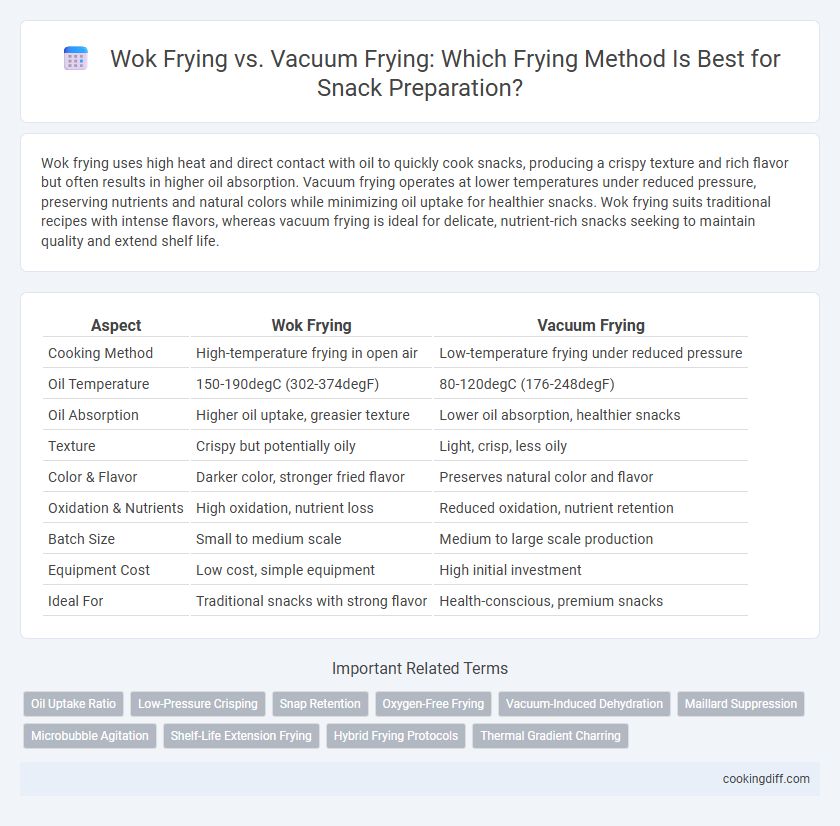
Wok frying uses high heat and direct contact with oil to quickly cook snacks, producing a crispy texture and rich flavor but often results in higher oil absorption. Vacuum frying operates at lower temperatures under reduced pressure, preserving nutrients and natural colors while minimizing oil uptake for healthier snacks. Wok frying suits traditional recipes with intense flavors, whereas vacuum frying is ideal for delicate, nutrient-rich snacks seeking to maintain quality and extend shelf life.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Wok Frying | Vacuum Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | High-temperature frying in open air | Low-temperature frying under reduced pressure |
| Oil Temperature | 150-190degC (302-374degF) | 80-120degC (176-248degF) |
| Oil Absorption | Higher oil uptake, greasier texture | Lower oil absorption, healthier snacks |
| Texture | Crispy but potentially oily | Light, crisp, less oily |
| Color & Flavor | Darker color, stronger fried flavor | Preserves natural color and flavor |
| Oxidation & Nutrients | High oxidation, nutrient loss | Reduced oxidation, nutrient retention |
| Batch Size | Small to medium scale | Medium to large scale production |
| Equipment Cost | Low cost, simple equipment | High initial investment |
| Ideal For | Traditional snacks with strong flavor | Health-conscious, premium snacks |
Introduction to Wok Frying and Vacuum Frying
Wok frying involves cooking snacks in a round-bottomed pan at high temperatures using minimal oil, preserving flavor and texture. Vacuum frying cooks snacks under reduced pressure at lower temperatures, enhancing crunchiness while reducing oil absorption.
- Wok Frying - Uses high heat and rapid oil circulation for a crispy surface and distinct taste.
