Stir frying involves cooking food quickly over high heat with continuous stirring, preserving texture and flavor while creating a slight crispness. Sous vide frying combines precise temperature control by pre-cooking food in a water bath and finishing with frying to achieve tender interiors and evenly crispy exteriors. This method enhances juiciness and reduces overcooking compared to traditional stir frying.
Table of Comparison
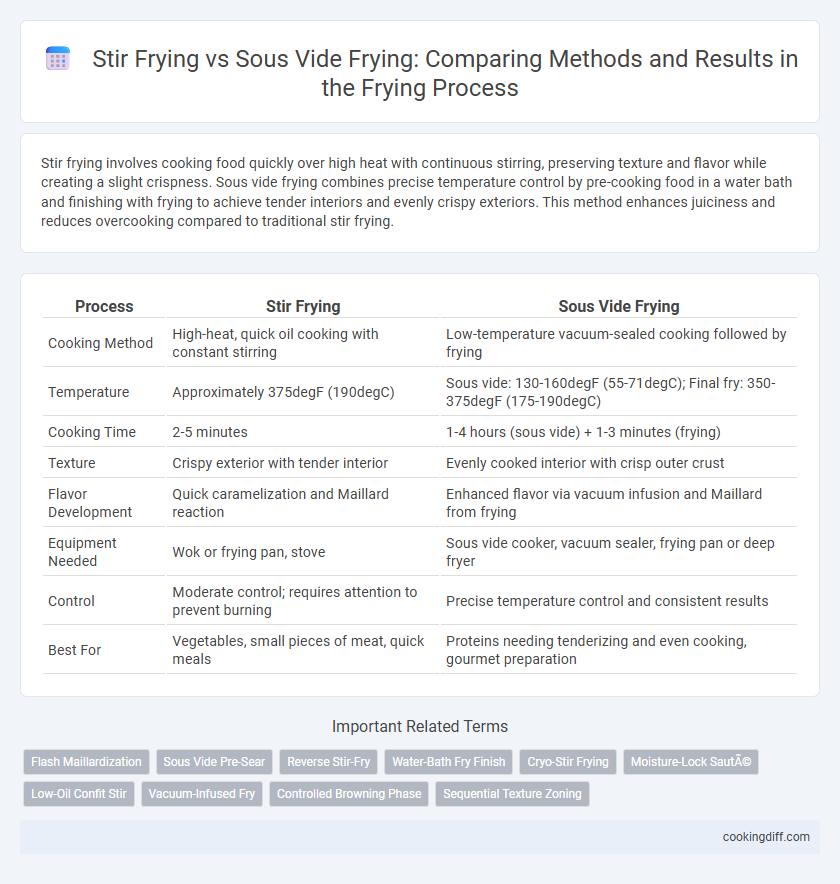
| Process | Stir Frying | Sous Vide Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | High-heat, quick oil cooking with constant stirring | Low-temperature vacuum-sealed cooking followed by frying |
| Temperature | Approximately 375degF (190degC) | Sous vide: 130-160degF (55-71degC); Final fry: 350-375degF (175-190degC) |
| Cooking Time | 2-5 minutes | 1-4 hours (sous vide) + 1-3 minutes (frying) |
| Texture | Crispy exterior with tender interior | Evenly cooked interior with crisp outer crust |
| Flavor Development | Quick caramelization and Maillard reaction | Enhanced flavor via vacuum infusion and Maillard from frying |
| Equipment Needed | Wok or frying pan, stove | Sous vide cooker, vacuum sealer, frying pan or deep fryer |
| Control | Moderate control; requires attention to prevent burning | Precise temperature control and consistent results |
| Best For | Vegetables, small pieces of meat, quick meals | Proteins needing tenderizing and even cooking, gourmet preparation |
Understanding Stir Frying: Quick Heat Technique
Stir frying is a quick heat cooking technique that uses high temperatures to rapidly cook small, evenly cut pieces of food while preserving texture and flavor. Unlike sous vide frying, which relies on precise temperature control and longer cooking times, stir frying emphasizes speed and constant stirring to ensure even cooking.
