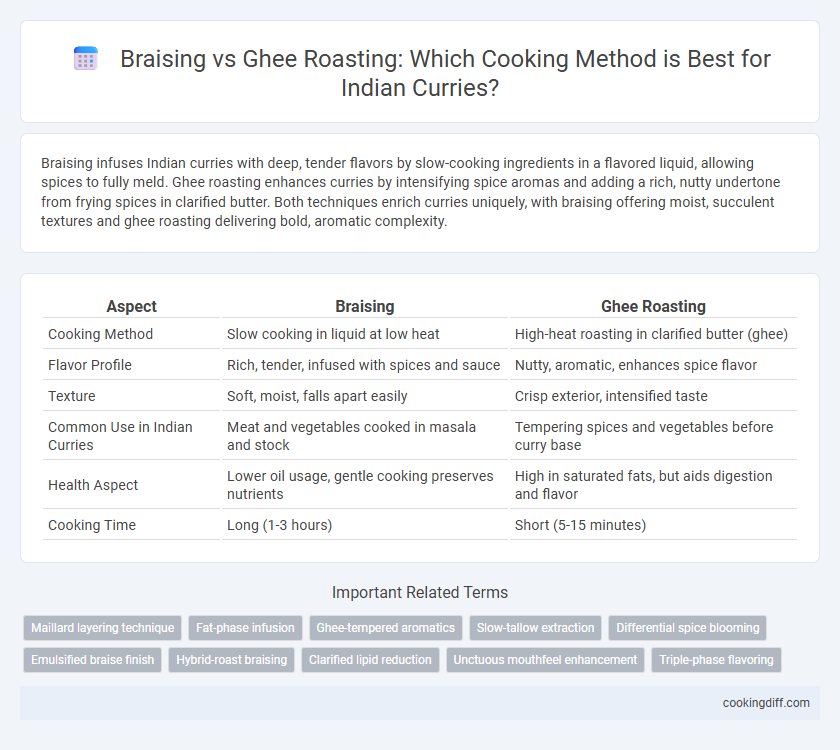
Braising infuses Indian curries with deep, tender flavors by slow-cooking ingredients in a flavored liquid, allowing spices to fully meld. Ghee roasting enhances curries by intensifying spice aromas and adding a rich, nutty undertone from frying spices in clarified butter. Both techniques enrich curries uniquely, with braising offering moist, succulent textures and ghee roasting delivering bold, aromatic complexity.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Braising | Ghee Roasting |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Slow cooking in liquid at low heat | High-heat roasting in clarified butter (ghee) |
| Flavor Profile | Rich, tender, infused with spices and sauce | Nutty, aromatic, enhances spice flavor |
| Texture | Soft, moist, falls apart easily | Crisp exterior, intensified taste |
| Common Use in Indian Curries | Meat and vegetables cooked in masala and stock | Tempering spices and vegetables before curry base |
| Health Aspect | Lower oil usage, gentle cooking preserves nutrients | High in saturated fats, but aids digestion and flavor |
| Cooking Time | Long (1-3 hours) | Short (5-15 minutes) |
Understanding Braising in Indian Curries
Braising in Indian curries involves slow cooking meat or vegetables in a small amount of liquid to develop deep, rich flavors and tender textures. This method differs from ghee roasting, which primarily enhances aroma and adds a nutty taste through high-heat fat cooking.
- Braising uses moisture - It combines dry and wet heat, where food is first seared and then simmered in liquid for extended periods.
- Flavor infusion - Slow cooking allows spices and ingredients to meld, creating complex, well-rounded curry profiles.
- Texture development - Braising breaks down connective tissues, ensuring tender, juicy curries unlike the crispier outcome of ghee roasting.
Ghee Roasting: A Classic Indian Technique
Ghee roasting enhances Indian curries by infusing rich, nutty flavors through slow cooking spices in clarified butter. This technique differs from braising by focusing on initial spice tempering rather than prolonged simmering with liquid.
- Rich Flavor Development - Ghee roasting allows spices to bloom in clarified butter, intensifying aroma and taste in curries.
- Traditional Method - Rooted in Indian culinary heritage, ghee roasting forms the flavor base for authentic dishes like butter chicken and masala gravies.
- Texture and Color - The slow roasting process imparts a deeper color and smoother texture compared to the wetter, slow-cooked braising method.
Flavor Profiles: Braising vs Ghee Roasting
Braising intensifies Indian curries by slowly cooking ingredients in a flavorful liquid, allowing spices to deeply infuse and create a rich, tender texture. Ghee roasting enhances the flavor profile by using clarified butter to caramelize spices and vegetables, imparting a nutty aroma and slightly smoky depth.
Braising develops complex, layered flavors through prolonged heat and moisture, perfect for tougher cuts of meat and dense vegetables. The moist environment preserves the curry's natural juices, ensuring intense spice absorption and succulence. In contrast, ghee roasting introduces a crispy, golden exterior with concentrated spice notes, ideal for a vibrant, aromatic curry base.
Texture Differences in Braised and Ghee-Roasted Curries
Braising in Indian curries results in tender, succulent textures as slow cooking allows spices and ingredients to meld deeply with moisture. Ghee roasting imparts a rich, slightly crisp texture by frying spices and ingredients in clarified butter, enhancing aromatic complexity and surface caramelization. The contrast lies in braised curries being moist and soft, while ghee-roasted dishes offer a distinct, roasted texture with intensified flavors.
Effect on Spices: Braising Compared to Ghee Roasting
Braising Indian curries allows spices to infuse gradually, creating a deep, mellow flavor profile as the heat and moisture extract their essence. Ghee roasting intensifies spices by enhancing their aromatic oils through a dry, high-heat process, delivering a richer and more vibrant spice complexity.
