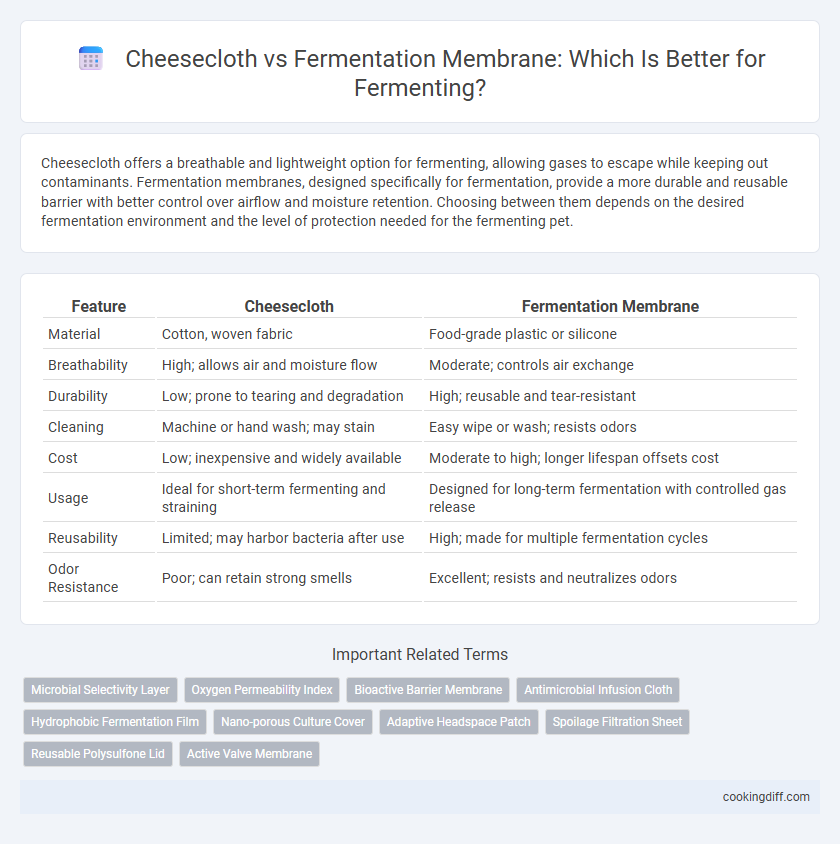
Cheesecloth offers a breathable and lightweight option for fermenting, allowing gases to escape while keeping out contaminants. Fermentation membranes, designed specifically for fermentation, provide a more durable and reusable barrier with better control over airflow and moisture retention. Choosing between them depends on the desired fermentation environment and the level of protection needed for the fermenting pet.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cheesecloth | Fermentation Membrane |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Cotton, woven fabric | Food-grade plastic or silicone |
| Breathability | High; allows air and moisture flow | Moderate; controls air exchange |
| Durability | Low; prone to tearing and degradation | High; reusable and tear-resistant |
| Cleaning | Machine or hand wash; may stain | Easy wipe or wash; resists odors |
| Cost | Low; inexpensive and widely available | Moderate to high; longer lifespan offsets cost |
| Usage | Ideal for short-term fermenting and straining | Designed for long-term fermentation with controlled gas release |
| Reusability | Limited; may harbor bacteria after use | High; made for multiple fermentation cycles |
| Odor Resistance | Poor; can retain strong smells | Excellent; resists and neutralizes odors |
Introduction: Understanding Fermenting Covers
Cheesecloth and fermentation membranes both serve as breathable covers that protect fermenting foods from contaminants while allowing gases to escape. Cheesecloth is a loosely woven cotton fabric that is reusable and widely accessible for home fermentation projects.
Fermentation membranes are designed specifically for fermentation, featuring a fine mesh that prevents bugs and dust with improved breathability. Choosing the right cover depends on the type of fermentation and desired airflow control to ensure optimal microbial activity.
