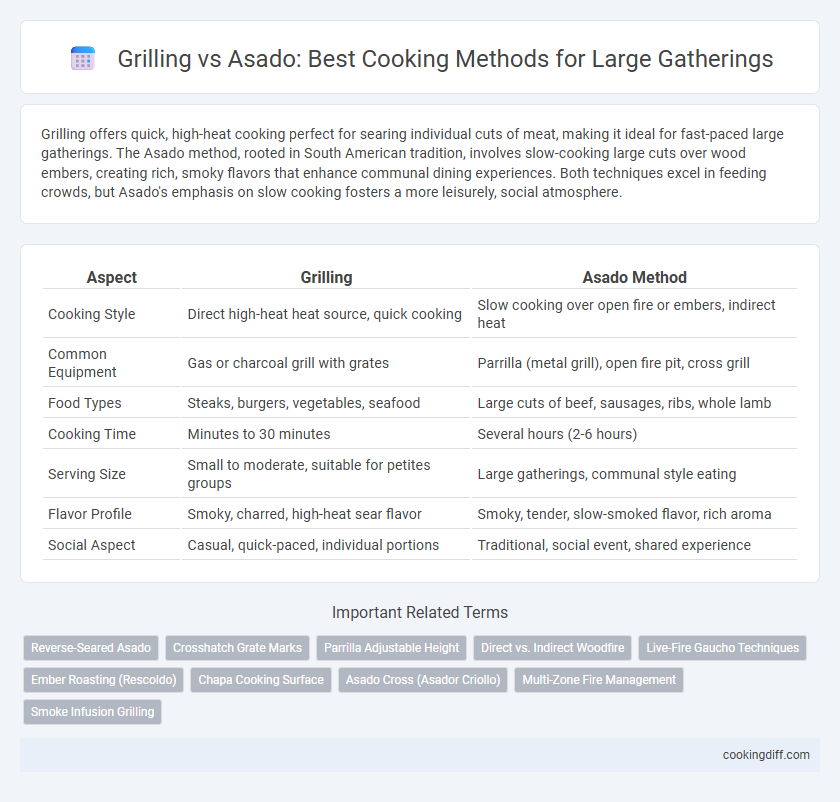
Grilling offers quick, high-heat cooking perfect for searing individual cuts of meat, making it ideal for fast-paced large gatherings. The Asado method, rooted in South American tradition, involves slow-cooking large cuts over wood embers, creating rich, smoky flavors that enhance communal dining experiences. Both techniques excel in feeding crowds, but Asado's emphasis on slow cooking fosters a more leisurely, social atmosphere.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Grilling | Asado Method |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Style | Direct high-heat heat source, quick cooking | Slow cooking over open fire or embers, indirect heat |
| Common Equipment | Gas or charcoal grill with grates | Parrilla (metal grill), open fire pit, cross grill |
| Food Types | Steaks, burgers, vegetables, seafood | Large cuts of beef, sausages, ribs, whole lamb |
| Cooking Time | Minutes to 30 minutes | Several hours (2-6 hours) |
| Serving Size | Small to moderate, suitable for petites groups | Large gatherings, communal style eating |
| Flavor Profile | Smoky, charred, high-heat sear flavor | Smoky, tender, slow-smoked flavor, rich aroma |
| Social Aspect | Casual, quick-paced, individual portions | Traditional, social event, shared experience |
Introduction to Grilling and Asado for Large Gatherings
Grilling involves cooking food quickly over direct heat, making it ideal for large gatherings where speed and efficiency are essential. Popular for its ability to sear meats and lock in flavors, grilling is widely used in outdoor events and barbecues.
Asado, a traditional South American method, emphasizes slow-cooking large cuts of meat over an open flame or embers, creating rich, smoky flavors perfect for communal meals. It fosters a social atmosphere where guests gather around the fire, making it both a cooking technique and cultural experience. Both grilling and asado require specific equipment and preparation to accommodate large groups effectively.
Key Differences Between Grilling and Asado Methods
Grilling and Asado methods offer distinct approaches to cooking meat for large gatherings, with variations in technique and flavor development. Grilling typically uses direct high heat over charcoal or gas, while Asado relies on slow, indirect cooking over wood embers.
- Heat Source - Grilling employs direct heat from charcoal or gas flames, whereas Asado uses embers from hardwood for a smoky influence.
- Cooking Time - Grilling cooks meat quickly at high temperatures, but Asado involves slow roasting over several hours.
- Flavor Profile - Grilling emphasizes seared, caramelized crusts, while Asado infuses deep smoky aromas and tender textures.
Choosing between grilling and Asado depends on the desired taste, time availability, and cultural tradition for the event.
Equipment Needed for Grilling vs Asado
Grilling for large gatherings typically requires a versatile gas or charcoal grill equipped with multiple burners and a spacious cooking surface to handle various foods simultaneously. Essential accessories include grill grates, tongs, and a thermometer to ensure precise temperature control and even cooking.
In contrast, the Asado method demands a traditional parrilla or open fire pit, complemented by a cross or metal grill grate suspended above hot embers. Additional equipment such as spits for whole animal roasting, heavy-duty skewers, and tools for managing live coals are crucial for maintaining authentic flavor and consistent heat distribution.
Fuel Sources: Charcoal, Wood, and Beyond
Grilling commonly uses charcoal, which provides consistent heat and a smoky flavor ideal for quick cooking, while Asado relies heavily on wood for slower, more even cooking over open flames. Both methods offer unique fuel options that influence the flavor and cooking style, making fuel choice crucial for large gatherings.
