Electric grills offer precise temperature control and even heat distribution, making them ideal for consistent grilling indoors or on balconies. Infrared grills use radiant heat to sear food quickly, locking in juices and enhancing flavor with high-temperature cooking. Both options provide efficient grilling, but your choice depends on preferences for speed, flavor intensity, and cooking environment.
Table of Comparison
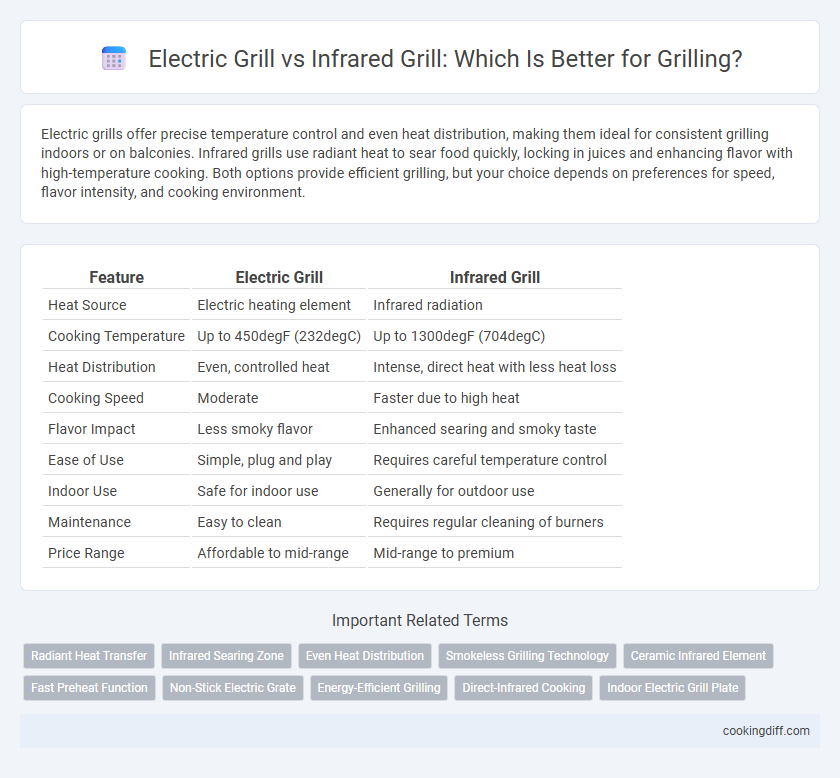
| Feature | Electric Grill | Infrared Grill |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Electric heating element | Infrared radiation |
| Cooking Temperature | Up to 450degF (232degC) | Up to 1300degF (704degC) |
| Heat Distribution | Even, controlled heat | Intense, direct heat with less heat loss |
| Cooking Speed | Moderate | Faster due to high heat |
| Flavor Impact | Less smoky flavor | Enhanced searing and smoky taste |
| Ease of Use | Simple, plug and play | Requires careful temperature control |
| Indoor Use | Safe for indoor use | Generally for outdoor use |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean | Requires regular cleaning of burners |
| Price Range | Affordable to mid-range | Mid-range to premium |
Introduction to Electric and Infrared Grills
Electric grills use heating elements to provide consistent and controllable heat, making them ideal for indoor grilling with minimal smoke. Infrared grills utilize infrared technology to generate intense, even heat that sears food quickly, preserving moisture and enhancing flavor. Both options offer distinct advantages depending on grilling preferences, space availability, and desired cooking results.
How Electric Grills Work
Electric grills use an electric heating element to generate consistent heat for cooking, making them ideal for indoor grilling and controlled temperature settings. They operate by passing an electric current through a resistive element, which heats up and transfers heat directly to the grilling surface.
Infrared grills, in contrast, use an infrared element to produce radiant heat, allowing for faster cooking and higher temperatures that sear food more efficiently. Electric grills provide uniform heat distribution but may lack the intense searing capability of infrared grills. Choosing between the two depends on cooking style preferences, heat control needs, and indoor or outdoor use suitability.
Understanding Infrared Grill Technology
Infrared grills use radiant heat generated by ceramic or metal plates that absorb and emit infrared energy directly to the food, leading to faster cooking times and more efficient heat retention. This technology differs from traditional electric grills, which transfer heat through exposed heating elements and rely on convection airflow.
- Direct Infrared Radiation - Infrared grills emit radiation that heats food without heating the surrounding air, resulting in more consistent and intense cooking temperatures.
- Rapid Heat Response - Infrared burners reach cooking temperature within minutes, improving energy efficiency and reducing wait times compared to conventional electric grills.
- Enhanced Searing Capability - The concentrated heat from infrared technology creates superior sear marks and caramelization on meats, enhancing flavor and texture.
Heat Distribution: Electric vs Infrared Grills
How does heat distribution compare between electric and infrared grills? Electric grills provide consistent heat through embedded heating elements, offering even cooking across the surface. Infrared grills use radiant heat to deliver intense, focused heat, creating faster searing but potential hot spots in some areas.
Cooking Performance and Flavor Comparison
Electric grills offer consistent temperature control, making them ideal for precise cooking of delicate items, while infrared grills deliver intense, direct heat that sears meat quickly and locks in juices. Infrared technology reaches higher temperatures faster, enhancing the Maillard reaction for richer, smoky flavors compared to the milder taste from electric grills. For grilling enthusiasts seeking robust flavor and char marks, infrared grills provide superior cooking performance, whereas electric grills excel in convenience and ease of use.
