Shallow frying involves cooking food in a small amount of oil, providing a crispy texture and rich flavor through direct contact with hot fat. Waterless frying, on the other hand, uses minimal or no added oil, relying on the natural moisture of the food and a tightly sealed pan to steam and cook ingredients evenly. Choosing between these methods depends on the desired texture, health considerations, and the type of food being prepared.
Table of Comparison
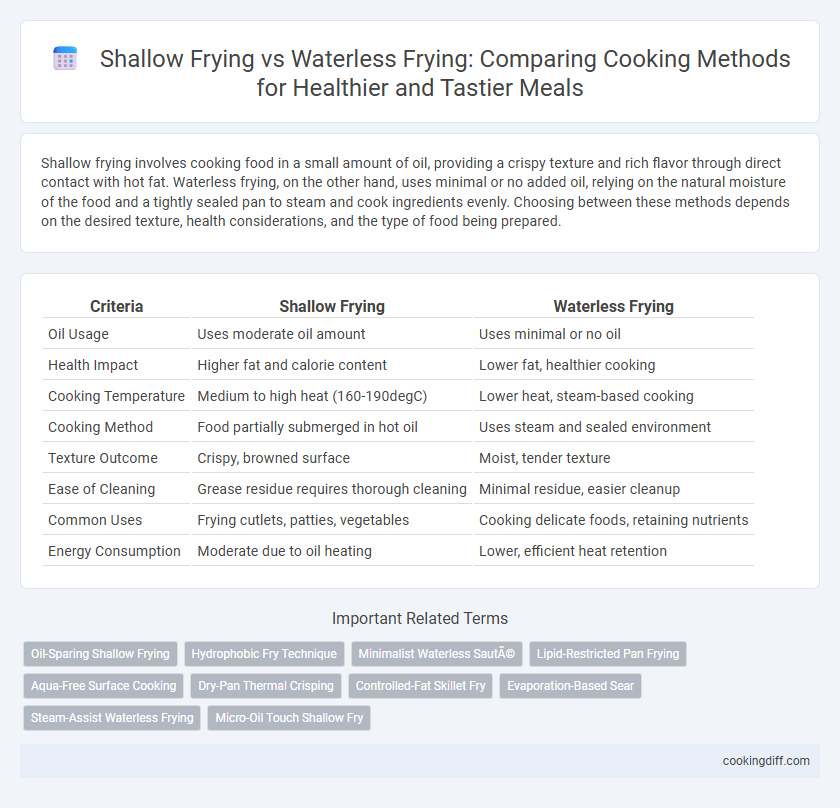
| Criteria | Shallow Frying | Waterless Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Usage | Uses moderate oil amount | Uses minimal or no oil |
| Health Impact | Higher fat and calorie content | Lower fat, healthier cooking |
| Cooking Temperature | Medium to high heat (160-190degC) | Lower heat, steam-based cooking |
| Cooking Method | Food partially submerged in hot oil | Uses steam and sealed environment |
| Texture Outcome | Crispy, browned surface | Moist, tender texture |
| Ease of Cleaning | Grease residue requires thorough cleaning | Minimal residue, easier cleanup |
| Common Uses | Frying cutlets, patties, vegetables | Cooking delicate foods, retaining nutrients |
| Energy Consumption | Moderate due to oil heating | Lower, efficient heat retention |
Understanding Shallow Frying: Definition and Basics
Shallow frying involves cooking food in a moderate amount of oil, typically covering only half the thickness of the food. This method allows for even browning while maintaining moisture inside the food.
- Oil Usage - Requires enough oil to partially submerge the food, providing a crispy texture on the outside.
- Heat Level - Cooked at medium to medium-high heat to ensure proper browning without burning.
- Food Types - Ideal for foods like cutlets, patties, and thin slices of meat or vegetables.
What Is Waterless Frying? An Introduction
Waterless frying is a cooking technique that uses minimal or no oil by relying on the natural moisture of the food to prevent sticking and promote even cooking. This method preserves the nutritional value and flavor of ingredients while reducing fat content compared to traditional shallow frying.
- Cooking process - Involves sealing a pan with a tight-fitting lid to trap steam and cook food through its own moisture.
- Health benefits - Significantly lowers oil absorption, resulting in healthier, lower-calorie meals.
- Flavor retention - Enhances natural flavors and textures without the need for additional fats or oils.
Waterless frying offers a healthier alternative to shallow frying by utilizing moisture and steam for cooking instead of large amounts of oil.
Key Differences Between Shallow and Waterless Frying
Shallow frying involves cooking food in a moderate amount of hot oil, allowing for a crispy texture and even browning, whereas waterless frying uses minimal or no added fats, relying on the moisture in the food to prevent sticking and overcooking. Shallow frying typically requires higher oil temperatures around 160-190degC to achieve desired crispiness, while waterless frying operates at lower temperatures, preserving more nutrients and reducing calorie content. The key difference lies in oil usage and cooking technique, with shallow frying ideal for texture and flavor contrast, and waterless frying prioritizing health benefits and moisture retention.
Equipment Needed for Shallow vs Waterless Frying
Shallow frying requires a frying pan or skillet with enough oil to partially submerge the food, typically using cookware made from stainless steel, cast iron, or non-stick materials. A thermometer may be needed to monitor oil temperature for consistent frying results.
Waterless frying demands specialized non-stick cookware designed to trap steam and use minimal or no oil, often constructed from heavy-gauge aluminum or ceramic with tight-fitting lids. These pans promote even heat distribution and retain moisture, eliminating the need for additional fat or oil during cooking.
