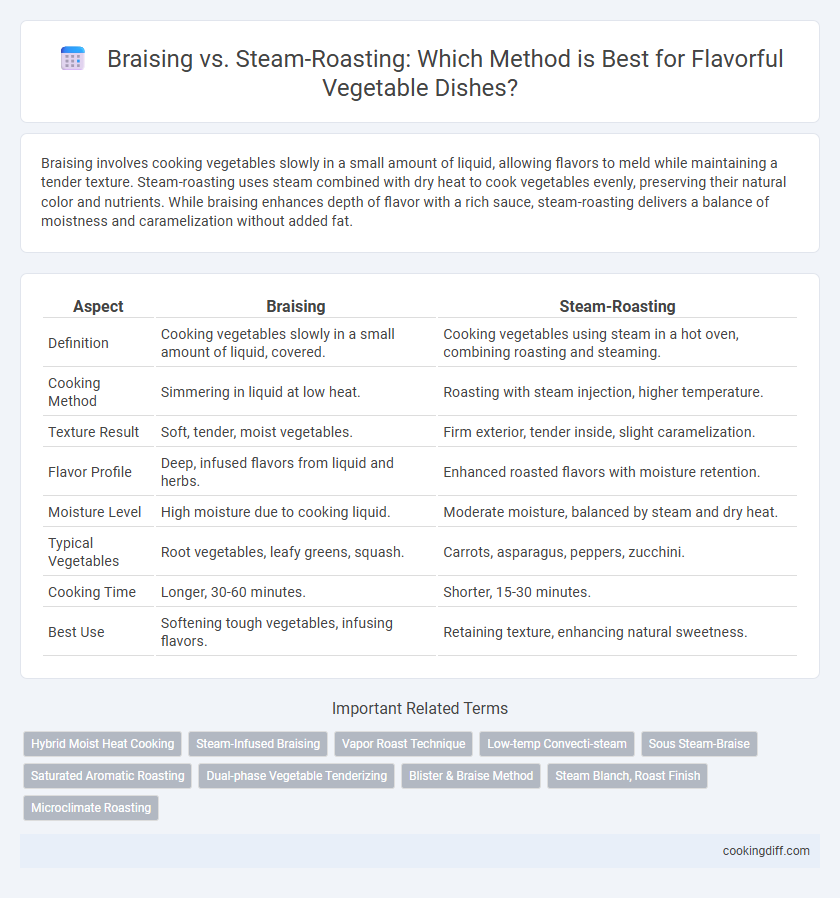
Braising involves cooking vegetables slowly in a small amount of liquid, allowing flavors to meld while maintaining a tender texture. Steam-roasting uses steam combined with dry heat to cook vegetables evenly, preserving their natural color and nutrients. While braising enhances depth of flavor with a rich sauce, steam-roasting delivers a balance of moistness and caramelization without added fat.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Braising | Steam-Roasting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cooking vegetables slowly in a small amount of liquid, covered. | Cooking vegetables using steam in a hot oven, combining roasting and steaming. |
| Cooking Method | Simmering in liquid at low heat. | Roasting with steam injection, higher temperature. |
| Texture Result | Soft, tender, moist vegetables. | Firm exterior, tender inside, slight caramelization. |
| Flavor Profile | Deep, infused flavors from liquid and herbs. | Enhanced roasted flavors with moisture retention. |
| Moisture Level | High moisture due to cooking liquid. | Moderate moisture, balanced by steam and dry heat. |
| Typical Vegetables | Root vegetables, leafy greens, squash. | Carrots, asparagus, peppers, zucchini. |
| Cooking Time | Longer, 30-60 minutes. | Shorter, 15-30 minutes. |
| Best Use | Softening tough vegetables, infusing flavors. | Retaining texture, enhancing natural sweetness. |
Introduction to Braising and Steam-Roasting
Braising involves cooking vegetables slowly in a small amount of liquid at low heat, allowing flavors to meld and textures to soften. This method is ideal for tougher vegetables, resulting in tender, flavorful dishes rich in nutrients.
