Gas grills offer precise temperature control and faster ignition, making them ideal for quick and consistent cooking sessions. In contrast, the Asado Cross excels in slow, even heat distribution over charcoal or wood, infusing meat with rich smoky flavors perfect for traditional, rustic barbecues. Choosing between these depends on whether you prioritize convenience and speed or authentic smoky taste and outdoor cooking experience.
Table of Comparison
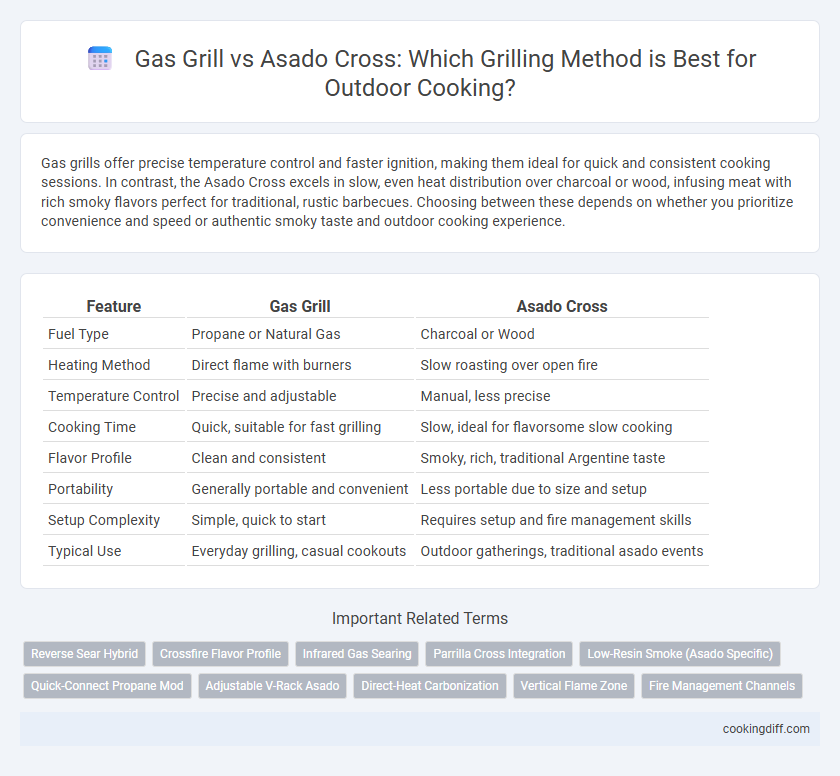
| Feature | Gas Grill | Asado Cross |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Type | Propane or Natural Gas | Charcoal or Wood |
| Heating Method | Direct flame with burners | Slow roasting over open fire |
| Temperature Control | Precise and adjustable | Manual, less precise |
| Cooking Time | Quick, suitable for fast grilling | Slow, ideal for flavorsome slow cooking |
| Flavor Profile | Clean and consistent | Smoky, rich, traditional Argentine taste |
| Portability | Generally portable and convenient | Less portable due to size and setup |
| Setup Complexity | Simple, quick to start | Requires setup and fire management skills |
| Typical Use | Everyday grilling, casual cookouts | Outdoor gatherings, traditional asado events |
Introduction: Gas Grill vs Asado Cross
Gas grills offer precise temperature control and quick ignition, making them ideal for fast and convenient grilling. The Asado Cross technique emphasizes slow cooking over open flames, imparting rich smoky flavors unique to traditional South American barbecue.
- Gas Grill Efficiency - Provides consistent heat distribution with adjustable burners for versatile cooking options.
- Asado Cross Flavor - Enhances meat taste through slow roasting using controlled wood or charcoal embers.
- Cultural Significance - The Asado Cross reflects Argentine grilling heritage, while gas grills prioritize modern convenience.
Core Differences in Grilling Techniques
Gas grills use controlled burners to provide consistent heat, allowing for precise temperature regulation and faster cooking times. In contrast, the Asado Cross method relies on slow-cooking meat over an open fire, using indirect heat and smoke for enhanced flavor development.
