Charcoal grilling offers a smoky flavor and high heat perfect for searing, while infrared grilling provides precise temperature control and faster cooking times. Infrared grills distribute heat evenly, reducing flare-ups and ensuring consistent results. Choosing between the two depends on whether flavor depth or cooking efficiency is the priority for outdoor cooking.
Table of Comparison
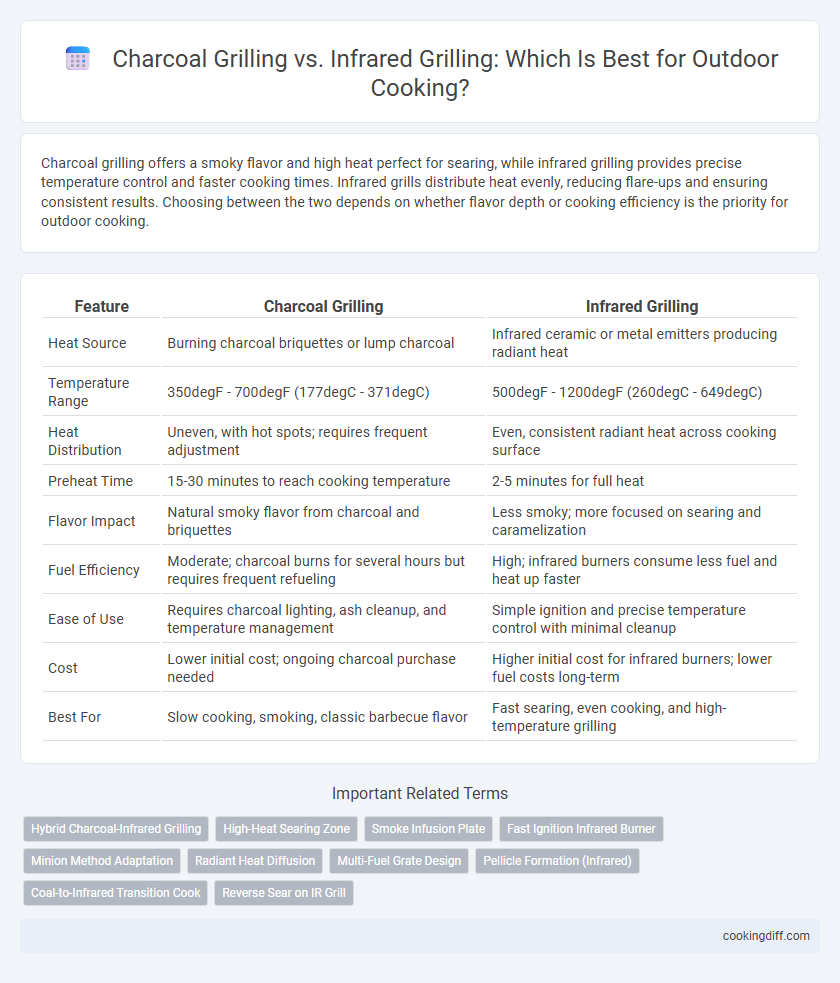
| Feature | Charcoal Grilling | Infrared Grilling |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Burning charcoal briquettes or lump charcoal | Infrared ceramic or metal emitters producing radiant heat |
| Temperature Range | 350degF - 700degF (177degC - 371degC) | 500degF - 1200degF (260degC - 649degC) |
| Heat Distribution | Uneven, with hot spots; requires frequent adjustment | Even, consistent radiant heat across cooking surface |
| Preheat Time | 15-30 minutes to reach cooking temperature | 2-5 minutes for full heat |
| Flavor Impact | Natural smoky flavor from charcoal and briquettes | Less smoky; more focused on searing and caramelization |
| Fuel Efficiency | Moderate; charcoal burns for several hours but requires frequent refueling | High; infrared burners consume less fuel and heat up faster |
| Ease of Use | Requires charcoal lighting, ash cleanup, and temperature management | Simple ignition and precise temperature control with minimal cleanup |
| Cost | Lower initial cost; ongoing charcoal purchase needed | Higher initial cost for infrared burners; lower fuel costs long-term |
| Best For | Slow cooking, smoking, classic barbecue flavor | Fast searing, even cooking, and high-temperature grilling |
Introduction to Charcoal and Infrared Grilling
Charcoal grilling uses burning charcoal briquettes or lump charcoal to generate intense heat and impart a distinctive smoky flavor to food. It requires a longer preheating time but offers superior heat control and a traditional outdoor cooking experience.
