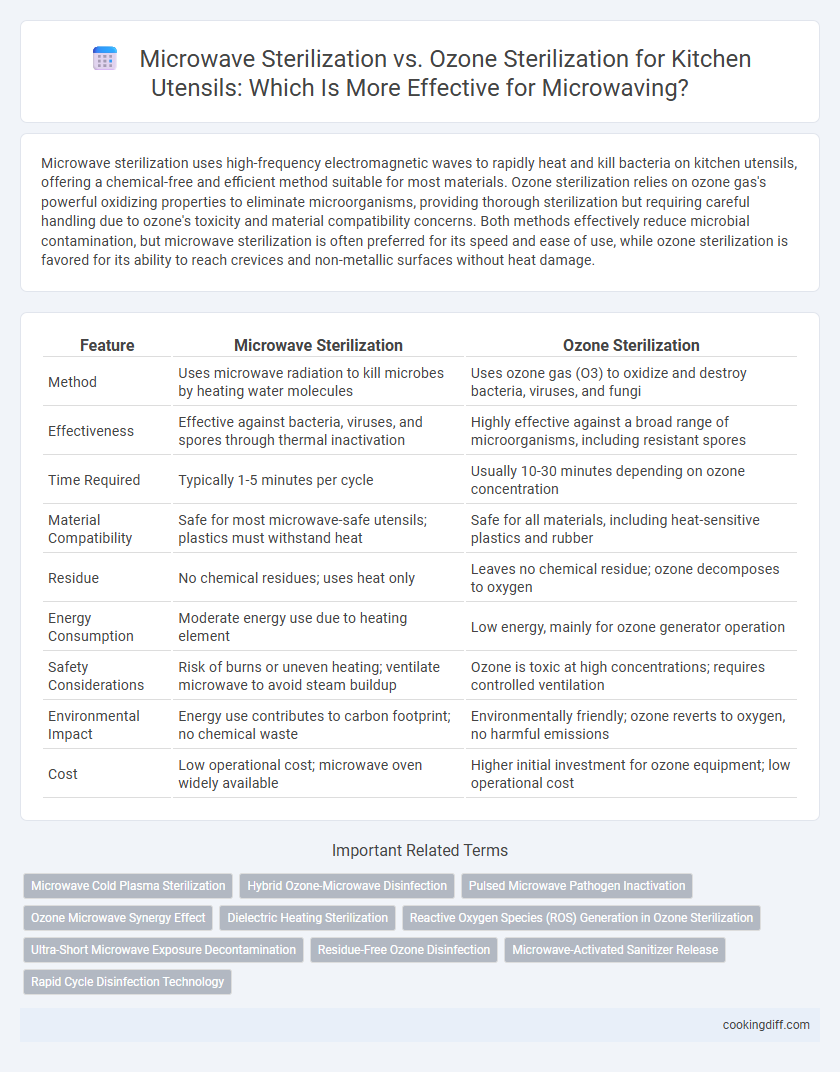
Microwave sterilization uses high-frequency electromagnetic waves to rapidly heat and kill bacteria on kitchen utensils, offering a chemical-free and efficient method suitable for most materials. Ozone sterilization relies on ozone gas's powerful oxidizing properties to eliminate microorganisms, providing thorough sterilization but requiring careful handling due to ozone's toxicity and material compatibility concerns. Both methods effectively reduce microbial contamination, but microwave sterilization is often preferred for its speed and ease of use, while ozone sterilization is favored for its ability to reach crevices and non-metallic surfaces without heat damage.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Microwave Sterilization | Ozone Sterilization |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Uses microwave radiation to kill microbes by heating water molecules | Uses ozone gas (O3) to oxidize and destroy bacteria, viruses, and fungi |
| Effectiveness | Effective against bacteria, viruses, and spores through thermal inactivation | Highly effective against a broad range of microorganisms, including resistant spores |
| Time Required | Typically 1-5 minutes per cycle | Usually 10-30 minutes depending on ozone concentration |
| Material Compatibility | Safe for most microwave-safe utensils; plastics must withstand heat | Safe for all materials, including heat-sensitive plastics and rubber |
| Residue | No chemical residues; uses heat only | Leaves no chemical residue; ozone decomposes to oxygen |
| Energy Consumption | Moderate energy use due to heating element | Low energy, mainly for ozone generator operation |
| Safety Considerations | Risk of burns or uneven heating; ventilate microwave to avoid steam buildup | Ozone is toxic at high concentrations; requires controlled ventilation |
| Environmental Impact | Energy use contributes to carbon footprint; no chemical waste | Environmentally friendly; ozone reverts to oxygen, no harmful emissions |
| Cost | Low operational cost; microwave oven widely available | Higher initial investment for ozone equipment; low operational cost |
Introduction to Kitchen Utensil Sterilization Methods
Kitchen utensil sterilization involves various methods to eliminate harmful bacteria and ensure food safety. Microwave sterilization and ozone sterilization are two innovative techniques gaining popularity for their efficiency and ease of use in household kitchens.
