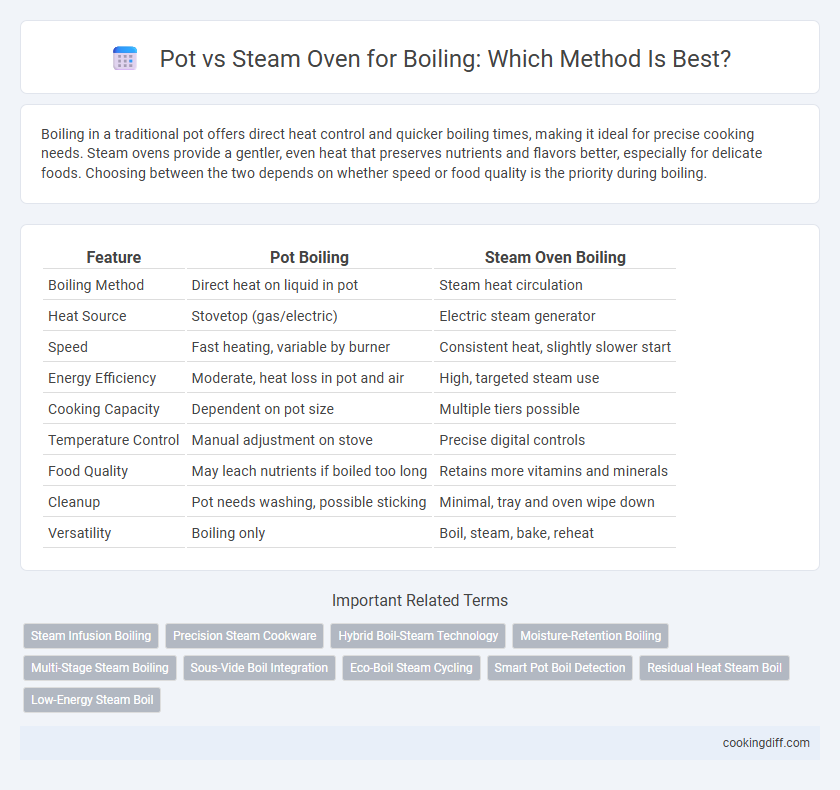
Boiling in a traditional pot offers direct heat control and quicker boiling times, making it ideal for precise cooking needs. Steam ovens provide a gentler, even heat that preserves nutrients and flavors better, especially for delicate foods. Choosing between the two depends on whether speed or food quality is the priority during boiling.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pot Boiling | Steam Oven Boiling |
|---|---|---|
| Boiling Method | Direct heat on liquid in pot | Steam heat circulation |
| Heat Source | Stovetop (gas/electric) | Electric steam generator |
| Speed | Fast heating, variable by burner | Consistent heat, slightly slower start |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate, heat loss in pot and air | High, targeted steam use |
| Cooking Capacity | Dependent on pot size | Multiple tiers possible |
| Temperature Control | Manual adjustment on stove | Precise digital controls |
| Food Quality | May leach nutrients if boiled too long | Retains more vitamins and minerals |
| Cleanup | Pot needs washing, possible sticking | Minimal, tray and oven wipe down |
| Versatility | Boiling only | Boil, steam, bake, reheat |
Introduction: Boiling Basics
Boiling is a cooking method that uses water heated to 100degC to cook food thoroughly and quickly. Choosing between a pot and a steam oven affects how evenly and efficiently heat is transferred during boiling.
- Pot Boiling - Involves submerging food directly in boiling water, ensuring fast heat transfer and even cooking.
- Steam Oven Boiling - Utilizes steam circulation to cook food gently while retaining moisture and nutrients.
- Heat Distribution - Pot boiling offers direct contact with water, whereas steam ovens provide uniform heat with less water contact.
Pot Boiling: Traditional Method Explained
| Pot Boiling | Utilizes direct contact with boiling water, ensuring rapid heat transfer and efficient cooking of vegetables, pasta, and eggs. |
| Temperature Control | Maintains a consistent 100degC (212degF) boiling point at sea level, allowing precise cooking times and texture control. |
| Energy Efficiency | Depends on stovetop type; gas and induction burners provide fast temperature adjustments, reducing overall cooking time. |
Steam Oven Boiling: Modern Approach Unveiled
Steam ovens utilize precise steam injection to maintain consistent boiling temperatures, ensuring evenly cooked foods with enhanced nutrient retention. Unlike traditional pots, steam ovens reduce water usage and prevent overcooking by controlling humidity levels accurately. This modern approach to boiling offers energy efficiency and improved texture, making it ideal for delicate ingredients and health-conscious cooking.
Energy Efficiency: Pot versus Steam Oven
Boiling food in a pot on the stovetop typically consumes more energy due to heat loss to the surrounding air, making it less efficient than a steam oven. Steam ovens use convection and steam circulation to cook food evenly while retaining moisture, reducing overall cooking time and energy usage.
Energy efficiency ratings for steam ovens often surpass traditional pots, as steam ovens reach and maintain optimal temperatures with less energy waste. Choosing a steam oven for boiling tasks can result in lower utility bills and a smaller environmental footprint compared to conventional pot boiling methods.
Time Comparison: Which Is Faster?
