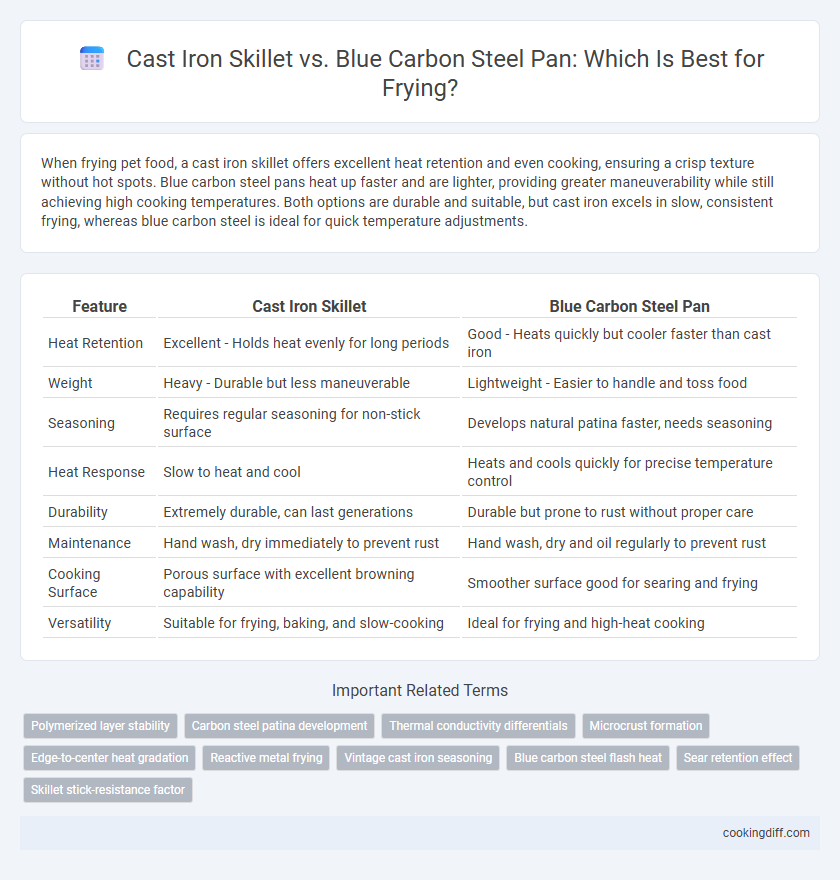
When frying pet food, a cast iron skillet offers excellent heat retention and even cooking, ensuring a crisp texture without hot spots. Blue carbon steel pans heat up faster and are lighter, providing greater maneuverability while still achieving high cooking temperatures. Both options are durable and suitable, but cast iron excels in slow, consistent frying, whereas blue carbon steel is ideal for quick temperature adjustments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cast Iron Skillet | Blue Carbon Steel Pan |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Retention | Excellent - Holds heat evenly for long periods | Good - Heats quickly but cooler faster than cast iron |
| Weight | Heavy - Durable but less maneuverable | Lightweight - Easier to handle and toss food |
| Seasoning | Requires regular seasoning for non-stick surface | Develops natural patina faster, needs seasoning |
| Heat Response | Slow to heat and cool | Heats and cools quickly for precise temperature control |
| Durability | Extremely durable, can last generations | Durable but prone to rust without proper care |
| Maintenance | Hand wash, dry immediately to prevent rust | Hand wash, dry and oil regularly to prevent rust |
| Cooking Surface | Porous surface with excellent browning capability | Smoother surface good for searing and frying |
| Versatility | Suitable for frying, baking, and slow-cooking | Ideal for frying and high-heat cooking |
Introduction: Comparing Cast Iron and Blue Carbon Steel for Frying
Cast iron skillets offer exceptional heat retention and even cooking, making them ideal for frying at consistent temperatures. Blue carbon steel pans heat up quickly and respond faster to temperature changes, providing greater control during frying.
The durability of cast iron ensures long-lasting performance with proper seasoning, while blue carbon steel pans are lighter and easier to maneuver. Both materials develop a natural non-stick surface through seasoning, enhancing their frying capabilities over time.
Heat Retention and Distribution
Cast iron skillets offer exceptional heat retention, maintaining steady temperatures ideal for frying, while blue carbon steel pans heat up faster but lose heat more quickly. The superior thermal mass of cast iron ensures even heat distribution, reducing hotspots during cooking.
Blue carbon steel pans provide more responsive temperature control, heating and cooling rapidly, which is beneficial for delicate frying tasks requiring precise heat management. Cast iron's robustness makes it better suited for high-heat searing and prolonged frying without temperature drops. Both materials develop a natural non-stick patina, enhancing their frying performance over time.
Seasoning and Nonstick Properties
Cast iron skillets develop a robust seasoning over time, enhancing their natural nonstick properties especially with regular use and proper maintenance. Blue carbon steel pans season faster and offer a smoother nonstick surface but require more frequent upkeep to prevent rust.
- Durability - Cast iron's thick material retains seasoning longer, making it ideal for high-heat frying.
- Seasoning Build-up - Blue carbon steel builds seasoning rapidly, providing a slick cooking surface within fewer uses.
- Maintenance - Cast iron needs less frequent seasoning than carbon steel but requires slow drying to avoid rust.
Choosing between the two depends on balancing seasoning durability with ease of maintenance in frying tasks.
Weight and Maneuverability
Cast iron skillets are significantly heavier than blue carbon steel pans, which can impact ease of handling during frying. Blue carbon steel pans offer superior maneuverability due to their lighter weight and thinner construction, making them ideal for frequent tossing and flipping of food.
