Pan frying requires a stovetop and a frying pan, offering direct heat control for crisp, evenly cooked food with a rich, oily texture. Air frying uses a specialized appliance that circulates hot air to cook food with minimal oil, resulting in a healthier option with a crispy exterior and tender interior. Choosing between pan frying and air frying depends on preferences for flavor, texture, and convenience in meal preparation.
Table of Comparison
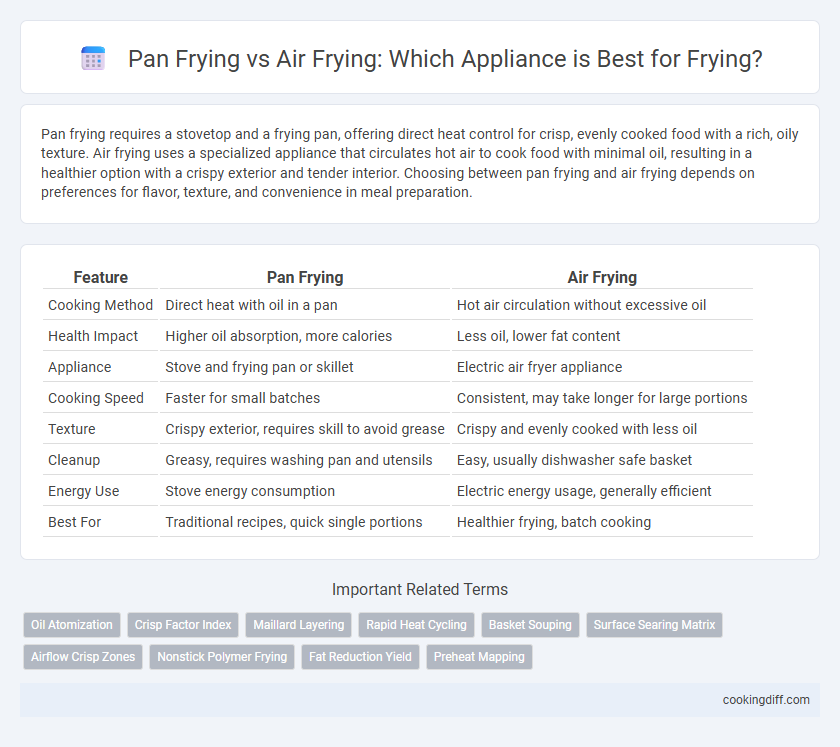
| Feature | Pan Frying | Air Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Direct heat with oil in a pan | Hot air circulation without excessive oil |
| Health Impact | Higher oil absorption, more calories | Less oil, lower fat content |
| Appliance | Stove and frying pan or skillet | Electric air fryer appliance |
| Cooking Speed | Faster for small batches | Consistent, may take longer for large portions |
| Texture | Crispy exterior, requires skill to avoid grease | Crispy and evenly cooked with less oil |
| Cleanup | Greasy, requires washing pan and utensils | Easy, usually dishwasher safe basket |
| Energy Use | Stove energy consumption | Electric energy usage, generally efficient |
| Best For | Traditional recipes, quick single portions | Healthier frying, batch cooking |
Understanding Pan Frying and Air Frying Techniques
Pan frying involves cooking food in a small amount of oil over direct heat, creating a crispy texture and rich flavor due to Maillard reaction. Air frying uses hot air circulation to cook food with minimal oil, producing a similar crispiness while reducing fat content and cooking time. Both techniques require temperature control and appropriate cookware to achieve optimal results, with pan frying suited for a variety of ingredients and air frying preferred for healthier meal preparation.
Key Differences Between Pan Fryers and Air Fryers
Pan frying uses direct heat and oil to cook food, resulting in a crispy texture and rich flavor. Air frying circulates hot air around the food, producing a similar crispiness with significantly less oil.
- Cooking Method - Pan fryers rely on oil and stovetop heat, while air fryers use rapid air circulation technology to cook food evenly.
- Health Impact - Air frying reduces fat content by using minimal oil, making it a healthier alternative compared to traditional pan frying.
- Cooking Speed - Pan frying generally cooks food faster due to direct contact with the hot pan, whereas air frying may take longer but provides consistent results.
Cooking Results: Texture and Flavor Comparison
How do pan frying and air frying compare in terms of cooking results, specifically texture and flavor? Pan frying typically produces a crispier exterior and richer flavor due to direct oil contact, which enhances Maillard browning. Air frying offers a lighter texture with less oil absorption, resulting in a slightly less intense flavor but a healthier option with similar crispness.
Health Implications: Oil Usage and Nutritional Value
Pan frying typically uses more oil, increasing fat content and calorie intake, whereas air frying requires minimal to no oil, preserving a lower fat profile. The reduced oil usage in air frying generally results in healthier meals with fewer harmful compounds generated by excessive oil heating.
- Oil Usage - Pan frying often involves submerging food in oil, leading to higher fat absorption compared to air frying's hot air circulation method.
- Nutritional Value - Air frying helps retain nutrients that might be degraded by prolonged contact with hot oil in pan frying.
- Health Implications - Reduced oil in air frying lowers the risk of cardiovascular issues linked to high-fat diets when compared to pan frying.
Appliance Cost: Upfront and Long-Term Expenses
Pan frying requires minimal upfront investment, typically needing only a skillet, which ranges from $20 to $100, making it a low-cost appliance option. Air fryers have a higher initial cost, usually between $70 and $200, but they offer energy efficiency that can reduce utility bills over time.