Boiling with a pot heats water directly on the stove, typically reaching boiling point faster due to direct contact with the heat source. Steam ovens use indirect steam heat, which can take longer to generate and maintain boiling temperatures for cooking. For time-sensitive boiling tasks, a pot is generally faster, while steam ovens offer more controlled, even cooking ideal for delicate foods.
Flavor and Texture: Impact on Food Quality
How does using a pot compare to a steam oven in terms of flavor and texture when boiling food? Boiling in a pot can sometimes cause loss of delicate flavors and nutrients due to direct water contact, leading to a softer, less vibrant texture. Steam ovens preserve more natural flavors and maintain a firmer, more appealing texture by cooking food with moist heat without submersion in water.
Versatility: Uses Beyond Boiling
Pot boiling allows for various cooking methods such as simmering, blanching, and preparing soups, offering greater control over liquid-based recipes. Steam ovens provide the advantage of gentle, even heat distribution, making them ideal for steaming vegetables, reheating, and baking alongside boiling tasks.
While pots excel in directly boiling and reducing liquids for sauces, steam ovens can multitask by preserving nutrients and textures in food through steam infusion. This versatility makes steam ovens suitable for both cooking and gentle reheating, expanding their use beyond traditional boiling.
Safety Considerations: Pot and Steam Oven
Boiling with a traditional pot requires careful monitoring to prevent overflows and burns from hot water or steam. Steam ovens provide a safer environment by enclosing steam, reducing direct contact with boiling liquids.
- Risk of Burns in Pot Boiling - Open boiling water in pots poses a higher risk of accidental burns due to splashing and steam exposure.
- Enclosed Environment in Steam Ovens - Steam ovens contain steam within a sealed chamber, minimizing exposure and improving user safety.
- Temperature Control - Steam ovens offer precise temperature regulation, reducing the risk of overheating compared to stovetop pots.
Cleaning and Maintenance Differences
Cleaning a pot after boiling typically involves scrubbing off residue and soaking to remove stubborn stains, which can be time-consuming. Steam ovens require less manual cleaning as steam loosens food particles, making it easier to wipe down surfaces.
- Pot cleaning intensity - Pots often accumulate burnt deposits that require thorough scrubbing and soaking.
- Steam oven maintenance - Steam ovens rely on self-cleaning cycles and moisture to minimize residue buildup.
- Time investment - Cleaning pots generally takes more time compared to quick wipe-downs for steam ovens.
Choosing a steam oven for boiling reduces cleaning effort and maintenance frequency compared to traditional pots.
Related Important Terms
Steam Infusion Boiling
Steam infusion boiling in a steam oven delivers precise temperature control and uniform heat distribution, preserving nutrients and enhancing food texture compared to traditional pot boiling. This method reduces cooking time and moisture loss, resulting in efficiently cooked, flavorful dishes with consistent results.
Precision Steam Cookware
Precision steam cookware in a steam oven offers superior temperature control and consistent boiling compared to traditional pots, enhancing nutrient retention and flavor. Unlike pots that rely on direct water contact and manual monitoring, steam ovens deliver precise, evenly distributed steam, reducing the risk of overboiling and ensuring efficient cooking times.
Hybrid Boil-Steam Technology
Hybrid Boil-Steam Technology combines the rapid heat transfer of boiling water with the gentle, even heat distribution of steam ovens, enhancing cooking efficiency and nutrient retention. This method outperforms traditional pots by reducing cooking time while maintaining food texture and flavor.
Moisture-Retention Boiling
Boiling in a steam oven preserves moisture more effectively than a traditional pot by circulating steam at consistent temperatures, preventing water loss and maintaining food juiciness. In contrast, pot boiling often results in nutrient leaching and moisture evaporation due to direct contact with boiling water and open-air exposure.
Multi-Stage Steam Boiling
Multi-stage steam boiling in a steam oven ensures precise temperature control and uniform heat distribution, which significantly preserves nutrients and texture compared to traditional pot boiling. This method leverages calibrated steam pulses to cook food evenly while minimizing overcooking or water loss, enhancing flavor and efficiency in culinary applications.
Sous-Vide Boil Integration
Sous-vide boil integration merges precise temperature control with consistent heat distribution, favoring steam ovens for maintaining stable water temperatures over traditional pots, which often experience fluctuations. Steam ovens enhance sous-vide cooking accuracy by providing uniform steam circulation, reducing water evaporation and ensuring even heat transfer essential for delicate food textures.
Eco-Boil Steam Cycling
Eco-Boil Steam Cycling in steam ovens uses precise steam pulses to maintain optimal boiling temperatures, reducing energy consumption compared to traditional pot boiling methods. This technology minimizes water usage and shortens cooking times, making steam ovens a more efficient and environmentally friendly option.
Smart Pot Boil Detection
Smart pot boil detection in steam ovens uses advanced sensors to precisely monitor water temperature and vapor pressure, ensuring efficient boiling without overflows or energy waste. This technology provides consistent results by automatically adjusting heat levels, outperforming traditional pot boiling methods in speed and precision.
Residual Heat Steam Boil
Residual heat steam boil in steam ovens offers precise temperature control and energy efficiency by maintaining consistent steam circulation, resulting in evenly cooked foods without over-boiling. In contrast to traditional pots, steam ovens minimize nutrient loss and prevent scorching by harnessing controlled residual heat, making them ideal for delicate boiling tasks.
Pot vs Steam Oven for boiling. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com