Braising relies on consistent, low heat applied directly from a stovetop or oven, allowing the meat to tenderize slowly in liquid. Wonderbag cooking uses insulated heat retention to continue cooking food after initial boiling without added fuel, maintaining temperature for hours. While braising provides precise heat control, the Wonderbag excels in energy efficiency and slow, gentle cooking.
Table of Comparison
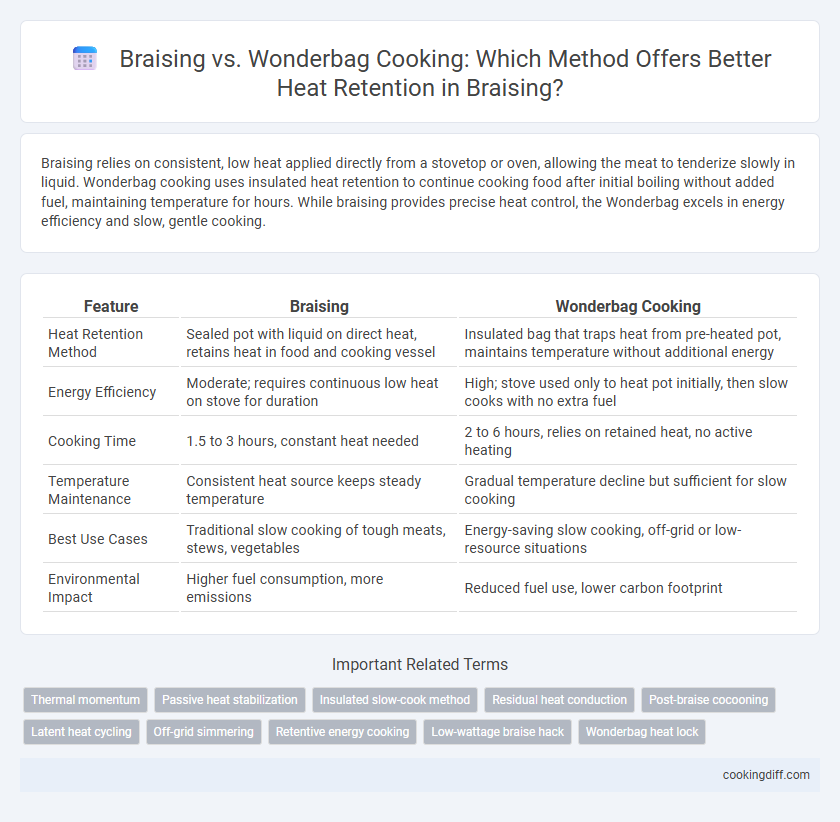
| Feature | Braising | Wonderbag Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Retention Method | Sealed pot with liquid on direct heat, retains heat in food and cooking vessel | Insulated bag that traps heat from pre-heated pot, maintains temperature without additional energy |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate; requires continuous low heat on stove for duration | High; stove used only to heat pot initially, then slow cooks with no extra fuel |
| Cooking Time | 1.5 to 3 hours, constant heat needed | 2 to 6 hours, relies on retained heat, no active heating |
| Temperature Maintenance | Consistent heat source keeps steady temperature | Gradual temperature decline but sufficient for slow cooking |
| Best Use Cases | Traditional slow cooking of tough meats, stews, vegetables | Energy-saving slow cooking, off-grid or low-resource situations |
| Environmental Impact | Higher fuel consumption, more emissions | Reduced fuel use, lower carbon footprint |
Introduction to Braising and Wonderbag Cooking
Braising involves cooking food slowly in a small amount of liquid at low heat, often using a heavy pot to retain heat and moisture. Wonderbag cooking is a heat-retention method where a preheated pot is placed inside an insulated bag, allowing food to continue cooking without continuous external heat. Both techniques optimize energy efficiency, but braising relies on steady heat application while Wonderbag uses insulation to maintain cooking temperature.