- Braising softens spices - Slow cooking in liquid reduces the sharpness of spices, blending them smoothly within the curry.
- Ghee roasting amplifies aroma - High heat in ghee unlocks volatile oils, producing a robust and fragrant spice layer.
- Braising integrates flavors - Moist heat helps spices penetrate ingredients, fostering balanced and unified taste profiles.
Braising offers subtle spice integration, while ghee roasting maximizes pungency and aroma for Indian curries.
Cooking Time: Braising Versus Ghee Roasting Methods
How does cooking time compare between braising and ghee roasting in Indian curries? Braising typically requires a longer cooking duration, often slow-cooked for 1 to 3 hours to tenderize tougher cuts and develop deep flavors. Ghee roasting, in contrast, is a quicker method, usually completed within 20 to 40 minutes, relying on high-heat fat cooking to infuse spices rapidly.
Nutritional Impact of Braising and Ghee Roasting
Braising Indian curries preserves moisture and nutrients by cooking ingredients slowly in a liquid, resulting in lower fat content and enhanced absorption of water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex. This method reduces the formation of harmful compounds often associated with high-heat cooking techniques.
Ghee roasting intensifies flavors and adds healthy fats such as omega-3 and antioxidants like vitamin E but increases calorie content and saturated fat intake. The high heat can cause slight nutrient degradation but also promotes the Maillard reaction, enhancing the curry's taste and aroma.
Best Curries for Braising in Indian Cooking
Braising is ideal for slow-cooking tough cuts of meat and dense vegetables in Indian curries, allowing flavors to deeply infuse and tenderize the ingredients. Curries like Rogan Josh, Nihari, and Lamb Curry benefit from braising due to their rich, hearty nature and extended cooking times.
Ghee roasting, by contrast, enhances the aroma and texture upfront, suitable for quicker dishes such as Paneer Butter Masala or Chicken Tikka Masala. Braising excels in curries that require prolonged simmering, ensuring a melt-in-the-mouth consistency and robust, well-developed flavors.
When to Choose Ghee Roasting for Your Curry
Ghee roasting is ideal for Indian curries that require a rich, nutty flavor and a slightly caramelized texture, such as butter chicken or paneer tikka masala. This technique enhances the depth of spices by tempering them in hot ghee, resulting in a more aromatic and flavorful curry. Choose ghee roasting when you want a smoother, buttery base that complements creamy or mildly spiced dishes without the long cooking times braising demands.
Related Important Terms
Maillard layering technique
Braising Indian curries involves slow-cooking ingredients in liquid, allowing Maillard reactions to develop deep, complex flavors through gentle heat and moisture, which enhances the layered taste profile. Ghee roasting intensifies Maillard browning by applying direct heat and fat, creating a richer, nuttier aroma and distinct caramelized notes that elevate the curry's depth.
Fat-phase infusion
Braising Indian curries involves slow cooking in liquid, allowing spices to infuse gradually into the fat phase, creating rich, deeply layered flavors, while ghee roasting intensifies spice aromas through direct heat, rapidly releasing essential oils into the fat. The fat-phase infusion in braising enhances complexity and mouthfeel by integrating spices over time, whereas ghee roasting offers a bold, immediate spice profile with a distinct nuttiness from browned ghee.
Ghee-tempered aromatics
Ghee roasting infuses Indian curries with rich, caramelized aromatics by tempering spices in clarified butter, enhancing depth and complexity unmatched by traditional braising techniques. Braising often relies on slow cooking in liquid, whereas ghee-tempered aromatics provide a vibrant, fragrant base that intensifies flavor layers in dishes like curries and masalas.
Slow-tallow extraction
Braising Indian curries allows slow-tallow extraction, enhancing flavor complexity and tenderizing tough cuts through prolonged low-heat cooking in liquid, whereas ghee roasting quickly infuses richness but lacks the depth achieved by gradual fat rendering. Slow-tallow extraction during braising improves mouthfeel and aroma by slowly melting connective tissues and fats, creating a richer, more succulent curry experience.
Differential spice blooming
Braising Indian curries gently simmers spices in a moist environment, enhancing complex flavor extraction by slowly dissolving essential oils into the sauce. Ghee roasting intensifies spice blooming through high-heat fat infusion, quickly releasing volatile aromas and resulting in a richer, more robust spice profile.
Emulsified braise finish
Braising Indian curries creates a rich, emulsified sauce where slow cooking breaks down collagen into gelatin, enhancing mouthfeel and depth, unlike ghee roasting which imparts a direct browned fat flavor without emulsification. The emulsified braise finish ensures a velvety, well-integrated curry texture essential for authentic taste and optimal spice fusion.
Hybrid-roast braising
Hybrid-roast braising combines the deep caramelization effects of ghee roasting with the slow, moist heat of traditional braising, enhancing the flavor complexity and tenderness of Indian curries. This method allows spices to bloom in ghee first, locking in aroma before slow cooking absorbs rich, succulent textures, offering a superior alternative to each technique used independently.
Clarified lipid reduction
Braising Indian curries uses slow cooking with minimal oil, reducing clarified lipid content compared to ghee roasting which involves high heat and extensive use of ghee, leading to higher saturated fat levels. Opting for braising preserves flavor while lowering overall clarified lipid intake, making it a healthier cooking method for traditional Indian dishes.
Unctuous mouthfeel enhancement
Braising enhances unctuosity in Indian curries by slowly breaking down collagen and fats, creating a rich, velvety texture that deeply infuses spices into the sauce. Ghee roasting intensifies flavor with caramelized notes but offers a lighter mouthfeel compared to the gelatinous, luscious body developed through braising.
Braising vs Ghee roasting for Indian curries Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com