Deep-frying involves submerging food completely in hot oil, ensuring rapid cooking and a crispy texture through high temperatures. Oil infusion frying, by contrast, uses lower temperatures and the gradual absorption of flavored oils, enhancing taste without the intense heat exposure. This technique offers a healthier alternative by reducing oil degradation and imparting unique flavors.
Table of Comparison
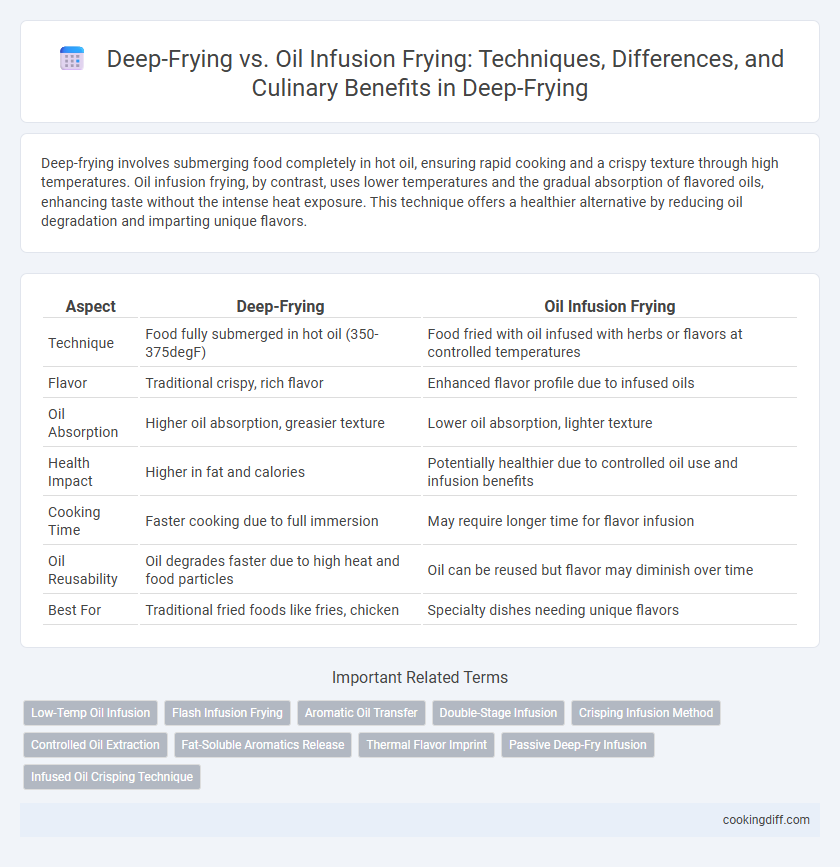
| Aspect | Deep-Frying | Oil Infusion Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Food fully submerged in hot oil (350-375degF) | Food fried with oil infused with herbs or flavors at controlled temperatures |
| Flavor | Traditional crispy, rich flavor | Enhanced flavor profile due to infused oils |
| Oil Absorption | Higher oil absorption, greasier texture | Lower oil absorption, lighter texture |
| Health Impact | Higher in fat and calories | Potentially healthier due to controlled oil use and infusion benefits |
| Cooking Time | Faster cooking due to full immersion | May require longer time for flavor infusion |
| Oil Reusability | Oil degrades faster due to high heat and food particles | Oil can be reused but flavor may diminish over time |
| Best For | Traditional fried foods like fries, chicken | Specialty dishes needing unique flavors |
Understanding Deep-Frying: Key Principles
What distinguishes deep-frying from oil infusion frying in culinary techniques? Deep-frying involves submerging food completely in hot oil, typically between 350degF and 375degF, which cooks food quickly by heat transfer through oil. Oil infusion frying, on the other hand, uses infused oils to impart flavors during frying, enhancing taste while maintaining the rapid cooking benefits of traditional deep-frying.
What Is Oil Infusion Frying?