What is Cheesecloth? Definition and Uses
Cheesecloth is a loosely woven cotton fabric primarily used in food preparation and preservation processes. It allows air circulation while preventing contaminants from entering fermenting vessels, making it ideal for straining liquids and wrapping cheese during fermentation.
In fermentation, cheesecloth serves as a breathable cover that protects kombucha, sauerkraut, and other fermenting foods from insects and dust. Its porous texture facilitates airflow essential for the fermentation process, preventing mold growth while maintaining an anaerobic environment. Compared to fermentation membranes, cheesecloth is more affordable but may require more frequent replacement due to its lower durability and susceptibility to tearing.
What is a Fermentation Membrane? Overview and Features
A fermentation membrane is a specialized covering designed to regulate airflow and moisture during fermentation processes. It provides a more controlled environment compared to traditional cheesecloth, reducing contamination risks while allowing gases to escape.
- Material Composition - Made from breathable, food-grade polymers that maintain optimal humidity levels.
- Durability - Reusable and resistant to tearing, offering long-term use across multiple fermenting cycles.
- Functionality - Prevents dust and insects from entering while allowing fermentation gases to vent efficiently.
Fermentation membranes enhance the safety and consistency of fermenting byproducts compared to porous cheesecloth alternatives.
Airflow and Oxygen Control: Cheesecloth vs. Membranes
Cheesecloth offers excellent airflow but provides minimal oxygen control during fermentation, which can lead to inconsistent fermenting environments. Fermentation membranes regulate oxygen flow more precisely, promoting stable fermentation with reduced risk of contamination.
- Cheesecloth allows high airflow - Its loosely woven fibers enable ample oxygen exchange essential for aerobic fermentation phases.
- Limited oxygen barrier of cheesecloth - This can result in unintended exposure to airborne contaminants and variable fermentation results.
- Fermentation membranes provide controlled oxygen permeability - Designed to maintain optimal oxygen levels, they support consistent microbial activity and prevent spoilage.
Contamination Risks: Comparing Protective Barriers
Which protective barrier offers better contamination control during fermentation, cheesecloth or fermentation membrane? Cheesecloth, being loosely woven, allows more airflow but also increases exposure to airborne contaminants, raising the risk of mold and unwanted bacteria growth. Fermentation membranes provide a tighter seal, effectively minimizing contamination while maintaining necessary gas exchange for fermentation processes.
Moisture Retention and Evaporation Differences
Cheesecloth offers moderate moisture retention by allowing excess liquid to evaporate, which helps prevent sogginess during fermentation. Its loosely woven fabric promotes airflow but may lead to higher evaporation rates compared to specialized membranes.
Fermentation membranes are engineered to optimize moisture balance by minimizing evaporation while still permitting gas exchange. This controlled environment ensures consistent humidity levels, enhancing fermentation quality and preventing drying of the fermenting product.
Reusability and Sustainability of Cheesecloth vs. Membranes
| Material | Reusability | Sustainability |
|---|---|---|
| Cheesecloth | Highly reusable when washed properly; natural cotton fibers allow multiple fermentation cycles. | Biodegradable and compostable, made from renewable cotton, reducing environmental impact. |
| Fermentation Membrane | Often single-use or limited reuse due to synthetic materials that degrade with washing. | Less sustainable as membranes are generally made from plastics, contributing to waste and microplastic pollution. |
Ease of Use and Cleaning Considerations
Cheesecloth is lightweight and easy to handle, but its loosely woven fabric can trap residue, making cleaning more time-consuming. Fermentation membranes feature a finer mesh that prevents contamination while allowing easy rinsing and quick drying, enhancing ease of maintenance. Choosing between the two depends on whether convenience in cleaning or traditional breathability during fermentation is prioritized.
Flavor Development: Impact on Fermentation Process
Cheesecloth allows more airflow during fermentation, promoting bacterial activity that enhances complex flavor profiles in fermented foods. Fermentation membranes provide controlled oxygen exchange, resulting in a more consistent but subtler flavor development.