- Microwave Sterilization - Uses microwave radiation to produce heat that kills microorganisms on utensils quickly and effectively.
- Ozone Sterilization - Employs ozone gas to oxidize and destroy bacteria and viruses without using heat or chemicals.
- Comparison of Methods - Microwave sterilization offers fast, heat-based disinfection, while ozone sterilization provides a chemical-free alternative suitable for heat-sensitive utensils.
How Microwave Sterilization Works
Microwave sterilization kills bacteria and pathogens on kitchen utensils by using electromagnetic waves to generate heat within the items, effectively disrupting microbial cells. This process is rapid and penetrates deeply, ensuring thorough sanitization without chemical residues.
- Electromagnetic Radiation - Microwaves produce high-frequency waves that cause water molecules in utensils to vibrate, generating intense heat.
- Thermal Inactivation - The heat destroys microbial cell walls and denatures proteins, leading to the elimination of bacteria and viruses.
- Uniform Penetration - Microwaves penetrate materials evenly, allowing sterilization of complex surfaces and hard-to-reach areas.
This method contrasts with ozone sterilization, which relies on reactive oxygen species rather than heat to eliminate contaminants.
Principles of Ozone Sterilization
Ozone sterilization operates by generating ozone (O3) gas, a powerful oxidizing agent that penetrates and disrupts the cellular structure of bacteria, viruses, and molds on kitchen utensils. This method effectively eliminates microorganisms without the use of heat, preserving the integrity of heat-sensitive materials.
Unlike microwave sterilization which relies on thermal energy to kill pathogens, ozone sterilization involves a chemical process that breaks down contaminants through oxidation. The ozone gas naturally reverts to oxygen after sterilization, leaving no harmful residues on utensils or in the environment.
Effectiveness of Microwave vs Ozone Sterilization
Microwave sterilization effectively eliminates bacteria and viruses on kitchen utensils by using high-frequency electromagnetic waves to generate heat rapidly, achieving microbial kill within minutes. Ozone sterilization, a powerful oxidizing process, disrupts microbial cell walls and is particularly effective against bacteria, viruses, and fungi without heat exposure.
Microwave sterilization provides rapid, thermal-based microbial reduction but may struggle with uneven exposure or heat-sensitive utensils. Ozone sterilization penetrates hard-to-reach surfaces and is non-thermal, preserving delicate materials while ensuring broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. Both methods offer eco-friendly, chemical-free alternatives with distinct advantages depending on utensil type and sterilization time requirements.
Safety Considerations for Both Sterilization Methods
Microwave sterilization uses electromagnetic waves to eliminate bacteria on kitchen utensils, requiring careful attention to avoid overheating and potential burns. Ozone sterilization employs ozone gas, which is highly effective against microorganisms but demands proper ventilation due to ozone's toxicity at high concentrations.
Both methods necessitate safety measures: microwaving calls for monitoring utensil material compatibility to prevent damage, while ozone sterilization requires sealed environments or exhaust systems to protect users from inhalation risks. Proper training and adherence to safety protocols are critical to minimizing health hazards with either sterilization technique.
Time and Energy Efficiency Comparison
Microwave sterilization typically requires 5 to 10 minutes to effectively eliminate bacteria on kitchen utensils, consuming moderate energy levels due to rapid heating. Ozone sterilization, while effective, often takes 15 to 30 minutes and uses more energy to generate sufficient ozone concentration for thorough disinfection. Microwave sterilization offers superior time and energy efficiency, making it a practical choice for quick and eco-friendly kitchen utensil sterilization.
Impact on Utensil Materials and Longevity
Microwave sterilization uses high-frequency electromagnetic waves to kill bacteria, posing minimal risk to most kitchen utensil materials but potentially weakening plastics over frequent use due to heat exposure. Ozone sterilization employs strong oxidizing agents that can degrade metal surfaces and cause brittleness in certain plastics, potentially shortening the lifespan of utensils. Selecting the appropriate sterilization method depends on the utensil's material composition and desired durability, with microwave sterilization generally favored for preserving overall longevity.