Oil infusion frying is a technique where flavors are infused into cooking oil before frying food, enhancing the taste and aroma. Unlike traditional deep-frying, which relies solely on hot oil for cooking, oil infusion frying introduces additional ingredients to create a more complex flavor profile.
- Flavor enhancement - Infusing herbs, spices, or aromatics into oil allows deeper flavor penetration into fried foods.
- Temperature control - Oil infusion requires careful temperature management to preserve infused flavors and avoid burning.
- Health benefits - This method can reduce the need for added seasonings post-frying, potentially lowering sodium intake.
Temperature Control in Both Methods
Deep-frying requires maintaining oil temperatures typically between 350degF and 375degF to ensure proper cooking and crispiness, while avoiding excessive oil absorption. Precise temperature control prevents food from becoming greasy or undercooked during deep-frying.
Oil infusion frying operates at slightly lower temperatures around 300degF to 325degF, which allows the oil to transfer infused flavors without burning the food. Careful temperature regulation in oil infusion frying enhances flavor extraction and preserves texture more effectively than traditional deep-frying.
Oil Selection: Suitability for Each Technique
Deep-frying requires oils with high smoke points such as peanut, canola, or sunflower oil to withstand the intense heat without breaking down. Oil infusion frying utilizes oils rich in flavor compounds, like olive or sesame oil, to impart distinctive tastes during cooking at lower temperatures. Selecting the right oil based on smoke point and flavor profile optimizes results for each frying technique and enhances the overall dish quality.
Flavor Development: Deep-Frying vs Oil Infusion
| Technique | Flavor Development |
|---|---|
| Deep-Frying | Enhances flavor through Maillard reaction and caramelization, creating a crispy texture and rich, savory taste by rapidly cooking food in hot oil at high temperatures (350-375degF). |
| Oil Infusion Frying | Adds infused, aromatic flavors directly to the oil, allowing the food to absorb nuanced tastes from herbs, spices, or other ingredients during frying, resulting in a more complex and layered flavor profile. |
Texture Differences Between the Two Methods
Deep-frying produces a crispy, evenly browned exterior due to the complete submersion of food in hot oil at temperatures between 350degF and 375degF. Oil infusion frying, by contrast, uses lower temperatures and infused oils, resulting in a more delicate texture with subtle flavor integration.
Deep-fried foods have a crunchy crust and a moist interior because of rapid moisture evaporation and Maillard reaction. Oil infusion frying creates a tender bite with enhanced aroma from infused herbs or spices absorbed during cooking. Texture differences stem from variations in heat transfer and oil absorption rates in the two techniques.
Cooking Times: Fast vs Slow Processes
Deep-frying typically involves cooking food at high temperatures ranging from 350degF to 375degF, resulting in rapid cooking times often under 10 minutes. This fast process creates a crispy outer layer while sealing moisture inside, making it ideal for items like french fries or fried chicken.
Oil infusion frying operates at lower temperatures and uses longer cooking durations, often exceeding 20 minutes, to slowly transfer flavors from infused oils into the food. This method enhances taste complexity but requires more precise temperature control to avoid overcooking or oil degradation.
Safety Considerations in Deep-Frying and Oil Infusion
Deep-frying involves submerging food in hot oil, posing risks like burns and grease fires, whereas oil infusion frying uses controlled infusion techniques that minimize oil splatter. Both methods require strict temperature monitoring to prevent overheating and ensure user safety.
- Temperature Control - Maintaining oil temperature below its smoke point reduces fire hazards in both techniques.
- Oil Handling - Proper handling and disposal of used oil are critical to prevent environmental and health risks.
- Protective Equipment - Using heat-resistant gloves and eye protection minimizes injury from hot oil splashes.
Adopting proper safety protocols enhances the overall safety of deep-frying and oil infusion frying processes.