Infrared grilling employs infrared technology to produce high and consistent heat by radiating energy directly to the food surface. This method allows for rapid cooking with less flare-up and often results in juicier meats due to even heat distribution.
How Charcoal Grilling Works
Charcoal grilling uses lump charcoal or briquettes heated until they form glowing embers, providing direct heat for cooking. The combustion process releases smoke that imparts a distinctive smoky flavor to the food, enhancing outdoor grilling experiences.
Heat is regulated by adjusting air vents on the grill, controlling oxygen flow to maintain desired cooking temperatures. This traditional method creates a high heat environment ideal for searing meats and achieving a crispy exterior.
How Infrared Grilling Works
Infrared grilling utilizes electromagnetic radiation to directly heat food, producing intense and even heat. This process minimizes flare-ups and retains moisture, resulting in juicier and faster-cooked meals compared to traditional charcoal grilling.
- Direct heat transfer - Infrared grills use ceramic or metal emitters that radiate heat directly onto the food surface.
- Temperature control - Infrared grills can reach higher temperatures rapidly, allowing precise heat management for searing and cooking.
- Reduced flare-ups - The radiant heat method eliminates the need for open flames, reducing grease flare-ups during grilling.
Heat Distribution: Charcoal vs Infrared Grills
How does heat distribution compare between charcoal and infrared grills? Charcoal grills provide a more uneven yet smoky heat distribution, ideal for slow-cooking and imparting traditional barbecue flavors. Infrared grills deliver consistent, high-intensity heat with precise temperature control, ensuring faster cooking and reduced flare-ups.
Flavor Differences: Smoky vs Clean Taste
Charcoal grilling imparts a rich, smoky flavor to food due to the combustion of natural wood and charcoal briquettes, enhancing the taste of meats and vegetables with a distinct aroma. Infrared grilling uses radiant heat to cook food quickly and evenly, preserving the natural flavors without adding any smoky notes.
The choice between charcoal and infrared grilling significantly affects the flavor profile of outdoor-cooked meals. Charcoal grills produce a complex, smoky taste that many barbecue enthusiasts prefer, thanks to the slow burning of coals and smoke infusion. Infrared grills offer a cleaner, purer taste by reducing flare-ups and minimizing smoke, making them ideal for those seeking a more straightforward, natural flavor in their grilled dishes.
Temperature Control and Cooking Precision
Charcoal grilling offers variable temperature control through adjusting air vents, enabling authentic smoky flavor but requiring skill to maintain steady heat. Infrared grilling provides precise and consistent temperature control via radiant heat elements, allowing for faster cooking and even heat distribution. For outdoor cooking enthusiasts prioritizing exact temperature management and precision, infrared grilling often delivers superior performance compared to traditional charcoal methods.
Fuel Efficiency and Operational Costs
Charcoal grilling typically consumes more fuel due to longer heat-up times and less efficient heat retention compared to infrared grilling. Infrared grills convert nearly 90% of energy into cooking heat, significantly reducing fuel usage and operational costs over time. Users of infrared grills benefit from faster cooking times and lower charcoal or propane consumption, making them more economical for frequent outdoor cooking.
Setup, Maintenance, and Cleaning
Charcoal grilling requires more time for setup and cleanup due to handling and disposing of ashes, while infrared grilling offers quicker ignition and minimal residue. Maintenance of infrared grills is generally less frequent because of their sealed burners and simpler design.
- Charcoal Setup - Involves arranging charcoal briquettes and lighting them, which can take up to 20 minutes.
- Infrared Maintenance - Requires occasional burner checks and cleaning to maintain optimal heat distribution.