- Cheesecloth enhances oxygen exposure - This increased airflow stimulates diverse microbial growth, enriching the flavor complexity of the ferment.
- Fermentation membranes regulate oxygen levels - Controlled permeability limits oxidation and produces a cleaner, milder taste.
- Choice affects acidogenesis and flavor compounds - Different oxygen exchanges influence the production of organic acids and aromatic molecules essential for flavor depth.
Related Important Terms
Microbial Selectivity Layer
Cheesecloth offers minimal microbial selectivity, allowing a broad spectrum of environmental microbes to interact with the fermenting substrate, which can lead to unpredictable fermentation results. In contrast, fermentation membranes provide a targeted microbial selectivity layer that controls oxygen flow and inhibits unwanted microbial contamination, ensuring a consistent and controlled fermentation environment.
Oxygen Permeability Index
Cheesecloth offers moderate oxygen permeability ideal for fermentation processes requiring gentle airflow, whereas fermentation membranes provide a more controlled Oxygen Permeability Index, ensuring optimal anaerobic conditions and preventing unwanted microbial contamination. Selecting the appropriate material directly influences fermentation quality by regulating oxygen exposure, essential for maintaining desired microbial activity and product consistency.
Bioactive Barrier Membrane
Bioactive barrier membranes provide superior protection during fermentation by preventing contaminants and oxygen exposure, preserving the integrity of microbial cultures more effectively than traditional cheesecloth. These membranes enhance fermentation outcomes by maintaining optimal moisture and airflow balance, which promotes the growth of beneficial microbes and inhibits spoilage organisms.
Antimicrobial Infusion Cloth
Cheesecloth offers breathability for fermenting but lacks antimicrobial properties, while fermentation membranes with antimicrobial infusion cloth actively inhibit mold and bacteria growth, enhancing fermentation safety. The antimicrobial infusion cloth's fine weave combined with biocidal agents supports optimal air flow and contamination prevention, improving the consistency and flavor of fermented products.
Hydrophobic Fermentation Film
Hydrophobic fermentation films offer superior moisture control and prevent contamination better than traditional cheesecloth, creating an ideal anaerobic environment for consistent fermentation. Unlike cheesecloth, these specialized membranes resist liquid absorption while allowing gas exchange, enhancing the quality and safety of fermented products.
Nano-porous Culture Cover
Nano-porous culture covers provide superior airflow control compared to traditional cheesecloth, creating an optimal microenvironment for fermentation by allowing precise gas exchange while preventing contamination. Unlike cheesecloth's larger pores, the nano-porous membrane ensures consistent humidity and temperature, enhancing microbial activity and resulting in more reliable fermentation outcomes.
Adaptive Headspace Patch
Cheesecloth offers breathable protection but lacks precise gas exchange control during fermentation, whereas fermentation membranes with Adaptive Headspace Patch technology optimize oxygen permeability and CO2 release, enhancing microbial activity and ensuring consistent fermentation quality. Advanced membranes reduce contamination risks and moisture loss more effectively than traditional cheesecloth, resulting in improved flavor and texture development in fermented products.
Spoilage Filtration Sheet
Cheesecloth is a loosely woven cotton fabric ideal for straining liquids but often allows contaminants to pass through, increasing the risk of spoilage during fermentation. Fermentation membranes, specifically designed spoilage filtration sheets, provide a finer barrier that effectively filters out unwanted bacteria and mold spores, ensuring a cleaner fermentation process and improved product safety.
Reusable Polysulfone Lid
The reusable polysulfone lid offers superior durability and chemical resistance compared to traditional cheesecloth, ensuring consistent airflow control during fermentation and minimizing contamination risks. Its airtight seal optimizes microbial growth environments, enhancing the quality and safety of fermented products.
Cheesecloth vs Fermentation membrane for fermenting. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com