Long-term expenses for pan frying may include frequent oil purchases, which can add up depending on usage, as well as higher energy consumption from stovetop heating. Air fryers use significantly less oil and cook food faster, lowering both food and electricity costs across extended use. Considering maintenance and replacement parts, air fryers can be more cost-effective when factoring in durability and operational savings over several years.
Ease of Use: Setup, Cooking, and Cleaning
Pan frying requires manual temperature control and constant attention, making setup and cooking more hands-on compared to air frying, which features preset functions and automated timing. Cleaning a pan after frying can be more labor-intensive due to oil residue, whereas air fryers often have removable, dishwasher-safe parts that simplify cleanup.
- Setup - Pan frying demands preheating the pan and adding oil, while air fryers only require selecting a temperature and timer.
- Cooking - Pan frying involves flipping and monitoring food to avoid burning, but air frying uses circulating hot air for even cooking with minimal supervision.
- Cleaning - Frying pans may need scrubbing to remove stuck-on grease, whereas air fryer baskets are generally non-stick and easier to wash.
Air frying offers a more user-friendly experience in terms of setup, cooking management, and cleanup, making it a convenient choice for busy kitchens.
Versatility: What Foods Can You Cook?
Pan frying offers exceptional versatility by allowing you to cook a wide range of foods, from meats and vegetables to delicate items like eggs and pancakes. It provides precise control over cooking temperature, which is ideal for achieving various textures and flavors.
Air frying excels at preparing crispy foods such as fries, chicken wings, and frozen snacks with less oil, promoting healthier meals. However, it is less effective for dishes requiring constant stirring or delicate cooking techniques compared to traditional pan frying.
Energy Efficiency: Power Consumption Breakdown
| Appliance | Energy Consumption per Hour (kWh) | Average Cooking Time (minutes) | Energy Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pan Frying (Electric Stove) | 1.2 | 15 | Moderate energy use due to longer heating time and heat loss to surroundings |
| Air Frying | 1.0 | 12 | Higher energy efficiency with faster cooking and focused heat circulation |
Space and Storage Considerations
Pan fryers typically require more counter space and storage due to their larger size and additional accessories like frying pans and oil containers. Air fryers are compact, often designed with vertical space optimization, making them ideal for small kitchens or limited storage areas. Choosing an appliance depends on available kitchen space and preference for ease of storage and maintenance.
Related Important Terms
Oil Atomization
Pan frying relies on oil atomization to create a crispy texture by dispersing hot oil droplets evenly across the food surface, enhancing flavor and browning through Maillard reactions. Air frying uses rapid hot air circulation to achieve a similar crispness with minimal oil atomization, offering a healthier alternative by significantly reducing oil absorption while maintaining taste and texture.
Crisp Factor Index
Pan frying achieves a higher Crisp Factor Index by directly immersing food in hot oil, creating a golden, crunchy texture while preserving moisture. Air frying uses rapid air circulation with minimal oil to produce a crisp exterior, offering a healthier alternative with slightly lower crispness compared to traditional pan frying.
Maillard Layering
Pan frying enables direct contact with high heat, promoting rapid Maillard reaction and creating a thicker, more flavorful browning layer on foods, while air frying circulates hot air to achieve a similar effect with less oil and a lighter Maillard crust. The intensity and texture of the Maillard layer in pan frying generally surpass air frying, enhancing crispness and depth in flavor.
Rapid Heat Cycling
Pan frying offers rapid heat cycling through direct contact with a hot surface, delivering immediate and precise temperature control for evenly cooked food. Air frying relies on circulating hot air, which provides consistent heat but slower temperature changes, making rapid heat cycling less efficient compared to conventional pan frying.
Basket Souping
Pan frying offers direct heat and oil contact for a crispy texture, ideal for basket soupings that require even browning and rich flavor absorption. Air frying circulates hot air around the basket, reducing oil usage and allowing for healthier, low-fat soupings with a lighter, less greasy finish.
Surface Searing Matrix
Pan frying creates a superior surface searing matrix due to direct contact with a hot, oiled pan, producing a crisp, caramelized crust and Maillard reaction optimal for flavor and texture. Air frying, while convenient and healthier with less oil, relies on hot air circulation, resulting in a less intense surface sear and a drier crust that may lack the rich browning achieved by pan frying.
Airflow Crisp Zones
Air frying utilizes advanced Airflow Crisp Zones that circulate hot air evenly around the food, ensuring uniform cooking and a crispy texture with less oil compared to traditional pan frying. This technology enhances browning and crispiness by targeting specific zones within the appliance, optimizing heat distribution for healthier and faster frying results.
Nonstick Polymer Frying
Nonstick polymer frying surfaces in pan frying provide superior heat conduction and precise temperature control, promoting even browning and crisp texture without excessive oil absorption. In contrast, air frying utilizes rapid hot air circulation requiring minimal oil while preserving the nonstick coating's durability due to reduced direct oil contact.
Fat Reduction Yield
Pan frying typically uses a higher quantity of oil, resulting in greater fat absorption and higher calorie content in foods, whereas air frying significantly reduces fat intake by using hot air circulation to cook food with minimal or no added oil, offering up to 75-80% fat reduction compared to traditional frying methods. Studies show air frying can lower oil usage by approximately 90%, making it an effective appliance choice for healthier cooking with reduced fat content.
Pan frying vs air frying for appliance. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com