Gas grills offer quick ignition and precise temperature control, making them ideal for fast, consistent cooking. Pellet grills use wood pellets to infuse food with smoky flavor, providing a more authentic barbecue taste but requiring more time and monitoring. Choosing between gas and pellet depends on whether convenience or flavor complexity is the priority for your barbecuing experience.
Table of Comparison
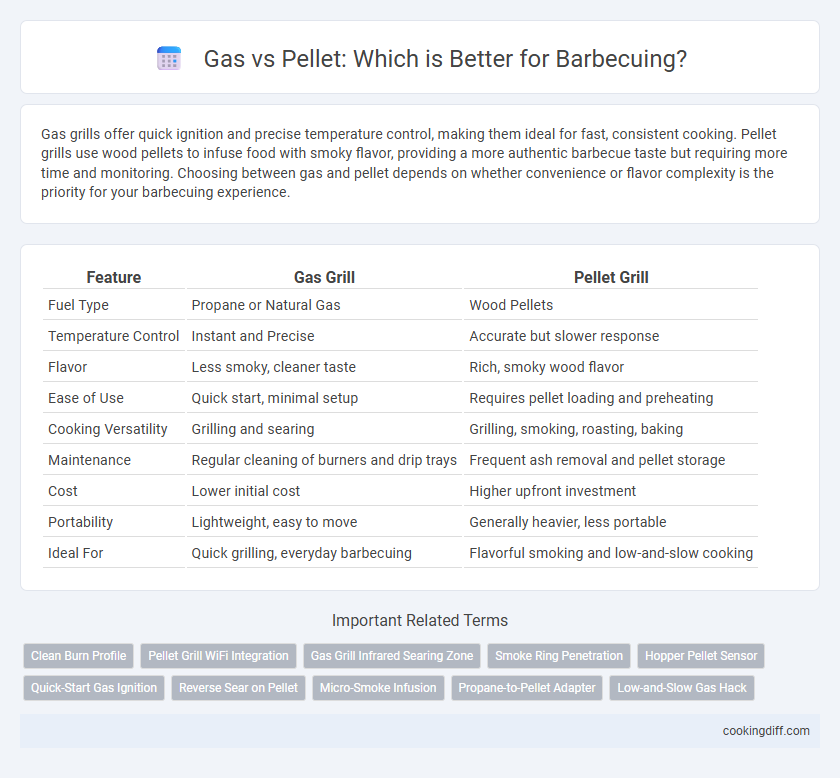
| Feature | Gas Grill | Pellet Grill |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Type | Propane or Natural Gas | Wood Pellets |
| Temperature Control | Instant and Precise | Accurate but slower response |
| Flavor | Less smoky, cleaner taste | Rich, smoky wood flavor |
| Ease of Use | Quick start, minimal setup | Requires pellet loading and preheating |
| Cooking Versatility | Grilling and searing | Grilling, smoking, roasting, baking |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning of burners and drip trays | Frequent ash removal and pellet storage |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher upfront investment |
| Portability | Lightweight, easy to move | Generally heavier, less portable |
| Ideal For | Quick grilling, everyday barbecuing | Flavorful smoking and low-and-slow cooking |
Introduction to Gas and Pellet Barbecuing
Gas barbecuing offers precise temperature control and quick startup, making it ideal for consistent grilling experiences. Propane or natural gas fuels these grills, providing convenience and ease of use for everyday cooking.
Pellet barbecuing utilizes wood pellets to infuse rich smoky flavors, combining traditional smoking with modern automation. These grills maintain steady heat through digital controllers, perfect for slow-cooked, flavorful dishes.
How Gas Grills Work: Key Features
Gas grills operate by igniting propane or natural gas through burners to produce an immediate, adjustable heat source, ideal for precise temperature control. These grills often feature metal heat tents or flavorizer bars that vaporize drippings, enhancing flavor while preventing flare-ups.
- Instant Heat - Gas grills ignite burners quickly, providing near-instant heat compared to pellet grills.
- Temperature Control - Adjustable knobs allow users to finely tune the cooking temperature for various grilling needs.
- Flavor Enhancement - Heat tents or flavorizer bars vaporize drippings, infusing food with smoky flavors and reducing flare-ups.
This combination of features makes gas grills a convenient and versatile option for casual to advanced barbecuing enthusiasts.
How Pellet Grills Work: The Basics
| Pellet grills use wood pellets fed from a hopper into a fire pot by an auger, controlled electronically for consistent heat. |
| An electric thermostat regulates the temperature by adjusting pellet feed rate and the fan, ensuring precise cooking conditions. |
| The combustion of pellets produces smoke for authentic flavor, combining indirect heat and smoke for even barbecuing. |
Flavor Profiles: Gas vs Pellet Barbecuing
How do flavor profiles differ between gas and pellet barbecuing? Gas grills provide a clean, consistent heat resulting in a more subtle smoky flavor, ideal for quick cooking and searing. Pellet grills infuse food with a rich, wood-fired taste by burning compressed wood pellets, enhancing complexity and depth in smoked meats.
Cooking Performance Comparison
Gas grills heat up quickly and offer precise temperature control, making them ideal for searing and fast-cooking meats. Pellet grills provide superior smoke infusion and maintain consistent low temperatures, enhancing flavor in slow-cooked dishes. When comparing cooking performance, pellet grills excel in flavor complexity while gas grills deliver convenience and speed.
