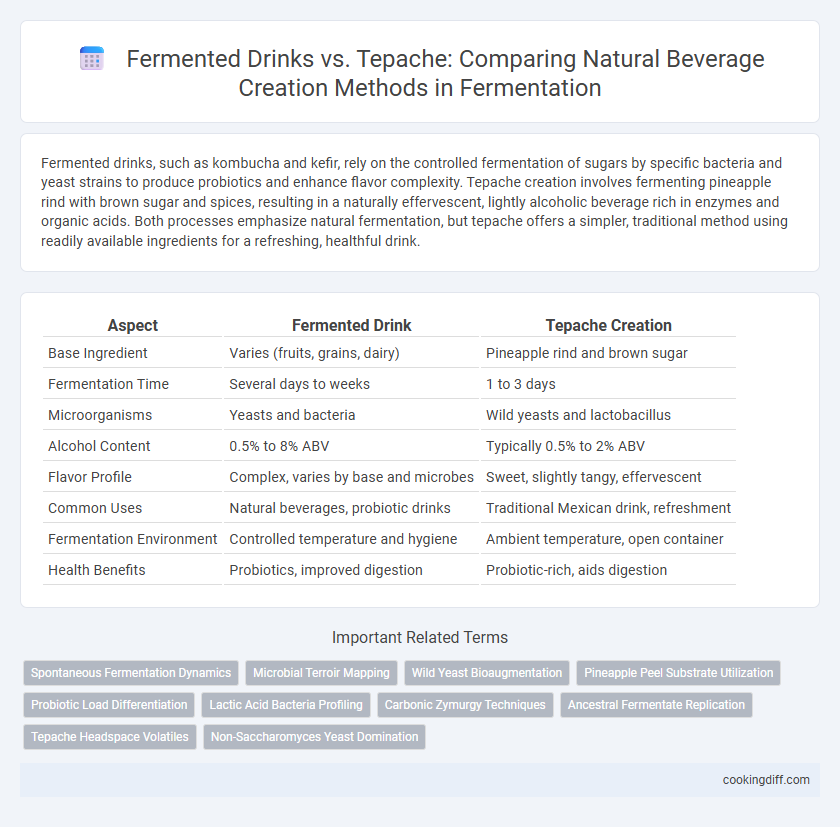
Fermented drinks, such as kombucha and kefir, rely on the controlled fermentation of sugars by specific bacteria and yeast strains to produce probiotics and enhance flavor complexity. Tepache creation involves fermenting pineapple rind with brown sugar and spices, resulting in a naturally effervescent, lightly alcoholic beverage rich in enzymes and organic acids. Both processes emphasize natural fermentation, but tepache offers a simpler, traditional method using readily available ingredients for a refreshing, healthful drink.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fermented Drink | Tepache Creation |
|---|---|---|
| Base Ingredient | Varies (fruits, grains, dairy) | Pineapple rind and brown sugar |
| Fermentation Time | Several days to weeks | 1 to 3 days |
| Microorganisms | Yeasts and bacteria | Wild yeasts and lactobacillus |
| Alcohol Content | 0.5% to 8% ABV | Typically 0.5% to 2% ABV |
| Flavor Profile | Complex, varies by base and microbes | Sweet, slightly tangy, effervescent |
| Common Uses | Natural beverages, probiotic drinks | Traditional Mexican drink, refreshment |
| Fermentation Environment | Controlled temperature and hygiene | Ambient temperature, open container |
| Health Benefits | Probiotics, improved digestion | Probiotic-rich, aids digestion |
Understanding Fermented Drinks: Basics and Benefits
What distinguishes a fermented drink from tepache in natural beverage creation? Fermented drinks encompass a broad category involving controlled microbial growth to develop flavors and enhance probiotics, promoting gut health. Tepache, a specific fermented beverage originating from Mexico, utilizes pineapple peel fermentation with added spices, offering unique antioxidants and digestive benefits.
What is Tepache? Origins and Unique Qualities
Tepache is a traditional Mexican fermented beverage made primarily from pineapple rinds, sweetened with brown sugar and seasoned with cinnamon. Originating from pre-Hispanic Mesoamerican cultures, it offers a mildly alcoholic, tangy flavor profile distinct from other fermented drinks like kombucha or kefir. Its natural fermentation process harnesses wild yeast, creating unique probiotics that support digestive health and provide a refreshing, low-alcohol alternative.