Health Impacts: Comparing Oil Absorption Levels
Deep-frying generally results in higher oil absorption compared to oil infusion frying, leading to increased calorie intake and potential cardiovascular risks. Oil infusion frying utilizes pressurized oil absorption, which significantly reduces the amount of oil retained in the food, promoting a healthier alternative. Studies indicate that oil infusion frying can lower oil content by up to 30%, improving the health impact without sacrificing texture or flavor.
Related Important Terms
Low-Temp Oil Infusion
Low-temp oil infusion frying enhances flavor absorption by slowly infusing oils at temperatures below traditional deep-frying, preserving delicate aromas and nutrients that high heat often degrades. Unlike conventional deep-frying at temperatures of 350-375degF, this technique uses controlled temperatures typically under 250degF to achieve a richer taste profile and reduced oil oxidation.
Flash Infusion Frying
Flash infusion frying combines rapid heat transfer with oil infusion, resulting in faster cooking times and enhanced flavor penetration compared to traditional deep-frying. This technique uses high-pressure oil infusion to create a crisp texture while reducing oil absorption, offering a healthier and more efficient alternative to conventional methods.
Aromatic Oil Transfer
Deep-frying involves submerging food in hot oil to cook rapidly and create a crispy texture, while oil infusion frying enhances flavor by transferring aromatic compounds from herbs and spices directly into the oil, intensifying the taste profile. The aromatic oil transfer in infusion frying allows for a more complex flavor absorption compared to conventional deep-frying, where the oil primarily acts as a heat medium with minimal flavor impartation.
Double-Stage Infusion
Deep-frying involves submerging food in hot oil at temperatures typically between 160degC and 190degC, resulting in rapid cooking and a crispy exterior, while oil infusion frying, particularly Double-Stage Infusion, enhances flavor by first infusing oil with herbs or spices at low temperatures before deep-frying the food in the flavored oil to achieve both intense taste and optimal texture. Double-Stage Infusion optimizes heat transfer and flavor penetration, combining traditional deep-frying efficiency with the aromatic complexity of infused oils, making it a superior technique for gourmet culinary applications.
Crisping Infusion Method
The Crisping Infusion Method in Oil Infusion Frying enhances flavor penetration while maintaining a superior, even crispness compared to traditional Deep-frying, which often results in a heavier, less uniform texture. By slowly infusing oils with spices before frying, this technique achieves a delicate balance of taste and crunch, improving the overall sensory experience and reducing oil absorption.
Controlled Oil Extraction
Deep-frying involves immersing food in hot oil at temperatures typically between 160-190degC, resulting in rapid cooking and a crispy texture through controlled heat transfer but often leads to higher oil absorption. Oil infusion frying, by contrast, uses a lower temperature and oil infused with flavors to allow controlled oil extraction, reducing overall oil uptake while enhancing taste and maintaining food quality.
Fat-Soluble Aromatics Release
Deep-frying achieves intense flavor by rapidly releasing fat-soluble aromatics through high-temperature oil immersion, creating a crispy texture and deep aroma in food. Oil infusion frying, however, gently extracts and transfers these aromatics at lower temperatures, preserving delicate flavors without burning or degrading valuable aromatic compounds.
Thermal Flavor Imprint
Deep-frying creates a distinctive thermal flavor imprint by rapidly cooking food at high temperatures, causing Maillard reactions and caramelization that enhance aroma and taste. Oil infusion frying, by contrast, imparts subtle, layered flavors as infused oils transfer botanical or spice notes during cooking, offering a more controlled flavor profile with less intense thermal alterations.
Passive Deep-Fry Infusion
Passive Deep-Fry Infusion combines the high-heat, rapid cooking of traditional deep-frying with the gradual flavor penetration characteristic of oil infusion, enhancing taste without compromising texture. This technique uses controlled temperature variations to allow the infused oil to permeate food during frying, resulting in a crisp exterior and deeply flavored interior.
Deep-frying vs Oil infusion frying for technique. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com