Steam-roasting combines steaming and roasting techniques by cooking vegetables with steam in a hot oven, preserving moisture while creating a caramelized exterior. It enhances natural sweetness and maintains vibrant color, making it perfect for delicate vegetables that require quick, even cooking.
Understanding Braising: Techniques and Benefits
What distinguishes braising from steam-roasting in preparing vegetable dishes? Braising involves cooking vegetables slowly in a small amount of liquid, allowing flavors to meld and textures to soften evenly. This technique enhances nutrient retention and creates rich, tender results compared to the dry heat method used in steam-roasting.
Exploring Steam-Roasting: How It Works
Steam-roasting combines dry heat with steam to cook vegetables evenly while preserving their natural flavors and nutrients. This method uses a closed environment where water vapor circulates, maintaining moisture without diluting the taste.
- Moisture retention - Steam-roasting prevents vegetables from drying out, enhancing tenderness and juiciness.
- Flavor preservation - The steam environment locks in essential oils and nutrients for richer taste profiles.
- Even cooking - Consistent steam distribution ensures vegetables cook uniformly without burning or undercooking.
Steam-roasting offers a precise balance of moisture and heat, ideal for vibrant, flavorful vegetable dishes.
Key Differences Between Braising and Steam-Roasting
Braising involves cooking vegetables slowly in a small amount of liquid at low heat, allowing flavors to meld and the texture to become tender and rich. Steam-roasting, on the other hand, uses steam and dry heat together to cook vegetables quickly while preserving their natural color and crispness.
Key differences include moisture level and cooking time: braising relies on immersion in liquid for extended periods, whereas steam-roasting uses moist heat vapor combined with higher heat, resulting in a faster process. Nutrient retention in steam-roasting is typically higher due to shorter cooking times and minimal exposure to water.
Flavor Development: Braising vs Steam-Roasting
Braising enhances vegetable dishes by combining moist and dry heat, allowing flavors to meld deeply through slow cooking in a flavorful liquid. This method promotes caramelization and Maillard reactions, resulting in richer, more complex taste profiles compared to steam-roasting.
Steam-roasting preserves the natural texture and brightness of vegetables by cooking with steam at high temperatures, retaining subtle, fresh flavors. It minimizes nutrient loss and avoids overcooking, keeping vegetables tender yet crisp. While steam-roasting maintains a clean taste, braising intensifies and layers flavors for heartier dishes.
Texture Outcomes: What to Expect
Braising vegetables results in a tender, richly flavored texture as they slowly cook in a small amount of liquid, allowing the fibers to break down fully. Steam-roasting, by contrast, preserves more bite and firmness due to the combination of dry heat and steam, preventing over-softening. Expect braised vegetables to be softer and more infused with flavor, while steam-roasted vegetables retain a slightly crisp and vibrant texture.
Best Vegetables for Braising
Braising is ideal for dense, hearty vegetables like carrots, parsnips, and potatoes that benefit from slow cooking in liquid to develop deep flavors and tender textures. Steam-roasting suits more delicate vegetables, preserving their natural crunch and vibrant color while cooking quickly with steam and dry heat.
- Carrots - Their firm structure softens perfectly during braising, absorbing savory liquids for enhanced taste.
- Parsnips - Braising breaks down their fibrous texture, transforming them into creamy, flavorful bites.
- Potatoes - Slow braising creates a tender interior and rich flavor profile, unmatched by quicker steam-roasting methods.
