Plastic containers are affordable and lightweight options for fermenting, but they may retain odors and harbor bacteria more easily, potentially affecting the quality of the ferment. Fermentation vessels, typically made of glass, ceramic, or food-grade stainless steel, provide a non-reactive environment that maintains consistent temperature and prevents contamination. Choosing a proper fermentation vessel ensures better flavor development and reduces the risk of spoilage compared to standard plastic containers.
Table of Comparison
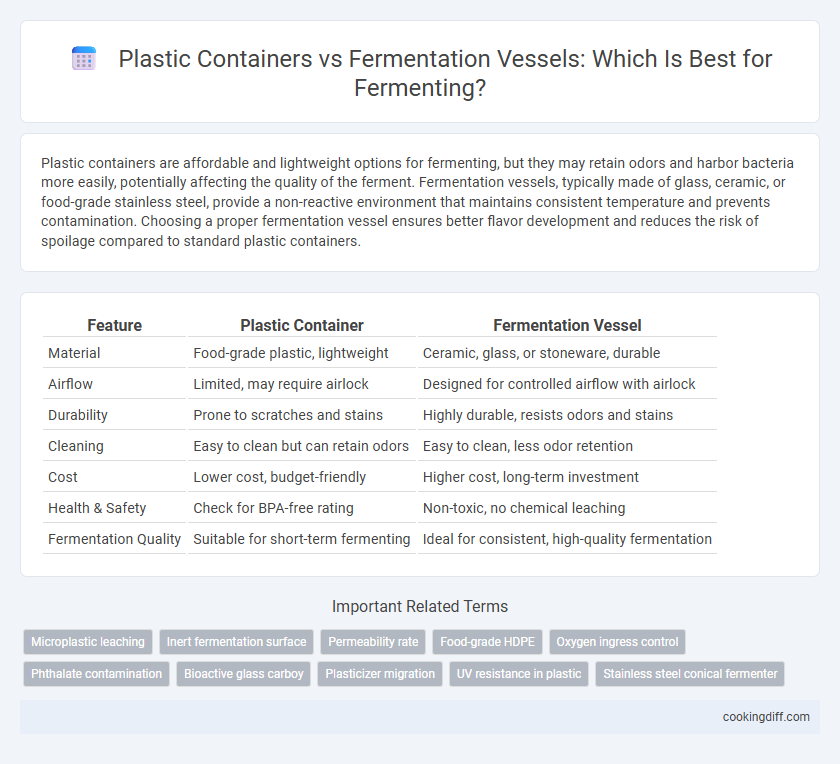
| Feature | Plastic Container | Fermentation Vessel |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Food-grade plastic, lightweight | Ceramic, glass, or stoneware, durable |
| Airflow | Limited, may require airlock | Designed for controlled airflow with airlock |
| Durability | Prone to scratches and stains | Highly durable, resists odors and stains |
| Cleaning | Easy to clean but can retain odors | Easy to clean, less odor retention |
| Cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly | Higher cost, long-term investment |
| Health & Safety | Check for BPA-free rating | Non-toxic, no chemical leaching |
| Fermentation Quality | Suitable for short-term fermenting | Ideal for consistent, high-quality fermentation |
Introduction: Choosing the Right Fermentation Container
Choosing between a plastic container and a traditional fermentation vessel significantly impacts the quality and safety of fermented foods. Plastic containers are lightweight and affordable but may harbor bacteria if scratched, whereas fermentation vessels like ceramic crocks offer non-reactive surfaces ideal for probiotic growth.
Fermentation vessels ensure consistent temperature control and proper gas release through airlocks, reducing spoilage risk. Selecting a container designed specifically for fermentation enhances microbial activity and preserves flavor profiles during the fermentation process.
Plastic Containers: Pros and Cons for Fermenting
Plastic containers are widely used for fermenting due to their lightweight and affordability, but they may pose risks like chemical leaching or scratches that harbor bacteria. Fermentation vessels made of glass or ceramic provide inert surfaces, reducing contamination risk, but are heavier and more fragile.
- Lightweight and affordable - Plastic containers are easy to handle and cost-effective for home fermentation projects.
- Risk of chemical leaching - Some plastics can release harmful substances into the ferment, especially with acidic contents.
- Scratches harbor bacteria - Plastic surfaces can develop scratches over time, increasing contamination chances.
Choosing the right vessel depends on balancing ease of use with long-term food safety considerations.
Traditional Fermentation Vessels: Benefits and Drawbacks
Traditional fermentation vessels such as ceramic crocks, glass jars, and wooden barrels offer natural breathability and help maintain consistent temperatures essential for optimal microbial activity. These materials resist chemical leaching, ensuring the purity and flavor integrity of fermented foods like sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha.
Plastic containers, while lightweight and inexpensive, may harbor micro-scratches that promote unwanted bacterial growth and can potentially leach chemicals during extended fermentation. The non-porous nature of plastic limits gas exchange, which can affect the development of complex fermentation flavors compared to traditional vessels.
Safety Concerns: Plastic Leaching vs. Inert Materials
Plastic containers may pose safety risks during fermentation due to the potential leaching of harmful chemicals like BPA and phthalates, especially under acidic and warm conditions. In contrast, fermentation vessels made from inert materials such as glass, ceramic, or stainless steel provide a non-reactive environment that prevents contamination and preserves the integrity of the ferment. Choosing inert fermentation vessels ensures safer fermentation by minimizing chemical exposure and maintaining optimal food safety standards.
