Flash frying preserves the natural color and texture of vegetables by cooking them quickly at high temperatures, resulting in a crisp exterior and tender interior. Cryo-frying combines freezing and frying techniques to lock in nutrients and reduce oil absorption, producing a healthier and longer-lasting product. Both methods enhance vegetable quality, but cryo-frying is ideal for maintaining freshness and nutritional value.
Table of Comparison
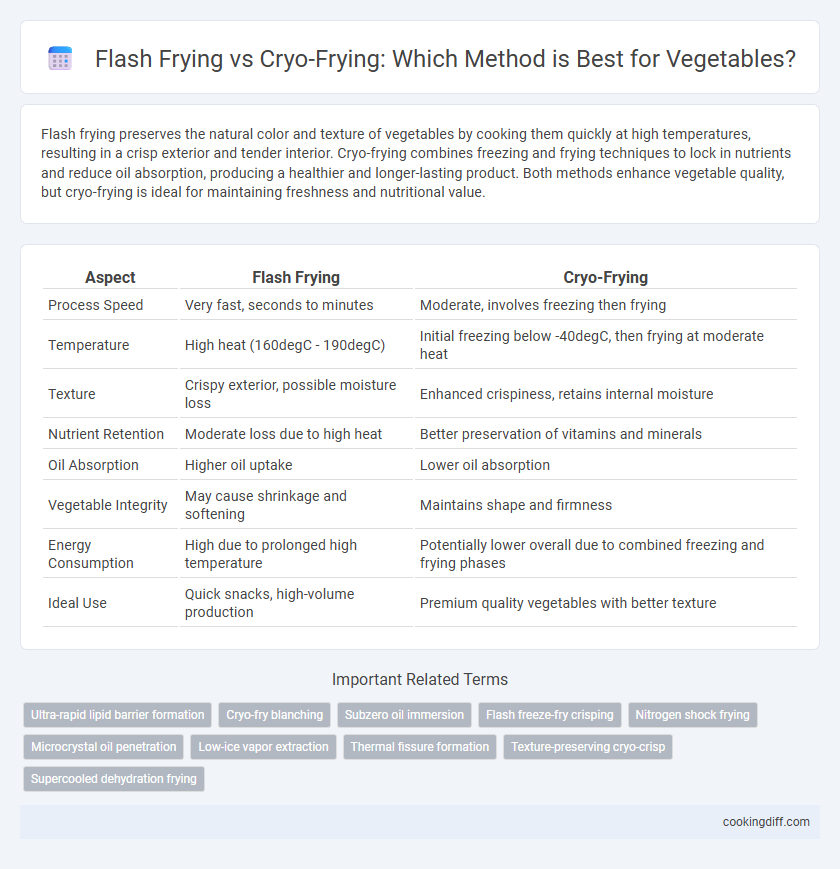
| Aspect | Flash Frying | Cryo-Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Process Speed | Very fast, seconds to minutes | Moderate, involves freezing then frying |
| Temperature | High heat (160degC - 190degC) | Initial freezing below -40degC, then frying at moderate heat |
| Texture | Crispy exterior, possible moisture loss | Enhanced crispiness, retains internal moisture |
| Nutrient Retention | Moderate loss due to high heat | Better preservation of vitamins and minerals |
| Oil Absorption | Higher oil uptake | Lower oil absorption |
| Vegetable Integrity | May cause shrinkage and softening | Maintains shape and firmness |
| Energy Consumption | High due to prolonged high temperature | Potentially lower overall due to combined freezing and frying phases |
| Ideal Use | Quick snacks, high-volume production | Premium quality vegetables with better texture |
Introduction to Advanced Vegetable Frying Techniques
Flash frying and cryo-frying represent cutting-edge methods in vegetable frying technology, each enhancing texture and flavor retention uniquely. These techniques offer innovative solutions for producing crispy, nutrient-rich vegetables with improved shelf life.
- Flash Frying - A rapid frying process using high temperatures for a short duration to preserve vegetable crispness and color.