- Vacuum Frying - Operates below atmospheric pressure to prevent oxidation and maintain natural colors.
- Health Benefits - Vacuum frying yields snacks with lower oil content compared to traditional wok frying methods.
How Wok Frying Works in Snack Preparation
Wok frying involves cooking snacks in a shallow, round-bottomed pan with hot oil, achieving rapid heat transfer and even cooking. The high temperature allows quick moisture evaporation, resulting in a crispy texture.
During wok frying, snacks are constantly stirred to prevent uneven cooking and ensure uniform flavor absorption. This method is ideal for small-batch snack preparation and enhances the aroma through Maillard reactions. Compared to vacuum frying, wok frying exposes snacks to atmospheric pressure, which may cause higher oil uptake and slightly reduced nutrient retention.
The Science Behind Vacuum Frying
| Vacuum frying utilizes reduced pressure to lower the boiling point of oil, resulting in frying at temperatures typically between 60-80degC compared to traditional wok frying at 160-180degC. This scientific approach minimizes oxidation and thermal degradation of snacks, preserving color, flavor, and nutritional content. The vacuum environment also reduces oil absorption, producing snacks with lower fat content and enhanced crispness. |
Oil Absorption Differences in Frying Methods
How do oil absorption levels compare between wok frying and vacuum frying for snacks? Wok frying typically results in higher oil absorption due to its high temperature and atmospheric pressure conditions, which allow oil to penetrate the snack surface more deeply. Vacuum frying reduces oil uptake by frying at lower temperatures under reduced pressure, creating a less porous texture and preserving crispness with healthier fat content.
Texture and Crunch: Wok vs Vacuum Frying
Wok frying imparts a traditional crispy texture and a satisfying crunch due to the high heat and agitation during cooking, enhancing snack appeal. Vacuum frying operates at lower temperatures under reduced pressure, preserving delicate textures and producing a lighter, less greasy crunch. Snacks fried in a vacuum fryer often retain more natural color and flavor, providing a unique textural experience compared to the intense crispiness achieved through wok frying.
Nutritional Impact of Wok and Vacuum Frying
Wok frying uses high temperatures and exposes snacks to oxygen, often leading to nutrient degradation and increased oil absorption. Vacuum frying operates under low pressure and temperature, preserving vitamins and reducing harmful oxidation while producing crunchier snacks.
- Wok frying nutrient loss - High heat and oxygen exposure cause significant degradation of heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex.
- Vacuum frying nutrient retention - Lower frying temperatures and oxygen levels minimize nutrient loss, maintaining higher antioxidant content.
- Oil absorption differences - Snacks fried in a wok typically absorb more oil, increasing fat content compared to vacuum-fried snacks.
Vacuum frying offers a nutritional advantage by better preserving essential nutrients and reducing fat content in snack products.
Flavor Profiles Achieved by Each Frying Method
Wok frying imparts a rich, smoky flavor to snacks due to the high heat and quick cooking time, enhancing the natural taste and creating a crispy texture. Vacuum frying preserves delicate flavors and nutrients by cooking at lower temperatures in a low-oxygen environment, resulting in a lighter, less oily snack with a subtle, fresh taste. Each method offers distinct flavor profiles, with wok frying producing bold, robust flavors and vacuum frying delivering a cleaner, more natural taste.
Equipment and Setup: Wok vs Vacuum Fryer
Wok frying utilizes a traditional open-pan setup requiring manual temperature control and constant stirring, while vacuum frying operates within a sealed chamber that maintains low pressure to reduce oil absorption. The equipment for vacuum frying involves more complex machinery including vacuum pumps and temperature sensors, leading to higher initial investment and maintenance costs.
- Equipment Complexity - Wok frying uses simple pans and stoves, whereas vacuum frying requires sophisticated sealed chambers with vacuum systems.
- Temperature Control - Wok frying depends on manual monitoring, but vacuum frying employs automated temperature regulation to ensure consistent product quality.