- Charcoal is favored in grilling - Charcoal briquettes burn steadily, providing reliable heat and a distinct smoky taste perfect for searing meats rapidly.
- Wood is central to Asado - Hardwood fuels in Asado impart deep, complex smoke flavors while allowing slow cooking over embers for tender results.
- Alternative fuels expand options - Gas and electric sources offer convenience and control but lack the authentic smoky profile prized in traditional grilling and Asado.
Preparing Meat: Grilling Cuts vs Asado Cuts
| Method | Preferred Cuts | Preparation Style |
|---|---|---|
| Grilling | Steaks, burgers, sausages | Individual portions, quickly cooked over direct high heat |
| Asado | Beef ribs, short ribs, flank steak | Large primal cuts slow-cooked over embers for extended time |
Cooking Techniques: Direct Heat vs Indirect Heat
Grilling uses direct heat, placing food directly over flames for fast cooking, ideal for smaller cuts like steaks or burgers. The Asado method employs indirect heat, slow-cooking large cuts of meat over embers or wood, ensuring even heat distribution and enhanced smoky flavor. For large gatherings, Asado provides tender, flavorful results by allowing extended cooking times and better control of temperature.
Flavor Profiles: Smoking, Seasoning, and Marinades
How do the flavor profiles of grilling compare to the asado method for large gatherings? Grilling relies on direct heat to create a charred, smoky flavor often enhanced by dry rubs and quick marinades that highlight the meat's natural taste. In contrast, the asado method uses slow cooking over embers with aromatic woods, producing deep smoke infusion and complex seasoning layers, making it ideal for rich, tender results.
Time Management: Cooking Speed and Serving Size
Grilling offers faster cooking speeds, making it ideal for large gatherings where quick serving is essential. Asado, with its slow-cooking process over indirect heat, allows for larger serving sizes but requires extended preparation time. Efficient time management depends on balancing grilling's rapid heat with asado's ability to feed a crowd leisurely and abundantly.
Social Experience: Atmosphere and Tradition
Grilling creates a lively social atmosphere centered around quick, direct cooking and casual interactions, making it ideal for spontaneous gatherings. The method emphasizes individual skill and fast-paced food preparation, fostering an energetic environment.
Asado is steeped in tradition, offering a slower, communal experience where guests gather around the fire to share stories and bond over the extended cooking process. This method transforms large gatherings into cultural celebrations, highlighting heritage and social connection.
Related Important Terms
Reverse-Seared Asado
Reverse-seared asado offers superior temperature control and even cooking for large gatherings, ensuring tender, juicy meat with a rich smoky flavor compared to traditional grilling methods. Its slow-cooking phase followed by a high-heat sear optimizes flavor development and texture, making it ideal for serving multiple guests with consistent quality.
Crosshatch Grate Marks
Grilling with crosshatch grate marks creates visually appealing sear lines, enhancing the presentation and flavor through intensified Maillard reaction hotspots, ideal for individual portions in large gatherings. The asado method, relying on broader, slower heat over wood embers, yields uniform smoky flavor but lacks the precise crosshatch aesthetics favored in high-volume, quick-serve events.
Parrilla Adjustable Height
The Parrilla adjustable height feature enhances temperature control during grilling and asado, allowing precise cooking over embers for large gatherings. This flexibility ensures even heat distribution and perfect doneness, accommodating various cuts of meat simultaneously.
Direct vs. Indirect Woodfire
Grilling uses direct woodfire heat that quickly sears meat for a smoky, charred flavor ideal for fast cooking in large gatherings. In contrast, the Asado method employs indirect woodfire, cooking meat slowly with ambient heat, producing tender, evenly cooked cuts perfect for communal celebrations.
Live-Fire Gaucho Techniques
Live-fire gaucho techniques emphasize slow-cooking large cuts of meat over open flames, infusing rich, smoky flavors ideal for communal gatherings. Unlike traditional grilling, asado methods use indirect heat and extended cooking times, ensuring tender, evenly cooked meat perfect for large groups.
Ember Roasting (Rescoldo)
Ember roasting (Rescoldo) in the Asado method offers consistent, slow heat ideal for large gatherings, infusing meats with rich smoky flavors and tender textures that conventional grilling often can't match. This technique uses glowing embers to cook food evenly over extended periods, ensuring flavorful results perfect for feeding numerous guests.
Chapa Cooking Surface
The chapa cooking surface in grilling offers even heat distribution and a larger flat area ideal for searing various cuts simultaneously, making it efficient for large gatherings. In contrast, the asado method relies on indirect heat and open flame, which imparts distinct smoky flavors but requires more careful heat management and longer cooking times.
Asado Cross (Asador Criollo)
The Asado Cross (Asador Criollo) method excels for large gatherings by slow-cooking meat vertically over an open flame, ensuring even heat distribution and smoky flavor infusion. Unlike traditional grilling, this technique allows for extensive control over temperature and tenderness, making it ideal for communal, extended cooking sessions.
Multi-Zone Fire Management
Multi-zone fire management in grilling allows precise temperature control by creating distinct heat zones, facilitating simultaneous cooking of diverse foods at varying heat levels. In contrast, the Asado method relies on a slower, consistent indirect heat over embers, ideal for large cuts but less flexible for multi-item cooking in large gatherings.
Grilling vs Asado Method for large gatherings. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com