- Cryo-Frying - Combines freezing and frying to lock in nutrients and create a distinctive crunchy texture.
- Advanced Vegetable Frying - Utilizes precise temperature control and timing to optimize flavor, nutrient content, and appearance in fried vegetables.
What is Flash Frying?
| Flash Frying | Flash frying is a cooking technique where vegetables are fried at extremely high temperatures for a very short duration, typically under 30 seconds, to preserve texture and nutrients. This rapid process minimizes oil absorption and maintains the vibrant color and crispness of the vegetables. Flash frying is ideal for preparing vegetables quickly while retaining their natural flavor and nutritional value compared to traditional frying methods. |
Understanding Cryo-Frying: The Science Explained
Cryo-frying involves freezing vegetables to ultra-low temperatures before rapid frying, preserving cellular structure and nutrients more effectively than traditional flash frying. This method minimizes oil absorption and maintains vibrant color and crunch by preventing cell wall rupture during cooking. Scientific studies highlight that cryo-frying significantly reduces oxidation and nutrient degradation compared to conventional frying techniques.
Key Differences Between Flash Frying and Cryo-Frying
Flash frying rapidly cooks vegetables at high temperatures to preserve texture and color. Cryo-frying involves freezing vegetables before frying, enhancing crispiness while retaining nutrients.
- Temperature Application - Flash frying uses hot oil at temperatures around 180-200degC, while cryo-frying involves frying frozen produce directly.
- Texture Outcome - Flash frying produces a slightly softer interior, whereas cryo-frying results in a crunchier texture due to ice crystal formation.
- Nutrient Retention - Cryo-frying better preserves vitamins and antioxidants compared to flash frying, which can degrade some heat-sensitive nutrients.
Texture and Flavor Impacts: Flash Frying vs Cryo-Frying
Flash frying rapidly cooks vegetables at high temperatures, creating a crispy exterior while retaining some natural moisture, which enhances texture contrast. This method intensifies flavor by caramelizing surface sugars and locking in freshness through quick cooking.
Cryo-frying freezes vegetables before frying, preserving cellular structure and resulting in a firmer, less soggy texture after frying. This technique maintains more of the vegetable's original flavor and nutrients by minimizing heat exposure during cooking.
Nutritional Effects: Preservation and Loss in Each Method
Flash frying preserves more water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C due to its shorter cooking time, while cryo-frying, involving freezing prior to frying, maintains structural integrity but can lead to slight nutrient degradation from ice crystal formation. Both methods impact antioxidant levels differently, with flash frying generally causing higher loss compared to cryo-frying, which better retains polyphenols and carotenoids.
- Vitamin Preservation - Flash frying minimizes vitamin C loss by rapidly cooking vegetables at high temperatures.
- Structural Impact - Cryo-frying maintains vegetable texture and nutrient density through initial freezing stages.
- Antioxidant Retention - Cryo-frying better retains antioxidants such as polyphenols and carotenoids compared to flash frying.
Choosing between flash frying and cryo-frying depends on the priority between vitamin retention and antioxidant preservation in vegetables.
Equipment and Setup: What You Need for Both Methods
Flash frying requires a deep fryer or a heavy-bottomed pan with precise temperature control, typically set between 350degF to 375degF, and a supply of oil with a high smoke point like canola or peanut oil. Cryo-frying combines cryogenic equipment, such as liquid nitrogen tanks or dry ice containers, with a standard deep fryer to flash-freeze vegetables before frying.
For flash frying, consistent oil temperature and proper ventilation are crucial to ensure even cooking and safety. Cryo-frying setups demand insulated storage for ultra-cold temperatures and specialized training to handle cryogenic materials safely while maintaining frying efficiency.
Best Vegetables for Flash Frying and Cryo-Frying
Which vegetables are best suited for flash frying and cryo-frying? Vegetables like green beans, bell peppers, and zucchini excel in flash frying due to their quick cooking time and ability to retain crispness. Cryo-frying favors starchy vegetables like potatoes and carrots, as freezing enhances texture and preserves nutrients during frying.