How Braising Works: Heat Retention Explained
How does braising compare to Wonderbag cooking in terms of heat retention? Braising works by cooking food slowly in a sealed pot, where heat is transferred evenly from the stove to the food, maintaining high temperatures for extended periods. Unlike the Wonderbag, which relies on insulation to retain residual heat after removing the pot from the heat source, braising continuously applies heat to achieve tender, flavorful results through consistent temperature control.
The Science Behind Wonderbag Cooking
| The Wonderbag utilizes insulation technology to retain heat by trapping thermal energy within its insulated fabric layers, enabling slow cooking without continuous heat supply. Braising relies on direct heat from a stove or oven to break down collagen in meats, whereas the Wonderbag maintains a consistent temperature by minimizing heat loss after initial boiling. Scientific studies show that the Wonderbag's heat retention reduces energy consumption and preserves nutrients by slowing the cooking process through a low thermal gradient environment. |
Key Differences: Braising vs Wonderbag Heat Efficiency
Braising relies on prolonged low heat in a covered pot to tenderize food, while Wonderbag cooking uses insulation to retain heat after initial boiling. The key difference lies in continuous heat application versus passive heat retention for cooking completion.
- Heat Source Duration - Braising requires a consistent heat source throughout cooking, whereas Wonderbag retains heat without ongoing energy input.
- Energy Efficiency - Wonderbag minimizes fuel use by insulating residual heat, making it more energy-efficient than traditional braising.
- Cooking Control - Braising allows precise temperature adjustments, but Wonderbag cooking depends on initial heat and thermal retention quality.
Understanding these differences helps optimize cooking methods based on heat efficiency and energy consumption.
Energy Consumption Comparison
Braising requires continuous heat input from a stovetop or oven, resulting in higher energy consumption compared to Wonderbag cooking, which utilizes retained heat to cook food slowly after initial heating. Studies show Wonderbag can reduce energy use by up to 50% due to its efficient insulation and minimal external heat requirements.
Energy consumption during braising varies based on cooking duration and appliance efficiency, often leading to increased fuel or electricity costs. Wonderbag cooking allows for significant savings by maintaining optimal temperatures without repeated heat sources, offering an eco-friendly alternative for slow-cooked meals.
Flavor Development: Braising vs Wonderbag Method
Braising uses direct heat to slowly break down tough fibers, enhancing deep, rich flavors through Maillard reactions, while the Wonderbag method relies on residual heat that preserves more subtle, natural tastes. The controlled temperature in braising intensifies flavor complexity, whereas Wonderbag maintains moisture and prevents overcooking, resulting in a lighter flavor profile.
- Braising generates intense flavor - Direct heat promotes caramelization and deep flavor development over extended cooking times.
- Wonderbag preserves natural flavors - Slow residual heat retains moisture and prevents flavor loss from evaporation.
- Heat retention differs in effect - Braising enhances flavor complexity through sustained high temperatures; Wonderbag favors gentle cooking preserving delicate taste nuances.
Nutrition Preservation in Both Techniques
Braising retains nutrients by slow-cooking food in a sealed pot, which minimizes nutrient loss through evaporation and heat exposure. Wonderbag cooking uses insulated heat retention to continue cooking food without additional energy, preserving vitamins sensitive to prolonged high temperatures. Both methods effectively maintain nutritional quality, but Wonderbag's gentle, consistent heat may better conserve heat-sensitive nutrients like vitamin C and folate.
Practicality and Ease of Use
Braising relies on consistent oven or stovetop heat, requiring active temperature monitoring and energy use, which can be less practical for busy cooks. Wonderbag cooking leverages insulated heat retention, allowing food to continue cooking without a constant energy source, enhancing ease of use and convenience.
The Wonderbag's portability and minimal supervision reduce the need for complex cooking setups compared to traditional braising methods. Braising offers precise control over cooking temperatures but demands more attention and equipment, making it less user-friendly in everyday scenarios.