The grilling technique on a gas grill emphasizes convenience and speed, suitable for searing and quick meals. The Asado Cross technique requires patience and skill in managing wood or charcoal embers, producing tender, smoky meat with a distinct aroma unique to traditional Argentine barbecue.
Fuel Types: Gas vs Wood and Charcoal
Gas grills use propane or natural gas, offering precise temperature control and quick ignition, making them convenient for everyday grilling. In contrast, Asado Cross grills utilize wood or charcoal, imparting a smoky flavor and authentic aroma unique to traditional open-fire cooking. Wood and charcoal fuels provide high heat and a natural smoky essence, essential for achieving classic Asado flavor profiles.
Flavor Profiles: Smoke, Aroma, and Taste
Gas grills provide consistent heat and a clean cooking environment, enhancing natural meat flavors with minimal smoke. In contrast, Asado Cross grills infuse food with robust smoky aromas and rich, complex tastes from direct contact with wood or charcoal embers.
- Gas grill flavor profile - Emphasizes pure, controlled heat that preserves the original taste of ingredients without overpowering smokiness.
- Asado Cross smoky aroma - Delivers deep, authentic wood-smoke characteristics essential to traditional Argentine grilling.
- Flavor intensity difference - Asado Cross offers a stronger, earthier flavor compared to the lighter, cleaner taste from a gas grill.
Temperature Control and Heat Distribution
Gas grills offer precise temperature control through adjustable burners, allowing for consistent heat levels crucial for even cooking. This precise control helps maintain optimal grilling conditions, especially for delicate foods that require steady temperatures.
Asado Cross grilling relies on radiant heat from charcoal or wood, providing uneven but intense heat distribution ideal for slow cooking and imparting smoky flavors. The open design promotes air circulation, affecting temperature variability and creating a unique, traditional grilling experience.
Cooking Capacity and Versatility
Which offers greater cooking capacity and versatility, a gas grill or an asado cross? Gas grills typically provide adjustable heat zones and larger cooking surfaces, allowing for multiple types of food to be grilled simultaneously. Asado crosses excel in slow-cooking whole animals or large cuts over open flames, offering unique flavor profiles but less surface area for varied cooking.
Preparation, Setup, and Cooking Time
Gas grills offer quick setup and precise temperature control, making them ideal for fast, convenient grilling sessions. In contrast, the Asado Cross requires more preparation time due to the need to arrange wood or charcoal and secure the meat on the cross structure for slow, even cooking.
The gas grill heats up within minutes, allowing direct and consistent cooking, which reduces overall grilling time. The Asado Cross method involves longer cooking times, often several hours, as meat is cooked slowly over indirect heat to achieve tender, smoky flavors. Preparation for the Asado Cross also includes marinating and securing large cuts of meat, making it less suited for quick meals but perfect for traditional, flavorful barbecues.
Maintenance, Cleaning, and Durability
| Aspect | Gas Grill | Asado Cross |
|---|---|---|
| Maintenance | Requires regular checking of gas lines and burners to ensure safe operation and prevent leaks. | Minimal mechanical parts reduce maintenance; occasional inspection for rust on steel components is recommended. |
| Cleaning | Grates need frequent scrubbing to remove grease buildup; drip trays must be emptied and cleaned to avoid flare-ups. | Cleaning involves removing ash and soot after use; simple rinsing and drying of the metal surfaces suffice. |
| Durability | Typically made from stainless steel and cast iron, offering long-term resistance to weather but may corrode if not protected. | Constructed from heavy-duty steel, the Asado cross withstands high heat and outdoor conditions, often lasting decades. |
Safety Features and Considerations
Gas grills typically offer advanced safety features like automatic shut-off valves and ignition protection, reducing fire hazards during grilling. Asado Cross grills, while traditional, require careful handling of open flames and hot coals to avoid burns and accidents.