Safety Considerations and Precautions
Flash frying vegetables involves high temperatures that can cause oil splatters and burns, necessitating the use of protective gear such as gloves and aprons. Cryo-frying, which incorporates ultra-low temperatures before frying, reduces oil absorption but requires careful handling of liquid nitrogen or dry ice to prevent frostbite and respiratory hazards.
Proper ventilation is essential in both methods to minimize exposure to harmful fumes and maintain air quality. Ensuring that frying equipment is regularly maintained and free from defects reduces the risk of accidents. Following manufacturer guidelines and conducting training for personnel handling cryogenic materials further enhances safety during cryo-frying operations.
Related Important Terms
Ultra-rapid lipid barrier formation
Flash frying creates an ultra-rapid lipid barrier on vegetable surfaces by exposing them to extremely high temperatures for a few seconds, effectively sealing in moisture and nutrients. Cryo-frying combines freezing with frying, slowing lipid barrier formation but preserving cellular integrity, resulting in a different texture and enhanced nutrient retention.
Cryo-fry blanching
Cryo-fry blanching preserves the nutritional content and vibrant color of vegetables by rapidly freezing them before frying, minimizing cell damage and moisture loss. This method enhances texture and flavor retention compared to traditional flash frying, which often results in nutrient degradation and uneven cooking.
Subzero oil immersion
Flash frying uses high-temperature oil to quickly cook vegetables, preserving texture and color, while cryo-frying employs subzero oil immersion to freeze and fry simultaneously, enhancing crispness and nutrient retention. Subzero oil immersion in cryo-frying reduces oil absorption and oxidation, resulting in healthier, longer-lasting vegetable snacks compared to conventional flash frying.
Flash freeze-fry crisping
Flash freeze-fry crisping preserves the nutritional value and texture of vegetables by rapidly freezing them before frying, minimizing moisture loss and enhancing crispness. This process contrasts with conventional flash frying, which may lead to uneven cooking and reduced structural integrity due to higher immediate heat exposure.
Nitrogen shock frying
Nitrogen shock frying uses liquid nitrogen to instantly freeze vegetables before flash frying, preserving texture, color, and nutrients far better than traditional flash frying alone. This cryo-frying method reduces oil absorption and extends shelf life while maintaining a crisp exterior and fresh interior in vegetables.
Microcrystal oil penetration
Flash frying uses high temperatures to rapidly cook vegetables, causing larger oil microcrystals to penetrate less deeply, preserving crispness but increasing surface oiliness. Cryo-frying involves freezing vegetables prior to frying, producing smaller oil microcrystals that penetrate more uniformly, enhancing texture and reducing oil absorption for healthier, crispier results.
Low-ice vapor extraction
Flash frying preserves vegetable texture and nutrients by rapidly cooking at high temperatures, minimizing moisture loss through efficient heat transfer; cryo-frying utilizes low-ice vapor extraction to freeze vegetables quickly before frying, enhancing moisture retention and resulting in crispier, more colorful produce with extended shelf life. Low-ice vapor extraction in cryo-frying reduces ice crystal formation, maintaining cellular integrity and improving overall frying quality compared to traditional flash frying methods.
Thermal fissure formation
Flash frying rapidly heats vegetables, causing thermal fissure formation due to abrupt moisture expansion, which can lead to uneven texture and nutrient loss. Cryo-frying minimizes thermal fissures by freezing vegetables before frying, preserving cell integrity and maintaining a crisp, nutrient-rich final product.
Texture-preserving cryo-crisp
Cryo-frying utilizes ultra-low temperatures to freeze vegetables rapidly before frying, preserving cellular structure and enhancing a crispy texture compared to traditional flash frying. This technique maintains the vegetable's natural crunch and moisture by preventing cell wall collapse, making cryo-crisp vegetables a superior choice for texture retention.
Flash frying vs cryo-frying for vegetables. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com