Preheating and Temperature Control
Electric grills typically require a longer preheating time and offer moderate temperature control, ideal for slow cooking. Infrared grills heat up swiftly and provide precise temperature adjustments, making them suitable for searing and high-heat grilling.
- Electric Grill Preheating - Often takes 10-15 minutes to reach optimal cooking temperature.
- Infrared Grill Preheating - Usually heats up in 5 minutes due to direct radiant heat technology.
- Temperature Control Precision - Infrared grills allow fine-tuned heat adjustments, improving cooking consistency compared to electric grills.
Choosing between the two depends on your cooking style and need for speed and temperature accuracy.
Energy Efficiency and Operating Costs
Electric grills generally consume more electricity and have higher operating costs compared to infrared grills, which use radiant heat for more efficient cooking. Infrared grills heat food faster, reducing energy consumption and lowering overall grilling expenses.
- Electric grills require continuous power - They rely on heating elements that consume electricity throughout the cooking process, increasing energy usage.
- Infrared grills use radiant heat - This method heats food directly and evenly, minimizing heat loss and saving energy.
- Operating costs favor infrared grills - Faster cooking times and greater energy efficiency reduce electricity bills over time.
Cleaning and Maintenance Differences
Electric grills typically have removable drip trays and non-stick plates, making cleaning straightforward and less time-consuming. Infrared grills, however, use intense heat that can burn off food residues, reducing the frequency of deep cleaning required.
Maintenance for electric grills often involves careful handling of electrical components to prevent damage. Infrared grills demand occasional cleaning of ceramic or quartz infrared burners to maintain optimal heat distribution and performance.
Safety Features and Considerations
Electric grills feature built-in thermostats and automatic shut-off mechanisms that reduce the risk of overheating and fire hazards, making them a safer choice for indoor use. Their enclosed heating elements minimize the exposure to open flames, lowering the chance of accidental burns or flare-ups.
Infrared grills utilize high-intensity radiant heat, which cooks food faster but requires caution due to the extreme surface temperatures that can cause burns if touched. Proper ventilation and heat-resistant gloves are essential safety considerations when operating infrared grills to prevent accidents and ensure safe grilling.
Related Important Terms
Radiant Heat Transfer
Electric grills rely on resistive heating elements to generate radiant heat that evenly cooks food at moderate temperatures, making them ideal for controlled and consistent grilling. Infrared grills use high-intensity infrared radiation from ceramic or metal emitters to deliver rapid, intense heat that sears food quickly while retaining moisture.
Infrared Searing Zone
Infrared grills utilize a radiant heat technology that creates a dedicated searing zone capable of reaching temperatures above 1,000degF, resulting in rapid caramelization and enhanced Maillard reaction for superior crust formation. This high-intensity searing zone outperforms traditional electric grills by delivering more precise temperature control and evenly distributed heat, reducing cooking time while preserving juiciness and flavor.
Even Heat Distribution
Electric grills provide consistent and evenly distributed heat through built-in heating elements, ensuring uniform cooking surfaces ideal for delicate foods. Infrared grills utilize radiant heat from gas-powered burners, generating rapid and intense heat but may cause hotspots, requiring careful temperature management for even cooking.
Smokeless Grilling Technology
Electric grills use electric heating elements to provide consistent, controlled heat while minimizing smoke through indirect cooking, ideal for indoor smokeless grilling. Infrared grills employ ceramic or metal infrared burners that generate intense, focused heat, reducing flare-ups and smoke production, which enhances flavor without excess smoke.
Ceramic Infrared Element
Ceramic infrared elements in infrared grills provide precise, even heat distribution that sears food quickly while retaining moisture, outperforming many electric grills that rely on conventional heating elements with slower heat response. The superior thermal efficiency and radiant heat of ceramic infrared technology enhance flavor and reduce cooking time compared to standard electric grills.
Fast Preheat Function
Electric grills offer a fast preheat function that typically reaches cooking temperatures within 5 to 10 minutes, making them convenient for quick meal preparation. Infrared grills surpass this speed by using radiant heat to preheat in as little as 3 to 5 minutes, providing more efficient and consistent cooking performance.
Non-Stick Electric Grate
Electric grills with a non-stick electric grate offer easy cleanup and even heat distribution, preventing food from sticking and ensuring consistent grilling results. Infrared grills, while providing intense and rapid heat, often lack the non-stick surface benefits that facilitate effortless cooking and maintenance.
Energy-Efficient Grilling
Electric grills use consistent electric heating elements that convert energy efficiently into direct heat, minimizing energy loss and enabling precise temperature control. Infrared grills generate intense radiant heat through electric or gas-powered infrared burners, offering faster preheating and higher heat output, which can reduce overall cooking time and energy consumption.
Direct-Infrared Cooking
Electric grills utilize resistive heating elements to provide consistent heat ideal for indoor use, while infrared grills employ radiant heat to achieve higher temperatures and faster searing through direct-infrared cooking technology. Direct-infrared cooking on infrared grills enhances flavor retention and creates perfect grill marks by delivering concentrated heat directly to the food surface.
Electric Grill vs Infrared Grill for grilling. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com