- Automatic Shut-off Valve - Gas grills include valves that cut fuel supply to prevent gas leaks and potential explosions.
- Open Flame Exposure - Asado Cross grills expose the user directly to flames, increasing the need for protective gear and caution.
- Stable Construction - Gas grills generally feature stable designs with heat shields, lowering the risk of tipping or flare-ups.
Choosing between a gas grill and an Asado Cross involves balancing modern safety technology against traditional grilling methods.
Related Important Terms
Reverse Sear Hybrid
The Reverse Sear Hybrid technique combines the precise temperature control of a gas grill with the intense, smoky flavor development of an Asado Cross, delivering perfectly seared meats with deep, charred crusts. Utilizing the gas grill's consistent heat for initial cooking and finishing on the Asado Cross maximizes flavor complexity and juiciness for superior grilling results.
Crossfire Flavor Profile
A Gas Grill offers convenience and consistent heat, ideal for quick cooking with subtle smoky notes, whereas the Asado Cross intensifies the Crossfire flavor profile by infusing meats with rich, smoky aromas and deep char marks from open flame contact. The Asado Cross method enhances the complexity of grilled foods, delivering authentic Argentinean flavors through prolonged exposure to wood embers and direct heat.
Infrared Gas Searing
Infrared gas searing on a gas grill provides rapid, intense heat that locks in juices and creates a perfect crust, making it ideal for quick, high-temperature cooking. In contrast, the Asado Cross method offers slow, indirect grilling over charcoal or wood, infusing meat with smoky flavors and tenderness but lacking the precise, high-heat searing capability of infrared gas grills.
Parrilla Cross Integration
The Asado Cross integrates seamlessly with a gas grill, combining the precise temperature control of gas grilling with the traditional, vertical roasting method of the Parrilla Cross for enhanced flavor and even heat distribution. This hybrid setup allows for versatile cooking styles, making it ideal for grilling meats slowly and achieving authentic smoky aromas while maintaining convenience.
Low-Resin Smoke (Asado Specific)
Gas grills offer precise temperature control and convenience but often lack the ability to produce the rich, low-resin smoke characteristic of traditional Asado grilling, which uses hardwood coals to infuse meat with distinct smoky flavors. The Asado Cross technique excels in generating low-resin smoke through slow, indirect grilling over native hardwoods, enhancing the meat's taste with natural aromatic compounds absent in gas grilling methods.
Quick-Connect Propane Mod
The Quick-Connect Propane Mod significantly enhances convenience and safety for both Gas Grill and Asado Cross setups by allowing fast, secure attachment of propane tanks without tools. While gas grills offer consistent heat control and ease of use, the Asado Cross paired with a Quick-Connect Propane Mod delivers authentic open-flame flavor with the flexibility to adjust height and temperature.
Adjustable V-Rack Asado
The Adjustable V-Rack Asado offers superior versatility and heat control compared to traditional gas grills, enabling precise positioning of meats for optimal smoke absorption and even cooking. Its durable, rust-resistant steel construction enhances durability and flavor development, making it an essential tool for authentic Argentine-style grilling.
Direct-Heat Carbonization
Gas grills provide consistent direct heat ideal for rapid carbonization and precise temperature control, enhancing flavor development through Maillard reactions. The Asado Cross method exposes meat to radiant heat over charcoal, delivering intense direct heat that creates a unique smoky crust and rich caramelization distinct from gas-grilled results.
Vertical Flame Zone
Gas grills offer precise temperature control and consistent heat distribution, ideal for quick searing in the vertical flame zone; in contrast, the Asado Cross utilizes an open flame method that imparts rich smoky flavors and allows for slow, even cooking through radiant heat exposure. The vertical flame zone in gas grills enables direct flame contact with minimal flare-ups, while the Asado Cross's design enhances drip fat caramelization and smoke infusion, creating distinct grilling experiences.
Gas Grill vs Asado Cross for grilling. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com