Airflow and Oxygen Control: Impact on Fermentation
| Plastic Container | Limited airflow due to tighter seals, which can reduce oxygen exposure and slow down aerobic fermentation processes; porous plastics may allow minor gas exchange but often retain unwanted oxygen, increasing risk of spoilage. |
| Fermentation Vessel (e.g., Glass or Ceramic) | Designed with airlocks or breathable lids to precisely control oxygen levels, promoting optimal anaerobic conditions essential for lactic acid bacteria activity and consistent fermentation outcomes. |
| Impact on Fermentation | Effective oxygen control in fermentation vessels minimizes aerobic contamination and ensures desired microbial growth, while plastic containers may compromise fermentation integrity by inconsistent airflow and oxygen infiltration. |
Cleaning and Maintenance: Plastic vs. Specialized Vessels
Plastic containers are lightweight and easy to clean but can retain odors and develop scratches that harbor bacteria over time. Specialized fermentation vessels, typically made of glass or ceramic, provide a non-porous surface that resists contamination and allows thorough sterilization for repeated use.
- Plastic surfaces absorb odors - Scratches in plastic containers can trap fermentation byproducts, making cleaning more challenging.
- Specialized vessels offer durability - Glass and ceramic materials can withstand high-temperature sterilization methods such as boiling or chemical sanitizers.
- Maintenance frequency varies - Plastic containers may need more frequent replacement due to wear, while fermentation vessels maintain hygiene longer with proper care.
Cost Comparison: Affordability and Longevity
Plastic containers generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to specialized fermentation vessels, making them an affordable option for beginners. However, fermentation vessels made from glass, ceramic, or stainless steel provide greater durability and longevity, reducing replacement expenses over time. Investing in a high-quality fermentation vessel often leads to better preservation of flavors and reduces the risk of contamination, enhancing overall value.
Flavor and Aroma Influence by Container Material
How does the choice between a plastic container and a fermentation vessel affect the flavor and aroma during fermenting? Plastic containers can absorb and retain odors, potentially transferring unwanted flavors to the fermenting product. Fermentation vessels made of glass or ceramic provide a neutral environment that preserves the original flavor and enhances aroma development.
Suitability for Different Fermented Foods
Plastic containers are suitable for fermenting short-term batches like yogurt and kimchi due to their lightweight and non-reactive nature. Fermentation vessels, typically made of glass, ceramic, or stainless steel, are ideal for long-term fermentations such as sauerkraut and kombucha, offering better temperature control and durability.
- Plastic containers resist acids well - making them appropriate for acidic ferments that do not require extended aging.
- Fermentation vessels provide airtight seals - essential for controlled environments in alcoholic and vegetable ferments.
- Material permeability affects flavor - vessels like glass prevent contamination and off-flavors compared to some plastics.
Related Important Terms
Microplastic leaching
Fermentation vessels made from glass or ceramic significantly reduce the risk of microplastic leaching compared to plastic containers, which can release harmful microplastics into fermented foods over time. Using non-plastic fermentation vessels ensures higher food safety and preserves the purity of probiotics and natural flavors during the fermenting process.
Inert fermentation surface
Plastic containers, while affordable and lightweight, can harbor micro-scratches that trap bacteria and impact fermentation quality over time, whereas fermentation vessels made from inert materials like glass, ceramic, or stainless steel provide a non-reactive surface that preserves the purity of the ferment. An inert fermentation surface prevents unwanted chemical reactions and contamination, ensuring consistent microbial activity and optimal flavor development during the fermentation process.
Permeability rate
Plastic containers generally have a higher permeability rate compared to specialized fermentation vessels, allowing more oxygen exchange which can affect the fermentation process. Fermentation vessels made from materials like glass or ceramic provide a lower permeability rate, creating an anaerobic environment ideal for controlled fermentation and minimizing the risk of contamination.
Food-grade HDPE
Food-grade HDPE plastic containers offer durability, chemical resistance, and lightweight convenience for fermentation, making them suitable for short to medium-term projects. Unlike traditional fermentation vessels made from glass or ceramic, HDPE containers provide excellent oxygen barrier properties and reduce the risk of breakage, but they may be prone to absorbing strong odors and are less ideal for long-term fermentation.
Oxygen ingress control
Fermentation vessels made of glass or ceramic provide superior oxygen ingress control compared to plastic containers, minimizing exposure to air and reducing the risk of spoilage and oxidation. Plastic containers are more permeable to oxygen, which can compromise fermentation quality by allowing unwanted aerobic bacteria to thrive.
Phthalate contamination
Plastic containers often pose a risk of phthalate contamination during fermentation due to chemical leaching, which can adversely affect the safety and flavor of fermented products. In contrast, fermentation vessels made from glass, ceramic, or stainless steel provide a non-reactive environment that minimizes phthalate exposure and preserves product integrity.
Bioactive glass carboy
Bioactive glass carboys offer superior chemical inertness and antimicrobial properties compared to standard plastic containers, ensuring a cleaner fermentation environment with minimal risk of contamination. Their durability and resistance to odors and staining make them an ideal fermentation vessel, preserving the integrity and flavor profile of fermented products.
Plasticizer migration
Plastic containers used for fermenting often pose risks due to plasticizer migration, which can contaminate the fermenting product and impact safety and flavor quality. Dedicated fermentation vessels made from glass, ceramic, or stainless steel provide inert surfaces, preventing chemical leaching and ensuring a pure fermentation environment.
UV resistance in plastic
Plastic containers used for fermenting often lack sufficient UV resistance, which can degrade the material and negatively affect the fermentation process by exposing it to harmful ultraviolet light. In contrast, fermentation vessels made from glass or specialized UV-resistant materials provide better protection against UV rays, ensuring a more stable environment for microbial activity and preserving the quality of the ferment.
Plastic container vs Fermentation vessel for fermenting. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com