- High heat application - Stir frying uses intense heat to sear ingredients quickly, sealing in moisture and nutrients.
- Rapid cooking process - The fast pace minimizes nutrient loss and maintains crispness in vegetables.
- Continuous stirring - Constant movement prevents burning and ensures even heat distribution across food.
The Basics of Sous Vide Frying
Sous vide frying involves vacuum-sealing food and cooking it in a precisely controlled water bath before finishing with a quick fry to achieve a crispy exterior. Stir frying, by contrast, uses high heat and constant stirring to cook food rapidly, preserving texture and flavor.
- Temperature Control - Sous vide allows precise temperature regulation, preventing overcooking and ensuring even doneness.
- Texture Enhancement - The slow, controlled cooking maintains moisture and tenderness before the final frying step adds crispiness.
- Flavor Development - Sous vide intensifies natural flavors through extended cooking times, while stir frying develops flavor quickly with high heat.
Sous vide frying combines careful heat management with a finishing fry for optimal texture and taste.
Equipment Needed for Each Frying Method
Stir frying requires a wok or a large skillet along with a high-heat stove for rapid cooking and tossing of ingredients. Sous vide frying involves precise temperature-controlled immersion equipment followed by a separate frying pan or deep fryer to achieve a crispy exterior. The key difference in equipment lies in the need for temperature-controlled water baths for sous vide, which is absent in traditional stir frying setups.
Temperature Control: Stir Fry vs Sous Vide Fry
Stir frying requires high heat, typically between 375degF and 450degF, allowing quick cooking while preserving texture and flavor through constant temperature fluctuations. Sous vide frying maintains precise temperature control, usually between 130degF and 185degF, ensuring even cooking and enhanced moisture retention by cooking food in a vacuum-sealed bag before finishing with a quick sear.
The variability in stir frying can lead to inconsistent heat distribution and potential overcooking in certain areas, whereas sous vide frying's regulated temperature prevents these issues by cooking food evenly throughout. This precise temperature control in sous vide frying results in superior tenderness and flavor consistency compared to the more intense and rapid heat of stir frying.
Cooking Time Comparison: Speed vs Precision
How does cooking time compare between stir frying and sous vide frying? Stir frying offers rapid cooking, often completing in just minutes due to direct high heat contact, making it ideal for quick meals. Sous vide frying requires significantly longer cooking times as food is gently cooked in a water bath at precise temperatures before finishing with a quick sear, emphasizing precision and even doneness.
Texture and Flavor Differences
Stir frying rapidly cooks food at high temperatures, creating a crisp texture with a slightly charred flavor. Sous vide frying, on the other hand, involves cooking food slowly in a temperature-controlled water bath before finishing with a quick fry, resulting in a tender interior and evenly cooked texture.
The texture of stir-fried dishes is typically firmer and more varied due to the intense direct heat and constant movement. Sous vide frying produces a consistently tender and juicy texture because the food is cooked gently and precisely throughout. Flavor differences arise as stir frying enhances caramelization and browning, while sous vide frying preserves the pure, natural taste of ingredients before adding a subtle crispy exterior during the final fry.
Nutritional Impact of Frying Methods
Stir frying preserves more nutrients such as vitamin C and B vitamins due to the quick cooking time at high heat, preventing significant nutrient loss. This method uses less oil, reducing fat absorption and maintaining a healthier fat profile in the food.
Sous vide frying involves cooking food at controlled, lower temperatures for longer periods, which can better retain water-soluble vitamins and antioxidants. However, the subsequent frying step can cause nutrient degradation and increased oil uptake, potentially diminishing nutritional benefits.
