has minimal preparation - This method typically involves seasoning meat on the spot and cooking directly on hot coals or stones.
- Equipment complexity varies - Barbecuing requires specialized smokers or grills, while caveman style can be done with basic fire and flat stones.
Choosing between barbecuing and caveman style depends on desired time investment and cooking precision.
Related Important Terms
Caveman Steak Technique
Caveman steak technique involves cooking the meat directly on hot coals, which intensifies flavor through smoky, charred crusts absent in traditional barbecuing that uses indirect heat and wood smoke. This primitive method enhances outdoor cooking by delivering a uniquely rustic texture and faster searing time, appealing to those seeking authentic, high-heat grilling experiences.
Direct-on-Coals Cooking
Direct-on-coals cooking intensifies flavors by searing food with primal heat, creating a smoky crust unlike traditional barbecuing's indirect cooking methods. Caveman style uses hot embers to cook meat directly, enhancing texture and imparting deep, earthy aromas that conventional barbecuing over grates cannot replicate.
Charcoal Reverse Sear
Charcoal reverse sear enhances barbecuing by slow-cooking meat over indirect heat before finishing with high direct heat for a perfect crust and juicy interior, a method more controlled than caveman style's open flame grilling. This technique leverages the even heat distribution of charcoal to develop deep smoky flavors while minimizing charring and uneven cooking typical of direct open fire approaches.
Ember Roasting
Ember roasting in caveman style involves cooking food directly on hot embers, allowing for intense, even heat and a distinctive smoky flavor that differs from traditional barbecuing with indirect heat and wood smoke. This method enhances natural flavors by using minimal tools and maximizing the primal interaction between food and fire, offering a unique outdoor cooking experience.
Live-Fire Crusting
Barbecuing achieves live-fire crusting by using indirect heat and smoke to slowly cook meat, developing a flavorful bark rich in Maillard reaction compounds. Caveman style relies on direct contact with hot embers, producing a charred, smoky crust quickly but with less control over internal doneness and smoke infusion.
Caveman Asado
Caveman Asado transforms traditional barbecuing by cooking meat directly on hot embers, enhancing smoky flavors and natural juiciness without the need for grills or skewers. This method, rooted in ancient techniques, offers a primal outdoor cooking experience that emphasizes simplicity and raw heat, distinguishing it from conventional barbecue setups.
Grill Grate Marks
Grill grate marks in barbecuing create distinct, caramelized sear lines that enhance flavor through the Maillard reaction, while caveman style, which involves cooking directly on hot stones or embers, produces more uneven char without defined grill marks. These characteristic sear patterns from traditional grilling not only improve aesthetic appeal but also contribute to texture and taste differences compared to the rustic, smoky finish of caveman cooking.
No-Equipment BBQ
No-equipment BBQ relies on basic skills such as controlling fire and using natural materials like hot coals or stones to cook food directly, offering a primitive and authentic outdoor cooking experience. Unlike traditional barbecuing that often requires grills or smokers, caveman style emphasizes simplicity, minimal tools, and direct contact with heat sources, perfect for survival situations and minimalist outdoor enthusiasts.
Flame-Kissed Method
Barbecuing uses controlled, low heat and smoke to slowly cook meat, while the caveman style involves direct, high-heat flame-kissed cooking over open flames for a charred exterior and juicy interior. The flame-kissed method intensifies flavor by searing natural juices quickly, creating a smoky, caramelized crust that enhances outdoor cooking experiences.
Barbecuing vs Caveman Style for Outdoor Cooking Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com