Key Ingredients: Fermented Drinks vs Tepache
Fermented drinks typically rely on a variety of fruits, sugars, and specific yeast strains to initiate fermentation, producing a wide range of alcoholic or probiotic beverages. Tepache, a traditional Mexican fermented drink, primarily uses pineapple rind, brown sugar (piloncillo), and cinnamon, creating a uniquely tangy and lightly effervescent beverage.
- Fermented Drinks Key Ingredients - Include diverse fruits like grapes, apples, or berries, combined with added sugars and yeast or bacteria cultures for fermentation.
- Tepache Ingredients - Focus on pineapple peel, piloncillo, and spices such as cinnamon, relying on natural yeasts for fermentation.
- Fermentation Process - Both use natural fermentation, but tepache fermentation is shorter, typically lasting 2-3 days at room temperature.
Natural Fermentation Processes Explained
| Fermented drinks such as kombucha and kefir utilize natural fermentation processes where beneficial bacteria and yeasts convert sugars into organic acids, enhancing flavor and probiotic content. |
| Tepache creation involves fermenting pineapple rind with natural yeasts and bacteria in an anaerobic environment, producing a mildly alcoholic tropical beverage rich in vitamins and enzymes. |
| Both fermentation methods rely on controlling temperature, sugar levels, and fermentation duration to optimize microbial activity and ensure safe, flavorful natural beverages. |
Health Advantages: Comparing Fermented Drinks and Tepache
Fermented drinks such as kombucha and kefir provide probiotics that improve gut health and boost the immune system. Tepache, a traditional Mexican beverage made from fermented pineapple, is rich in vitamins B and C, supporting digestion and enhancing nutrient absorption.
While fermented drinks contain live cultures that aid in maintaining a healthy microbiome, tepache offers natural antioxidants and enzymes that reduce inflammation and promote detoxification. The low sugar content of tepache compared to many commercial fermented beverages makes it a favorable option for those managing blood sugar levels. Both beverages contribute to overall wellness through their unique probiotic and nutritional profiles.
Flavor Profiles: Distinctions Between Fermented Drinks and Tepache
Fermented drinks showcase complex, tangy, and sometimes sour flavor profiles derived from diverse microbial activity, while tepache features a naturally sweet, mildly fermented taste primarily from pineapple and spices. The subtle effervescence and fruity undertones in tepache create a refreshing contrast to the often robust and acidic nature of traditional fermented beverages.
- Diverse Microbial Influence - Fermented drinks develop layered flavors through various bacteria and yeast strains that influence acidity and aroma.
- Sweet Pineapple Base - Tepache's flavor is dominated by the natural sugars in pineapple, resulting in a gentle sweetness balanced by light fermentation.
- Spice Integration - Tepache often incorporates cinnamon and cloves, adding warm, spicy notes that distinguish it from other fermented drinks.
Step-by-Step Tepache Creation Guide
Fermented drinks like tepache undergo a natural fermentation process using pineapple rind, brown sugar, and spices to create a tangy, probiotic-rich beverage. Tepache creation involves rinsing the pineapple rind, combining it with piloncillo or brown sugar in water, and allowing the mixture to ferment at room temperature for 2-3 days. This step-by-step fermentation encourages beneficial bacteria growth, resulting in a mildly effervescent, refreshing natural drink.
DIY Fermented Beverages: Tips for Beginners
Fermented drinks and tepache represent two popular categories of natural beverages that offer unique flavors and health benefits through natural fermentation processes. Tepache, a traditional Mexican drink made from pineapple rind and brown sugar, provides a beginner-friendly introduction to DIY fermentation due to its simple ingredients and quick fermentation time.
- Fermented Drink Variety - Fermented drinks include kombucha, kefir, and kvass, each requiring specific cultures and fermentation methods.
- Tepache Simplicity - Tepache involves fermenting pineapple rinds with piloncillo, allowing beginners to grasp fermentation fundamentals easily.
- Fermentation Time - Tepache ferments rapidly, typically within 2-3 days, whereas other fermented drinks may need longer periods for optimal taste.