Best Foods for Stir Frying vs Sous Vide Frying
| Cooking Method | Best Foods | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Stir Frying | Thinly sliced beef, chicken breast, shrimp, broccoli, bell peppers, snap peas, mushrooms | Quick cooking at high heat preserves nutrients and texture, ideal for vegetables and lean proteins |
| Sous Vide Frying | Steak, pork chops, thick chicken breasts, root vegetables, fish fillets | Precise temperature control ensures even cooking and tenderness before finishing with a crisp sear |
Energy Efficiency and Kitchen Setup
Stir frying uses high heat and continuous motion, allowing for quick cooking with moderate energy consumption in standard kitchen setups, making it energy efficient for small-scale operations. Sous vide frying involves precise temperature control and immersion in heated water followed by a quick sear, requiring specialized equipment and higher initial energy input but offering consistent cooking results. Kitchen setup for stir frying is simpler and more adaptable, while sous vide frying demands dedicated devices and more counter space, impacting energy use and workflow organization.
Related Important Terms
Flash Maillardization
Stir frying achieves flash Maillardization by exposing food to high heat quickly, creating a crisp, browned exterior while preserving texture and flavor. Sous vide frying, in contrast, utilizes precise temperature control to evenly cook food before a brief, high-heat sear enhances Maillard reaction without overcooking.
Sous Vide Pre-Sear
Sous vide pre-sear frying involves cooking food at precise low temperatures in a water bath before quickly searing it in a hot pan to develop flavor and texture, preserving moisture and ensuring even doneness. This method contrasts with stir frying, which uses high heat and rapid stirring to cook ingredients quickly but often results in less uniform internal cooking.
Reverse Stir-Fry
Reverse stir-fry combines the high-heat, quick-cooking advantages of traditional stir-frying with the precise temperature control of sous vide, enhancing texture and flavor by first cooking ingredients sous vide to retain moisture before rapidly stir-frying them for a crisp finish. This method optimizes Maillard browning and preserves nutrients while reducing overcooking risks commonly found in conventional frying processes.
Water-Bath Fry Finish
Stir frying involves quickly cooking food over high heat with continuous stirring, ensuring even browning and a crispy texture, while sous vide frying begins with vacuum-sealed food cooked in a precise temperature-controlled water bath, followed by a final frying step to achieve a perfectly tender interior and a crisp exterior. The water-bath fry finish in sous vide frying enhances moisture retention and flavor infusion, delivering consistent results that are difficult to replicate with traditional stir frying.
Cryo-Stir Frying
Cryo-stir frying combines rapid freezing and high-heat stir frying to preserve food texture and nutrients while enhancing flavor through precise temperature control, contrasting with sous vide frying that relies on low-temperature water immersion before searing. This method reduces cooking time and maintains cellular integrity, offering a superior alternative for achieving crispiness and freshness in stir-fried dishes.
Moisture-Lock Sauté
Stir frying rapidly cooks ingredients over high heat, preserving crisp textures while the Moisture-Lock Saute technique enhances flavor retention by sealing juices within the food. Sous vide frying involves precise temperature control to maintain optimal moisture levels but lacks the quick caramelization and textural contrast achieved through Moisture-Lock Saute in stir frying.
Low-Oil Confit Stir
Low-oil confit stir frying combines gentle, oil-minimized cooking with high-heat agitation to preserve texture and flavor while reducing fat content. In contrast, sous vide frying involves precise temperature control through water immersion before finishing with brief, high-heat frying, resulting in consistent doneness but higher oil usage compared to low-oil confit methods.
Vacuum-Infused Fry
Vacuum-infused frying combines the precision of sous vide with the high heat of stir frying, enhancing flavor infusion and texture retention by rapidly cooking food in a vacuum-sealed environment before applying intense heat. This process reduces oil absorption and preserves nutrients, making it an innovative alternative to traditional stir frying methods.
Controlled Browning Phase
Stir frying achieves a controlled browning phase through high heat and constant agitation, promoting Maillard reactions that enhance flavor and texture rapidly. In contrast, sous vide frying uses precise temperature control in an oil bath before a brief searing step, ensuring even browning without overcooking and retaining moisture.
Stir frying vs sous vide frying for process. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com