- Setup Space - Vacuum frying demands more space and infrastructure for machinery installation compared to the compact setup needed for wok frying.
Cost and Efficiency Comparison
Wok frying offers lower initial equipment costs compared to vacuum frying, making it more accessible for small-scale snack producers. However, vacuum frying provides higher oil efficiency and reduces oil degradation, resulting in lower long-term operational expenses.
Vacuum frying consumes less energy due to lower frying temperatures and improves product yield by minimizing moisture loss, enhancing overall efficiency. Wok frying demands more frequent oil changes and energy input, increasing maintenance costs and reducing process sustainability.
Related Important Terms
Oil Uptake Ratio
Wok frying generally results in a higher oil uptake ratio due to direct contact with hot oil, causing snacks to absorb more fat, which can affect texture and calorie content. Vacuum frying significantly reduces oil absorption by frying under low pressure and temperature, preserving crispness while producing healthier snacks with lower fat content.
Low-Pressure Crisping
Wok frying uses high heat and rapid stirring to produce crispy snacks with a traditional texture, while vacuum frying operates at low pressure and lower temperatures, preserving color and nutrients while delivering low-pressure crisping that enhances snack crunchiness without oxidation. Vacuum frying's controlled environment reduces oil absorption and thermal degradation, making it ideal for healthier, high-quality snack production compared to conventional wok frying.
Snap Retention
Wok frying preserves the crisp texture of snacks by quickly sealing moisture, enhancing snap retention through high heat and rapid cooking times. Vacuum frying reduces oil absorption and oxidation by frying at lower temperatures, which helps maintain a delicate crunch and longer-lasting snap in snacks.
Oxygen-Free Frying
Wok frying exposes snacks to oxygen at high temperatures, which can lead to oxidation, flavor degradation, and nutrient loss, whereas vacuum frying removes oxygen from the frying environment, significantly reducing oxidation and preserving the snacks' natural color, flavor, and nutritional value. Oxygen-free frying conditions in vacuum frying also result in lower oil absorption and healthier, crispier snacks compared to traditional wok frying methods.
Vacuum-Induced Dehydration
Vacuum frying utilizes low pressure to lower the boiling point of water, resulting in vacuum-induced dehydration that preserves snack texture, flavor, and nutrients better than conventional wok frying. This method reduces oil absorption and oxidation, producing healthier and crispier snacks with extended shelf life.
Maillard Suppression
Wok frying, with its high open-air temperatures, accelerates the Maillard reaction, resulting in stronger browning and flavor development in snacks, whereas vacuum frying operates under reduced pressure and lower temperatures, effectively suppressing Maillard browning to preserve natural colors and minimize acrylamide formation. This Maillard suppression in vacuum frying enhances the nutritional quality and extends shelf life by reducing the formation of potentially harmful compounds typically generated during traditional high-temperature frying methods.
Microbubble Agitation
Microbubble agitation in vacuum frying enhances heat transfer and moisture removal, preserving the texture and nutrients of snacks more effectively than wok frying. Wok frying relies on direct oil contact and high temperatures, often resulting in uneven cooking and higher oil absorption compared to the controlled microbubble-induced agitation in vacuum frying.
Shelf-Life Extension Frying
Wok frying preserves the traditional texture and flavor of snacks but typically results in a shorter shelf-life due to higher oil absorption and moisture retention. Vacuum frying extends shelf-life significantly by reducing oil uptake and oxidation through low-temperature frying in a low-oxygen environment, maintaining crispness and nutritional quality for longer storage.
Hybrid Frying Protocols
Hybrid frying protocols combine wok frying and vacuum frying techniques to enhance snack quality by balancing high heat exposure with reduced oxygen levels, resulting in crispy textures and lower oil uptake. This method optimizes flavor retention and nutrient preservation, making it a preferred approach for producing healthier, tastier snacks with extended shelf life.
Wok Frying vs Vacuum Frying for snacks. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com