Environmental Implications of Each Method
How do the environmental impacts of microwave sterilization compare to those of ozone sterilization for kitchen utensils? Microwave sterilization consumes electricity but emits no harmful chemicals, making it a cleaner option for energy use if renewable sources are employed. Ozone sterilization involves producing ozone gas, which can be harmful if released improperly, but it requires less energy and leaves no chemical residues, offering a more environmentally friendly choice when managed safely.
Cost Analysis: Microwave vs Ozone Sterilization
| Sterilization Method | Initial Equipment Cost | Operational Cost | Maintenance Cost | Energy Consumption |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microwave Sterilization | Moderate ($300-$1,000) | Low ($0.05-$0.15 per cycle) | Minimal (annual checks) | Relatively Low (900-1200 W) |
| Ozone Sterilization | High ($1,000-$3,000) | Moderate to High (ozone generation and ventilation costs) | Regular filter and ozone generator replacement | Moderate to High (varies by system size) |
Related Important Terms
Microwave Cold Plasma Sterilization
Microwave cold plasma sterilization effectively eliminates bacteria and pathogens on kitchen utensils by generating reactive species at low temperatures, preserving utensil integrity while ensuring high sterilization efficiency. Compared to ozone sterilization, this method offers faster microbial inactivation without harmful residue, making it an advanced and eco-friendly solution for kitchen hygiene.
Hybrid Ozone-Microwave Disinfection
Hybrid ozone-microwave disinfection combines the rapid heating effects of microwaves with the potent oxidative capabilities of ozone gas, achieving superior sterilization of kitchen utensils by effectively eliminating bacteria, viruses, and biofilms. This synergistic method enhances microbial inactivation rates while reducing sterilization time and energy consumption compared to conventional microwave or ozone sterilization alone.
Pulsed Microwave Pathogen Inactivation
Pulsed microwave pathogen inactivation offers rapid, energy-efficient sterilization by generating localized heat and nonthermal effects that disrupt microbial cell walls on kitchen utensils, outperforming ozone sterilization's slower, chemical-based process. Unlike ozone sterilization, which relies on oxidative reactions and requires careful handling due to toxic residues, pulsed microwave technology ensures safer, residue-free disinfection with minimal material degradation.
Ozone Microwave Synergy Effect
Microwave sterilization rapidly heats kitchen utensils to eliminate microbes, while ozone sterilization uses strong oxidative properties to destroy bacteria and viruses on surfaces. Combining microwave and ozone treatments leverages the synergy effect, enhancing sterilization efficacy by simultaneously applying heat and oxidative stress, resulting in faster and more thorough disinfection.
Dielectric Heating Sterilization
Microwave sterilization leverages dielectric heating to rapidly generate heat within kitchen utensils, effectively eliminating bacteria by agitating water molecules at the molecular level. Ozone sterilization relies on oxidative properties to disinfect surfaces but lacks the deep penetration and uniform heat distribution provided by microwave dielectric heating.
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Generation in Ozone Sterilization
Microwave sterilization relies on thermal effects to eliminate microorganisms on kitchen utensils, while ozone sterilization generates Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) such as ozone (O3), superoxide (O2-), and hydroxyl radicals (*OH) that disrupt microbial cell walls and DNA, enhancing sterilization efficacy. The ROS produced in ozone sterilization offer a powerful oxidative mechanism for decontamination, making it effective against a broader spectrum of pathogens compared to microwave heat alone.
Ultra-Short Microwave Exposure Decontamination
Ultra-short microwave exposure decontamination rapidly disrupts microbial cell structures on kitchen utensils through targeted dielectric heating, achieving effective sterilization without compromising material integrity. Compared to ozone sterilization, this method offers faster processing times and eliminates chemical residues, ensuring safer kitchenware and reducing environmental impact.
Residue-Free Ozone Disinfection
Microwave sterilization utilizes high-frequency electromagnetic waves to eliminate pathogens on kitchen utensils but may not completely remove chemical residues. Ozone sterilization offers residue-free disinfection by using ozone gas to oxidize and destroy bacteria and viruses, leaving no harmful byproducts on utensils.
Microwave-Activated Sanitizer Release
Microwave sterilization utilizes microwave-activated sanitizer release to effectively eliminate bacteria and viruses on kitchen utensils by generating heat and activating embedded sanitizing agents, ensuring rapid and thorough disinfection. This method contrasts with ozone sterilization, which relies on gaseous ozone exposure, offering chemical-free but slower sterilization without the immediate activation of sanitizers through microwave energy.
Microwave sterilization vs Ozone sterilization for kitchen utensils. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com