Top Vegetables Suited to Steam-Roasting
| Vegetable | Steam-Roasting Benefits |
|---|---|
| Asparagus | Retains vibrant color and crisp-tender texture through steam-roasting. |
| Brussels Sprouts | Develops a caramelized exterior while keeping a moist interior during steam-roasting. |
| Carrots | Enhances natural sweetness and preserves firmness better than braising. |
| Cauliflower | Maintains shape and achieves a nutty flavor due to dry heat combined with steam. |
| Broccoli | Prevents sogginess and intensifies flavor through gentle steam-roasting. |
Nutrition and Health Considerations
Braising vegetables retains more water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex due to the cooking liquid used in the process, enhancing nutrient absorption. Steam-roasting preserves antioxidants and mineral content by exposing vegetables to dry heat with minimal nutrient loss. Both methods promote health benefits, but braising offers better retention of vitamins sensitive to heat and oxidation.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Moist Heat Cooking
Braising and steam-roasting are hybrid moist heat cooking methods that combine both steaming and roasting techniques to enhance the texture and flavor of vegetable dishes. Braising involves slow cooking vegetables in a small amount of liquid to break down fibers and infuse flavors, whereas steam-roasting uses steam to maintain moisture while roasting at higher temperatures, resulting in tender yet slightly caramelized vegetables.
Steam-Infused Braising
Steam-infused braising combines the gentle heat of steam with liquid to cook vegetables evenly while preserving nutrients and enhancing natural flavors. Unlike steam-roasting, this method maintains a moist environment that prevents drying and encourages tender, richly flavored vegetable dishes with concentrated aromas.
Vapor Roast Technique
Vapor roast technique combines steam and dry heat to preserve vegetable nutrients while enhancing flavor through caramelization during braising. Unlike traditional steam-roasting, braising uses a liquid base to tenderize vegetables slowly, resulting in richer texture and deeper taste profiles.
Low-temp Convecti-steam
Low-temp convecti-steam offers precise temperature control and uniform moisture distribution, enhancing vegetable texture and flavor retention compared to braising. This method reduces nutrient loss and prevents overcooking, making it ideal for delicate vegetables requiring gentle, consistent heat.
Sous Steam-Braise
Sous steam-braise combines the benefits of braising and steam-roasting by using low-temperature steam to gently cook vegetables, preserving nutrients and enhancing natural flavors while maintaining a tender texture. Unlike traditional braising, which relies on liquid immersion, sous steam-braising uses controlled steam pressure, resulting in evenly cooked vegetables with intensified aromas and minimal nutrient loss.
Saturated Aromatic Roasting
Braising infuses vegetables with rich, deep flavors through prolonged cooking in a small amount of liquid, while saturated aromatic roasting enhances the natural sweetness and caramelization by enveloping vegetables in steam and hot air, creating a tender texture with intensified aromatic notes. Saturated aromatic roasting maximizes Maillard reactions, resulting in a complex flavor profile distinct from the moist, infused essence achieved by braising.
Dual-phase Vegetable Tenderizing
Braising combines low-temperature cooking in a small amount of liquid with gentle heat to effectively break down vegetable fibers, resulting in tender, flavorful dishes. Steam-roasting utilizes dual-phase cooking by first steaming to soften vegetables before roasting to enhance caramelization and texture, offering a balance between moisture retention and Maillard reaction development.
Blister & Braise Method
The Blister & Braise method combines high-heat searing to develop caramelized flavors on vegetables before slowly cooking them in liquid, enhancing depth and texture compared to steam-roasting, which relies mainly on moist heat and preserves a lighter, fresher vegetable profile. Braising intensifies savory notes through Maillard reactions during blistering, while steam-roasting emphasizes natural vegetable sweetness and tenderness without browning.
Steam Blanch, Roast Finish
Steam blanching preserves the vibrant color and nutrients of vegetables by briefly exposing them to steam before quickly cooling, creating a perfect base for steam-roasting. Steam-roasting combines this technique with dry heat roasting, enhancing flavor development while maintaining texture, contrasting with braising, which involves longer cooking in liquid resulting in softer vegetables.
Braising vs Steam-roasting for vegetable dishes Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com