Temperature Control and Consistency
Gas grills offer precise temperature control through adjustable knobs, allowing quick changes in heat levels for consistent cooking. This makes gas ideal for grilling delicate foods that require steady temperatures.
Pellet grills use automated feed systems to maintain consistent temperatures by regulating pellet consumption, providing even heat distribution for long cooking sessions. This consistency enhances flavor and smoke infusion while requiring less manual adjustment.
Ease of Use and Convenience
Gas grills offer superior ease of use with quick ignition and precise temperature control, making them ideal for fast and convenient barbecuing. Pellet grills provide consistent heat and smoke flavor through automated pellet feeding but require electricity and regular pellet refills, adding some complexity. For those prioritizing convenience and minimal setup, gas grilling remains the preferred choice due to its simple operation and faster preheating times.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Gas grills typically require less frequent and simpler cleaning due to their controlled flames and fewer grease buildup areas, while pellet grills need regular ash removal and thorough cleaning of the pellet hopper and burn pot. Proper maintenance of both types ensures optimal performance and extends the lifespan of the equipment.
- Gas grills need occasional burner and drip tray cleaning - This prevents clogging and flare-ups caused by grease accumulation.
- Pellet grills require frequent ash removal - Ash buildup can obstruct airflow and affect temperature control.
- Pellet hoppers and burn pots need regular inspection - Cleaning these components avoids pellet jams and maintains consistent heat distribution.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term Expenses
Gas grills typically have a lower initial purchase price compared to pellet grills, making them more accessible for beginners. Over time, pellet grills incur higher operating costs due to pellet fuel prices and maintenance requirements.
- Initial Cost - Gas grills often cost between $200 and $500, whereas pellet grills can range from $500 to over $1,000.
- Fuel Expenses - Propane for gas grills is generally cheaper per cooking hour than wood pellets used for pellet grills.
- Maintenance Costs - Pellet grills require more frequent cleaning and parts replacement, increasing long-term expenses.
Related Important Terms
Clean Burn Profile
Gas grills offer a clean burn profile with minimal emissions, producing fewer particulates and carbon deposits compared to pellet grills. Pellet grills, while flavorful, generate more smoke and combustion byproducts due to the burning of wood pellets, which can affect air quality and require more frequent cleaning.
Pellet Grill WiFi Integration
Pellet grills with WiFi integration offer precise temperature control and remote monitoring, enhancing the barbecuing experience by allowing users to adjust heat settings from their smartphones. This advanced connectivity provides real-time alerts and automated cooking adjustments, making pellet grills a smarter option compared to traditional gas grills for consistent and convenient outdoor cooking.
Gas Grill Infrared Searing Zone
Gas grills with an infrared searing zone deliver intense, direct heat reaching up to 1800degF, perfect for creating a caramelized, flavorful crust on steaks within minutes. Compared to pellet grills, gas infrared zones offer faster preheating and precise temperature control, enhancing searing performance while maintaining juiciness and texture.
Smoke Ring Penetration
Gas grills offer quick heat control but typically produce less smoke ring penetration due to limited smoke generation, while pellet grills generate consistent smoke that enhances the depth and richness of the smoke ring on meats. The combustion of wood pellets releases flavorful smoke compounds that intensify the characteristic pink smoke ring, making pellet grills preferable for barbecue enthusiasts seeking optimal smoke ring development.
Hopper Pellet Sensor
Pellet grills use a hopper pellet sensor to monitor fuel levels, ensuring continuous smoke production and consistent cooking temperatures, which enhances flavor precision compared to gas grills. Gas grills provide quick temperature control but lack the automated fuel tracking and deep smoky infusion that pellet sensors facilitate during extended barbecuing sessions.
Quick-Start Gas Ignition
Gas grills provide quick-start ignition through built-in electronic or push-button igniters, allowing for immediate heat and consistent temperature control essential for efficient barbecuing. Pellet grills, while offering flavorful wood smoke, generally require longer startup times due to auger-fed pellets and heated combustion chambers, making gas grills preferable for rapid cooking sessions.
Reverse Sear on Pellet
Pellet grills excel in reverse searing due to their precise temperature control and consistent heat distribution, allowing for an even cook followed by a perfect, caramelized crust. Unlike gas grills that offer quick heat but less smoke flavor, pellet grills infuse rich smoky complexity while maintaining the steady low temperatures necessary for reverse searing prime cuts.
Micro-Smoke Infusion
Gas grills offer precise temperature control and convenience but lack the rich micro-smoke infusion produced by pellet grills, which use compressed wood pellets to generate consistent, flavorful smoke that enhances the taste of barbecued meats. Pellet grills excel at imparting nuanced smoky flavors with minimal effort, making them ideal for enthusiasts seeking authentic barbecue experiences.
Propane-to-Pellet Adapter
A propane-to-pellet adapter transforms a standard gas grill into a pellet grill by allowing propane tanks to fuel pellet burners, combining the convenience of gas with the smoky flavor of pellets. This adapter enhances versatility and temperature control for barbecuing, making it an efficient choice for outdoor cooking enthusiasts.
Gas vs Pellet for Barbecuing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com