Starting with tepache can help beginners develop fermentation skills before exploring more complex fermented beverages.
Safety and Storage for Natural Fermented Drinks
Fermented drinks such as kombucha and kefir require careful monitoring of pH levels to ensure safety by preventing harmful bacterial growth. Tepache, a traditional Mexican fermented beverage made from pineapple rind, undergoes a shorter fermentation process that typically results in a lower alcohol content and reduced risk of contamination.
Proper storage of natural fermented drinks involves refrigeration to slow fermentation and prolong shelf life, maintaining their probiotic benefits while minimizing spoilage. Tepache is best consumed fresh within a few days and stored in airtight containers at cool temperatures to preserve its flavor and safety.
Related Important Terms
Spontaneous Fermentation Dynamics
Spontaneous fermentation dynamics in fermented drinks rely on naturally occurring wild yeasts and bacteria, creating complex flavor profiles without added cultures. Tepache fermentation harnesses this process specifically through pineapple skins and sweeteners, emphasizing microbial diversity and natural sugar conversion for a refreshing, probiotic-rich beverage.
Microbial Terroir Mapping
Fermented drinks and tepache creation both rely heavily on microbial terroir mapping to enhance flavor profiles and ensure consistent fermentation quality by analyzing native microbial communities unique to each region. Harnessing indigenous bacteria and yeast strains through this mapping process allows producers to craft natural beverages that reflect local environmental influences and promote product differentiation.
Wild Yeast Bioaugmentation
Wild yeast bioaugmentation accelerates the fermentation process in the creation of natural beverages by introducing native microbial cultures that enhance flavor complexity and probiotic benefits in both fermented drinks and traditional tepache. This targeted inoculation improves fermentation consistency and promotes the development of unique aromatic profiles distinct from spontaneous fermentation methods.
Pineapple Peel Substrate Utilization
Fermented drinks and tepache both utilize pineapple peel as a substrate, harnessing its natural sugars and enzymes for probiotic-rich beverage production. The fermentation process in tepache specifically leverages naturally occurring yeasts on pineapple peels, enabling a quick, low-alcohol ferment that enhances flavor complexity and nutritional benefits.
Probiotic Load Differentiation
Fermented drinks like kefir and kombucha typically contain higher probiotic loads due to diverse bacterial strains and longer fermentation periods, enhancing gut microbiota health more effectively than tepache, which relies primarily on wild yeasts and lactobacillus with shorter fermentation. Tepache offers a milder probiotic profile with fewer live cultures, resulting in lower CFU counts while still providing beneficial enzymes and organic acids for digestive support.
Lactic Acid Bacteria Profiling
Fermented drinks benefit from diverse Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) profiles that enhance flavor complexity and probiotic properties, whereas tepache creation primarily involves specific LAB strains like Lactobacillus plantarum, which contribute to its characteristic mild acidity and natural preservation. Profiling these bacteria through genomic and metagenomic techniques enables optimization of fermentation conditions, improving beverage quality and health benefits.
Carbonic Zymurgy Techniques
Carbonic zymurgy techniques in fermented drinks enhance natural beverage profiles by utilizing anaerobic fermentation processes to retain more carbon dioxide, resulting in a naturally effervescent Tepache creation with intensified flavors. This method contrasts traditional Tepache fermentation, emphasizing rapid carbonation and preservation of raw fruit enzymes for a vibrant, refreshingly tangy drink.
Ancestral Fermentate Replication
Fermented drinks like tepache showcase ancestral fermentate replication by utilizing natural microbial cultures and traditional fruit fermentation methods, preserving authentic flavors and health benefits. This ancestral approach contrasts with modern commercial techniques by emphasizing spontaneous fermentation, local ingredients, and time-honored practices to create uniquely flavorful natural beverages.
Tepache Headspace Volatiles
Tepache creation harnesses natural fermentation of pineapple rinds, producing a complex blend of headspace volatiles such as ethyl acetate, acetic acid, and various esters that contribute to its distinctive fruity and tangy aroma profile. Compared to general fermented drinks, tepache's unique volatile compounds result from specific microbial interactions during fermentation, enhancing its sensory qualities and probiotic potential.
Fermented Drink vs Tepache Creation for natural beverages. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com