- Cast iron skillet weight - Typically ranges from 5 to 12 pounds, contributing to its durability but reducing ease of movement.
- Blue carbon steel pan weight - Generally lighter, averaging 2 to 4 pounds, which enhances control and quick maneuvering.
- Maneuverability impact - Lighter pans like blue carbon steel improve cooking speed and precision when frying delicate foods.
Preheating Times and Temperature Response
| Cast Iron Skillet | Blue Carbon Steel Pan |
|---|---|
| Requires longer preheating time, typically around 10-15 minutes to reach optimal frying temperature. | Heats up quickly, usually within 3-5 minutes, allowing faster cooking start. |
| Retains heat exceptionally well, providing steady and even temperature during frying. | Responds rapidly to temperature changes, offering precise heat control during cooking. |
Durability and Longevity
Cast iron skillets are renowned for their exceptional durability, often lasting generations with proper care due to their robust, heavy-duty material. Blue carbon steel pans, while also durable, are lighter and more prone to surface wear over time but maintain excellent heat distribution for consistent frying results. Both cookware types develop natural non-stick seasoning layers that enhance longevity, but cast iron generally withstands rougher handling and high temperatures better than blue carbon steel.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Which cookware demands simpler maintenance, cast iron skillet or blue carbon steel pan? Cast iron skillets require regular seasoning and thorough drying to prevent rust, while blue carbon steel pans also need seasoning but are more prone to rapid oxidation if not dried immediately. Proper cleaning without soap and quick drying are essential for both to maintain their non-stick surfaces and longevity.
Frying Performance: Texture and Flavor Outcomes
Cast iron skillets provide superior heat retention, creating a consistent sear that enhances the crispy texture of fried foods. Blue carbon steel pans heat up faster and respond quickly to temperature changes, offering precise control that preserves delicate flavors during frying.
- Cast iron skillet heat retention - Maintains steady high heat ideal for even browning and a crunchy crust.
- Blue carbon steel quick heating - Allows rapid temperature adjustments to prevent burning and retain moisture.
- Flavor development - Cast iron imparts a rich, smoky flavor while blue carbon steel preserves the food's natural taste.
Compatibility with Cooking Surfaces (Stovetop, Oven, Induction)
Cast iron skillets provide excellent compatibility with various cooking surfaces, including stovetops, ovens, and induction cooktops, due to their ferrous metal composition that responds well to magnetic fields. Blue carbon steel pans also work seamlessly on stovetops and in ovens and excel on induction surfaces because of their high iron content and thin structure, allowing rapid heat transfer.
Both cookware types distribute heat evenly, but cast iron tends to retain heat longer, making it ideal for slow frying and oven finishing. Blue carbon steel pans, lighter and faster to heat, are preferred for quick frying on induction or gas stovetops where responsive temperature changes are crucial.
Related Important Terms
Polymerized layer stability
Cast iron skillets develop a robust polymerized layer that enhances durability and resistance to high-heat frying, providing superior non-stick properties over time. Blue carbon steel pans form a thinner polymerized layer that requires more frequent maintenance but offers faster heat response and lighter weight for agile frying techniques.
Carbon steel patina development
Carbon steel pans rapidly develop a natural non-stick patina through seasoning, improving frying performance by enhancing heat retention and reducing food adhesion over time. Unlike cast iron skillets, blue carbon steel offers quicker heating and lighter weight, making it ideal for precise frying while building a durable, non-toxic seasoning layer.
Thermal conductivity differentials
Cast iron skillets have lower thermal conductivity (around 50 W/m*K) compared to blue carbon steel pans, which exhibit higher thermal conductivity (approximately 60-70 W/m*K), enabling faster and more even heat distribution during frying. This thermal advantage in blue carbon steel pans reduces hot spots and allows for quicker temperature adjustments, making them ideal for precise frying control.
Microcrust formation
Cast iron skillets develop a robust microcrust due to their excellent heat retention and porous surface that promotes even browning during frying. Blue carbon steel pans heat up more quickly and provide a smoother, thinner microcrust, enhancing delicate searing and crisping outcomes.
Edge-to-center heat gradation
Cast iron skillets exhibit a pronounced edge-to-center heat gradation due to their thick, dense material which retains heat unevenly, often resulting in hotter edges and cooler centers. Blue carbon steel pans offer more uniform heat distribution across the cooking surface, minimizing temperature gradients and providing consistent frying performance from edge to center.
Reactive metal frying
Cast iron skillets excel in retaining heat and developing a natural non-stick surface but can react with acidic foods, causing metallic flavors and discoloration; blue carbon steel pans heat up faster and offer superior responsiveness, yet also require seasoning to prevent rust and minimize reactivity. Both reactive metals demand careful maintenance and seasoning to enhance frying performance while reducing unwanted metallic interactions with food.
Vintage cast iron seasoning
Vintage cast iron skillets boast a well-developed, natural non-stick seasoning layer created from years of polymerized oils that enhance heat retention and even cooking during frying. Blue carbon steel pans offer quicker heat responsiveness but typically require more frequent seasoning maintenance to achieve a similarly durable, non-stick surface.
Blue carbon steel flash heat
Blue carbon steel pans excel in frying due to their rapid flash heat capability, allowing for quick temperature recovery and even heat distribution. This property enables superior searing and crisping compared to cast iron skillets, which heat more slowly and retain heat longer.
Sear retention effect
Cast iron skillets provide superior heat retention and even heat distribution, making them ideal for maintaining high temperatures essential for perfect searing and crust formation during frying. Blue carbon steel pans heat up faster and offer better responsiveness to temperature changes, but they retain heat less effectively than cast iron, which may affect consistent sear quality.
Cast iron skillet vs blue carbon steel pan for frying. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com