Oil Usage: Shallow Frying vs Waterless Frying
How does oil usage differ between shallow frying and waterless frying methods? Shallow frying requires a generous amount of oil to partially submerge the food, promoting even crispiness and flavor development. Waterless frying uses minimal to no oil by relying on the food's natural moisture and a tightly sealed pan, resulting in healthier meals with reduced fat content.
Health Considerations: Which Method Is Better?
Shallow frying involves cooking food in a moderate amount of oil, which can increase calorie intake and the risk of unhealthy fat consumption. Waterless frying uses minimal or no oil by relying on the natural moisture of food, preserving nutrients and reducing fat absorption. For those prioritizing heart health and lower fat intake, waterless frying is generally the healthier cooking method.
Texture and Flavor Comparison
Shallow frying uses a moderate amount of oil, creating a crispy, golden texture while enhancing flavor through Maillard reactions. This method imparts a rich, savory taste due to oil absorption and surface caramelization.
Waterless frying relies on the food's natural moisture and minimal oil, preserving the ingredient's original texture and resulting in a lighter, more natural flavor profile. It produces a tender texture with less greasiness and retains more nutrients compared to shallow frying.
Suitable Foods for Shallow Frying vs Waterless Frying
Shallow frying is ideal for foods that benefit from a crispy exterior like cutlets, fish fillets, and fritters. Waterless frying suits tender vegetables and lean meats that require gentle cooking to retain moisture and nutrients.
- Cutlets and fritters - Perfect for shallow frying to achieve a golden, crunchy crust.
- Leafy greens and mushrooms - Best suited for waterless frying to prevent nutrient loss and maintain texture.
- Lean meats such as chicken breasts - Waterless frying evenly cooks without drying out the meat.
Cooking Tips for Each Frying Method
Shallow frying requires moderate oil with consistent temperature control to ensure even cooking and prevent sogginess. Using oils with high smoke points like canola or peanut oil enhances flavor and maintains food crispness.
Waterless frying uses minimal to no oil, relying on the food's moisture, ideal for retaining nutrients and reducing fat intake. Preheating the pan and covering it helps to create steam that cooks food evenly. Selecting non-stick cookware simplifies the process and prevents sticking or burning.
Related Important Terms
Oil-Sparing Shallow Frying
Oil-sparing shallow frying uses minimal oil to cook food at moderate heat, retaining flavor and texture while reducing calorie intake compared to traditional shallow frying methods. This technique maximizes oil efficiency by coating the pan evenly and allowing the food's natural moisture to aid in cooking, distinguishing it from waterless frying, which relies on steam and typically requires no oil at all.
Hydrophobic Fry Technique
Shallow frying involves cooking food in a small amount of oil, creating a crispy texture through direct fat contact, while waterless frying employs the hydrophobic fry technique that uses minimal or no added water or oil by utilizing the natural moisture and non-stick properties of cookware. The hydrophobic fry technique enhances flavor retention and reduces oil absorption, promoting healthier cooking and preserving nutrients in vegetables and meats.
Minimalist Waterless Sauté
Minimalist waterless saute uses low heat and a tight-fitting lid to cook vegetables in their own moisture, preserving nutrients and natural flavors without added oil. This method contrasts with shallow frying, which relies on a layer of hot oil, potentially causing nutrient loss and added fat absorption.
Lipid-Restricted Pan Frying
Shallow frying uses a moderate amount of oil to cook food, allowing for crisp textures but increasing lipid content, whereas waterless frying employs steam and minimal or no added fats, significantly reducing lipid intake. Lipid-restricted pan frying emphasizes controlling oil quantity and maximizing moisture retention to achieve healthier cooking outcomes without compromising flavor or texture.
Aqua-Free Surface Cooking
Shallow frying uses a moderate amount of oil to cook food partially submerged, creating a crispy texture on the surface, whereas waterless frying relies on the food's natural moisture and minimal oil to achieve a similar result with less fat. Aqua-free surface cooking enhances flavor retention and nutrient preservation by eliminating excess water, resulting in healthier, evenly cooked meals.
Dry-Pan Thermal Crisping
Shallow frying uses a small amount of oil to achieve a crispy texture through direct heat contact, while waterless frying relies on steam released from the food itself to cook and crisp without added fat. Dry-pan thermal crisping enhances the surface texture by applying intense, dry heat, creating a golden, crunchy layer without the need for excessive oil or water.
Controlled-Fat Skillet Fry
Shallow frying in a controlled-fat skillet involves using a measured amount of oil to crisp food evenly while minimizing grease absorption, ensuring a balance between texture and health. Waterless frying relies on cooking food in its own moisture with little to no added fat, preserving nutrients and reducing calorie content without sacrificing flavor.
Evaporation-Based Sear
Shallow frying uses a moderate amount of oil to create an evaporation-based sear that crisps the food's surface while retaining moisture, enhancing flavor through Maillard reaction. Waterless frying relies on the natural moisture of ingredients and high heat to achieve a similar sear without added fat, minimizing oil absorption and preserving nutritional content.
Steam-Assist Waterless Frying
Shallow frying uses oil to cook food, creating a crispy texture through direct heat, while steam-assist waterless frying relies on minimal or no added fat, utilizing steam generated from the food's natural moisture to cook evenly and preserve nutrients. Steam-assist waterless frying reduces calorie intake and oil consumption, making it a healthier alternative that maintains flavor and texture without the need for excessive oil.
Shallow Frying vs Waterless Frying for method. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com