Braising develops deep, concentrated flavors by slowly cooking meat or vegetables in a small amount of liquid, allowing the ingredients to tenderize and absorb rich, complex tastes. Infused oil poaching imparts subtle, aromatic nuances through gentle cooking in flavored oils, preserving the food's texture and enhancing richness without heaviness. Both methods enhance richness differently, with braising offering bold, robust flavors and infused oil poaching providing delicate, fragrant infusions.
Table of Comparison
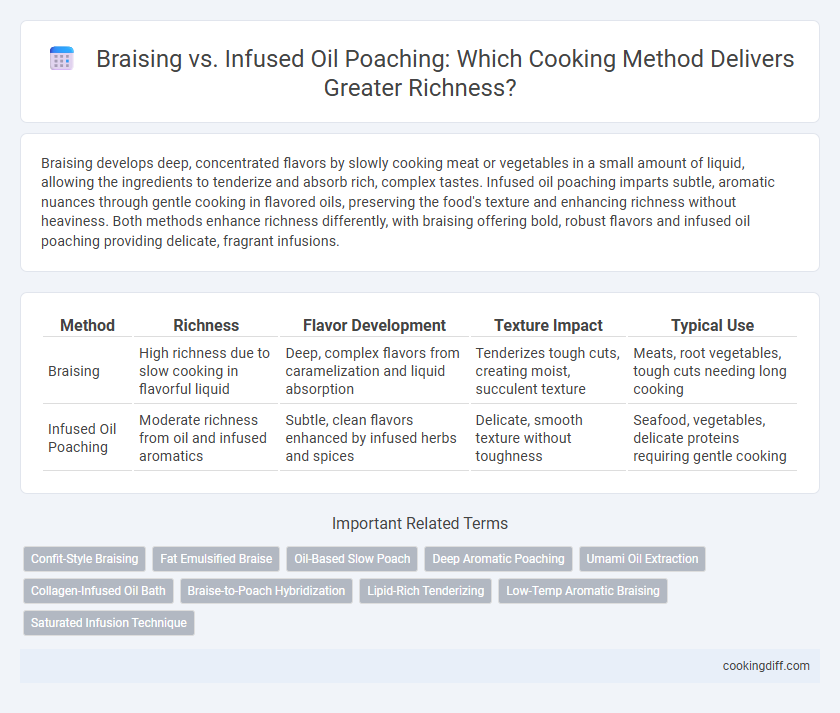
| Method | Richness | Flavor Development | Texture Impact | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Braising | High richness due to slow cooking in flavorful liquid | Deep, complex flavors from caramelization and liquid absorption | Tenderizes tough cuts, creating moist, succulent texture | Meats, root vegetables, tough cuts needing long cooking |
| Infused Oil Poaching | Moderate richness from oil and infused aromatics | Subtle, clean flavors enhanced by infused herbs and spices | Delicate, smooth texture without toughness | Seafood, vegetables, delicate proteins requiring gentle cooking |
Understanding Braising: The Fundamentals
Braising combines dry and moist heat to tenderize tougher cuts of meat while infusing deep, concentrated flavors through slow cooking in liquid. This method creates a richness distinct from infused oil poaching, which primarily imparts flavor through gentle oil immersion without the same level of texture transformation.
- Slow Cooking Process - Braising involves simmering food slowly in a small amount of liquid at low temperatures to break down collagen and soften meat fibers.
- Flavor Development - The combination of searing and prolonged cooking in aromatic liquids intensifies complex flavors and enhances richness.
- Texture Enhancement - Braising produces tender, moist dishes with deep, hearty textures compared to the lighter mouthfeel of infused oil poaching.
Infused Oil Poaching: A Flavorful Technique
Infused oil poaching enhances richness by slowly cooking ingredients in flavored oils, allowing deep absorption of herbs, spices, and aromatics. Unlike braising, which relies on a liquid base and prolonged simmering, infused oil poaching preserves vibrant flavors while maintaining a delicate texture. This technique intensifies taste profiles and adds a luxurious mouthfeel, making it ideal for meats, seafood, and vegetables.
Comparing Cooking Methods for Depth of Flavor
Braising enhances richness through slow cooking in flavorful liquids, allowing connective tissues to break down and infuse depth into the dish. In contrast, infused oil poaching imparts subtle herbal and aromatic notes without developing the same complex texture or richness.
- Braising Develops Deep Flavor - Slow cooking in stock or wine extracts gelatin and marrow, creating a robust, layered taste.
- Infused Oil Poaching Adds Delicate Aromatics - Poaching in flavored oils transfers herbal essences gently without altering texture significantly.
- Texture Differentiation - Braising yields tender, fall-apart meat while poaching maintains a firmer, more restrained mouthfeel.
Moisture Retention: Braising vs Infused Oil Poaching
Braising excels in moisture retention by cooking food slowly in a liquid, which creates a tender, flavorful texture through steam and simmering. The tightly sealed environment traps juices, preventing dryness and enhancing richness.
Infused oil poaching maintains moisture by gently cooking food in flavored oil at low temperatures, preserving delicate textures while infusing subtle richness. However, it may lack the deep, concentrated moisture absorption found in braising due to the absence of a water-based cooking medium.
Ingredient Compatibility and Versatility
Braising intensifies flavors by slow-cooking ingredients in a flavorful liquid, making it ideal for tougher cuts of meat and sturdy vegetables. Infused oil poaching imparts subtle aromatic richness, better suited for delicate proteins and vegetables that benefit from gentle heat without losing texture.
- Ingredient Compatibility - Braising accommodates robust, fibrous ingredients, allowing their flavors to meld deeply with the braising liquid.