Best Dishes for Braising and Wonderbag
Braising excels with tougher cuts of meat like short ribs and pork shoulder, allowing collagen to break down slowly for tender, flavorful dishes. Wonderbag cooking is ideal for slow-cooked stews and legumes that benefit from consistent low heat without continuous supervision.
Best dishes for braising include pot roast, osso buco, and coq au vin, where retained moisture and heat create rich, deep flavors. Wonderbag's insulation method suits dishes like chili, lentil stew, and curries, enabling energy-efficient slow cooking while preserving nutrients. Both methods optimize heat retention but serve different culinary purposes depending on the desired texture and cooking control.
Related Important Terms
Thermal momentum
Braising relies on sustained heat transfer through direct contact with a hot cooking vessel, maximizing thermal momentum to break down tough fibers and evenly cook ingredients. Wonderbag cooking enhances thermal momentum by utilizing insulated, slow-heat retention, allowing residual heat to continue the cooking process without ongoing energy input.
Passive heat stabilization
Braising relies on passive heat stabilization achieved through tightly sealed cookware that traps steam and maintains consistent internal temperatures, promoting tenderization over extended cooking periods. Wonderbag cooking uses insulated heat-retention bags to sustain residual heat without continuous external heat, enabling slow-cooked meals with minimal energy consumption and stable warmth.
Insulated slow-cook method
Braising relies on a tight-sealed pot and consistent stovetop heat to slowly tenderize food, while Wonderbag cooking uses an insulated slow-cook method that traps residual heat after brief stovetop heating to maintain temperature without continuous energy use. The Wonderbag's heat retention capability offers energy efficiency and gentle, even cooking, making it ideal for long-duration slow-cooks compared to traditional braising.
Residual heat conduction
Braising relies on slow, direct heat applied through a pot to break down tough fibers, whereas Wonderbag cooking maximizes residual heat conduction by insulating the pot, retaining thermal energy long after the initial heat source is removed. This method preserves moisture and emphasizes gentle, uniform cooking, reducing energy consumption while maintaining the flavor and tender texture typical of braised dishes.
Post-braise cocooning
Post-braise cocooning with braising relies on tightly sealed cookware that maintains direct heat and moisture for hours, enhancing flavor development and tenderness through consistent temperature retention. The Wonderbag, using insulation for passive heat retention, allows gradual cooking but offers less precise temperature control, making braising more effective for dishes requiring sustained, intense heat post-sear.
Latent heat cycling
Braising relies on consistent oven or stovetop heat, where latent heat cycling occurs as the cooking vessel alternates between absorbing and releasing heat to maintain temperature, resulting in tender, evenly cooked food. Wonderbag cooking enhances heat retention by utilizing insulated slow-cooking, minimizing heat loss and latent heat cycling, which preserves energy and sustains gentle, steady temperatures for prolonged braising.
Off-grid simmering
Braising relies on consistent heat from a stovetop to break down tough fibers in meat, while Wonderbag cooking maximizes off-grid simmering by using insulated heat retention to gently cook food over hours without continuous energy input. The Wonderbag's insulated design reduces fuel consumption and maintains steady temperatures, making it ideal for slow cooking in off-grid environments where heat control is crucial.
Retentive energy cooking
Braising relies on consistent low heat applied over time, typically in an oven or stovetop, which effectively breaks down tough fibers in meats and vegetables while maintaining moisture. Wonderbag cooking utilizes insulated, non-electric heat retention technology that traps residual heat to continue cooking food gently without additional energy input, making it a highly energy-efficient alternative for slow-cooked recipes.
Low-wattage braise hack
Braising with low wattage heat sources benefits significantly from the Wonderbag's superior insulation, which maintains consistent temperature and minimizes energy use during long cooking processes. This method enhances tenderization while reducing electricity consumption compared to traditional slow braising on stovetops or ovens.
Braising vs Wonderbag Cooking for heat retention. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com