- Cleaning Process - Charcoal grills need ash removal after each use, whereas infrared grills primarily require wiping down surfaces.
Infrared grilling provides a convenient, low-maintenance alternative ideal for quick outdoor cooking sessions.
Safety Considerations for Outdoor Grilling
| Charcoal Grilling Safety | Charcoal grills emit open flames and hot embers, increasing the risk of flare-ups and burns; proper ventilation and fire extinguisher accessibility are essential to prevent accidents. |
| Infrared Grilling Safety | Infrared grills use radiant heat, reducing flare-ups and ensuring more stable temperature control, which minimizes fire hazards but requires attention to hot surfaces to avoid burns. |
| General Safety Tips | Maintain a safe distance from structures, never leave grills unattended, keep children and pets away, and always clean grease buildup to prevent grease fires during outdoor cooking. |
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Charcoal-Infrared Grilling
Hybrid charcoal-infrared grilling combines the authentic smoky flavor of traditional charcoal with the consistent, high-heat cooking performance of infrared technology, ensuring evenly cooked meats and enhanced caramelization. This fusion allows outdoor cooks to harness the deep, rich taste of charcoal while benefiting from the precise temperature control and rapid heat-up times characteristic of infrared grills.
High-Heat Searing Zone
Charcoal grilling provides an intense high-heat searing zone ideal for creating a rich, smoky crust on meats through direct radiant heat and glowing embers. Infrared grilling offers rapid, even heat distribution with temperatures often exceeding 800degF, producing a consistent sear while minimizing flare-ups and preserving juiciness.
Smoke Infusion Plate
Charcoal grilling delivers rich, smoky flavors by burning natural charcoal that produces smoke infused directly into the food, while infrared grilling uses a Smoke Infusion Plate to evenly distribute intense heat and enhance flavor without excessive smoke. The Smoke Infusion Plate in infrared grills allows for precise temperature control and consistent cooking, making it an efficient option for outdoor chefs seeking both heat retention and subtle smoky notes.
Fast Ignition Infrared Burner
Fast Ignition Infrared Burners provide superior heat efficiency and rapid temperature achievement, grilling food evenly with less flare-up compared to traditional charcoal grills. Charcoal grilling offers smoky flavor and authentic outdoor experience but requires longer preheating and temperature control challenges.
Minion Method Adaptation
Charcoal grilling using the Minion Method allows for slow, consistent heat by arranging unlit charcoal around a small lit core, optimizing temperature control for extended cooking times, while infrared grilling delivers efficient, high-intensity heat with minimal smoke but requires different adaptations for indirect cooking. Adapting the Minion Method to infrared grills involves managing heat zones by combining low infrared elements with controlled airflow, ensuring even cooking and smoky flavors without the traditional charcoal combustion.
Radiant Heat Diffusion
Charcoal grilling produces radiant heat by combusting carbon, creating uneven heat zones with distinct hot spots essential for searing and smoky flavors. Infrared grilling utilizes electromagnetic radiation to evenly diffuse intense heat directly to food, resulting in faster cooking times and consistent temperature control.
Multi-Fuel Grate Design
Multi-fuel grate designs enhance outdoor cooking versatility by accommodating both charcoal and infrared heat sources, optimizing temperature control and flavor infusion. This innovation allows grillers to switch between traditional smoky charcoals and efficient infrared burners, delivering precise cooking performance and improved fuel efficiency.
Pellicle Formation (Infrared)
Infrared grilling accelerates pellicle formation by rapidly searing the meat's surface, creating a tacky layer essential for smoke adhesion and enhanced flavor development. This contrasts with charcoal grilling, where slower heat distribution results in less pronounced pellicle formation, affecting smoke penetration and overall taste complexity.
Coal-to-Infrared Transition Cook
Charcoal grilling offers traditional smoky flavors and high heat ideal for searing, while infrared grilling provides precise temperature control and faster cooking times through radiant heat technology. Transitioning from coal to infrared enhances efficiency and consistency in outdoor cooking, catering to modern culinary preferences without sacrificing authentic taste.
Charcoal grilling vs Infrared grilling for outdoor cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com