- Ingredient Compatibility - Infused oil poaching works best with tender, quick-cooking items that absorb infused herbs and spices without becoming tough.
- Versatility - Braising offers flexibility in flavor profiles with various liquids like wine, stock, or tomato-based sauces, enhancing a wide range of dishes.
Each technique uniquely enriches dishes by optimizing ingredient texture and flavor extraction based on cooking medium and heat application.
Fat Content and Texture Outcomes
| Method | Fat Content | Texture Outcomes |
| Braising | High fat content as cooking involves both oil and animal fats released during slow cooking. | Produces tender, moist meat with a rich, gelatinous texture due to collagen breakdown and fat infusion. |
| Infused Oil Poaching | Moderate fat content, primarily from flavored oils with minimal animal fat absorption. | Results in a delicate, smooth texture with enhanced aromatic flavor but less richness compared to braising. |
Extraction and Infusion of Aromatics
How does braising compare to infused oil poaching in extracting and infusing aromatics for richness? Braising uses slow cooking in a small amount of liquid to break down tough fibers and deeply extract flavors from herbs and spices into the dish. Infused oil poaching gently releases aromatic compounds into the oil, concentrating flavors without the dilution found in liquid braising mediums.
Time and Temperature Considerations
Braising involves cooking food slowly at low temperatures, typically between 275degF and 325degF, allowing collagen to break down and flavors to deepen over several hours. Infused oil poaching uses lower temperatures, around 160degF to 180degF, cooking more quickly while imparting the infused flavors through gentle heat. Time-intensive braising develops richer, more complex textures, whereas oil poaching emphasizes flavor infusion with shorter cooking duration.
Nutrient Preservation in Both Techniques
Braising retains a higher concentration of water-soluble vitamins by cooking food slowly in a closed environment, preventing nutrient loss. Infused oil poaching preserves fat-soluble vitamins and imparts richness without exposing ingredients to high temperatures, thus maintaining delicate flavors.
The gentle heat in braising enhances nutrient absorption while softening tough fibers, making minerals more bioavailable. Infused oil poaching uses moderate heat and fat medium, which reduces oxidation and protects heat-sensitive nutrients. Both techniques balance richness and nutrient preservation, but braising excels in retaining water-soluble vitamins, whereas infused oil poaching is superior for fat-soluble nutrient retention.
Related Important Terms
Confit-Style Braising
Confit-style braising enhances richness by cooking meat slowly in its own fat or a flavored oil, resulting in tender, deeply savory textures unmatched by infused oil poaching, which imparts gentle flavor without the same depth of succulence. The controlled low temperature and prolonged cooking time in confit-style braising allow collagen breakdown and fat infusion, producing a richer mouthfeel compared to the lighter, more delicate outcome of infused oil poaching.
Fat Emulsified Braise
Fat emulsified braising creates deep richness by breaking down connective tissues and integrating rendered fat into the cooking liquid, resulting in a velvety, flavorful sauce that coats the ingredients. In contrast, infused oil poaching imparts subtle flavors through gentle heat and fat infusion but lacks the intensified mouthfeel and complex texture developed by the slow emulsification process in braising.
Oil-Based Slow Poach
Oil-based slow poach in braising enhances richness by gently cooking food in infused oils, preserving natural flavors and infusing aromatic compounds deeply into the ingredients. Compared to infused oil poaching alone, this method combines low-temperature oil cooking with moisture retention, resulting in tender textures and intensified, complex taste profiles.
Deep Aromatic Poaching
Deep aromatic poaching infuses ingredients with layers of complex flavors using spiced oils at low temperatures, creating a delicate yet rich taste profile. Braising, while providing tenderization through slow cooking in liquid, lacks the intense aroma concentration and subtle flavor integration achieved by infused oil poaching.
Umami Oil Extraction
Braising enhances umami through slow cooking in flavorful liquids, allowing collagen and glutamates to break down and infuse the dish with rich depth. Infused oil poaching extracts umami compounds directly into the oil, concentrating savory flavors but with a lighter texture than braised dishes.
Collagen-Infused Oil Bath
Braising leverages slow cooking with moist heat to break down collagen into gelatin, enriching the dish with a tender texture and deep flavor, whereas infused oil poaching utilizes a collagen-infused oil bath to impart richness while maintaining a lighter mouthfeel. The collagen-infused oil bath in poaching delivers concentrated umami and nutritional benefits, enhancing moisture retention and delivering a nuanced taste profile distinct from the gelatinous texture developed through braising.
Braise-to-Poach Hybridization
Braise-to-poach hybridization combines the slow, moist heat of braising with the delicate infusion properties of oil poaching, creating a richer flavor profile and tender texture. This method enhances the depth of savory compounds by integrating braising's caramelization with infused oil's aromatic essence, resulting in a complex, succulent dish.
Lipid-Rich Tenderizing
Braising infuses dishes with deep, lipid-rich tenderness by slowly cooking proteins in flavorful, fat-containing liquids, enhancing moisture and texture through collagen breakdown. Infused oil poaching imparts subtle richness but lacks the complex lipid integration and gelatinous tenderizing that braising achieves, making braising superior for maximizing mouthfeel and juiciness in lipid-rich preparations.
Low-Temp Aromatic Braising
Low-temp aromatic braising enhances richness by slowly cooking ingredients in a flavorful liquid with herbs and spices, allowing deeper infusion of flavors and tenderizing proteins without the risk of overcooking. Unlike infused oil poaching, which imparts subtle aroma at moderate temperatures, braising at low heat develops complex, concentrated flavors and a luscious texture ideal for hearty dishes.
Braising vs Infused Oil Poaching for Richness Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com