Microwaving offers rapid heating by agitating water molecules, making it ideal for quick reheating and simple cooking tasks. A combi oven combines convection heat, steam, and microwave energy, delivering precise temperature control and even cooking results for a wide range of dishes. Choosing between the two depends on desired cooking speed, texture, and food quality, with combi ovens excelling in versatility and microwaves in convenience.
Table of Comparison
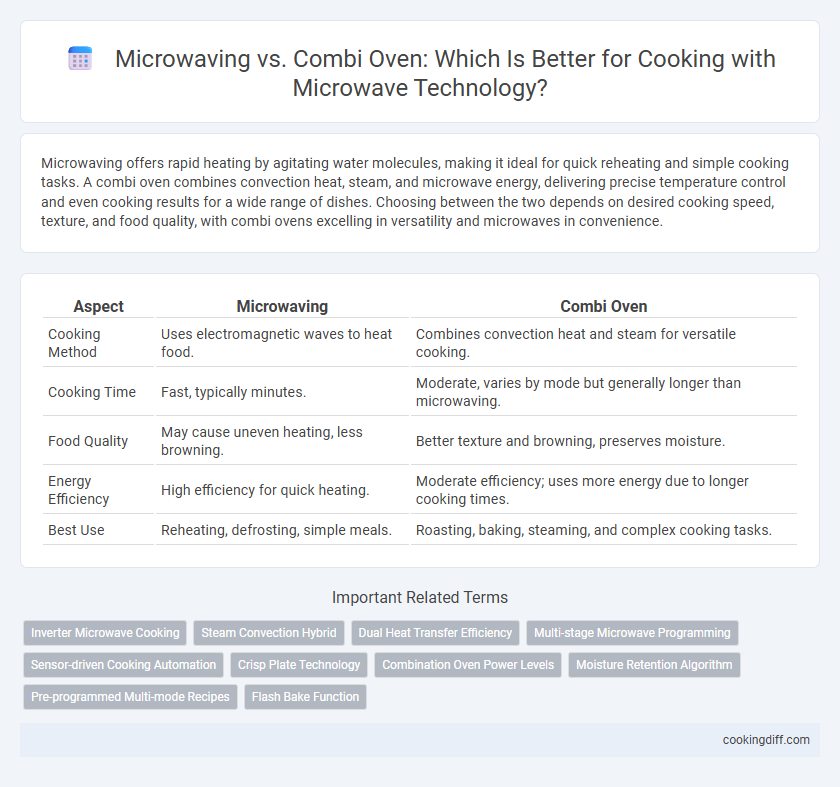
| Aspect | Microwaving | Combi Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Uses electromagnetic waves to heat food. | Combines convection heat and steam for versatile cooking. |
| Cooking Time | Fast, typically minutes. | Moderate, varies by mode but generally longer than microwaving. |
| Food Quality | May cause uneven heating, less browning. | Better texture and browning, preserves moisture. |
| Energy Efficiency | High efficiency for quick heating. | Moderate efficiency; uses more energy due to longer cooking times. |
| Best Use | Reheating, defrosting, simple meals. | Roasting, baking, steaming, and complex cooking tasks. |
Introduction to Microwaving and Combi Ovens
Microwaving uses electromagnetic waves at a frequency of 2.45 GHz to heat food quickly by agitating water molecules. Combi ovens combine convection heat and steam, offering precise temperature control and moisture retention for diverse cooking tasks. Both methods provide efficient cooking options, with microwaving excelling in speed and combi ovens in versatility and quality.
How Microwaves Work: The Science Explained
Microwaves cook food by emitting electromagnetic waves that cause water molecules to vibrate rapidly, generating heat through friction. Unlike combi ovens, which use steam and convection heat, microwaves heat food internally and quickly without browning or crisping.
- Electromagnetic Radiation - Microwaves operate at a frequency of about 2.45 GHz, targeting water molecules in food to produce heat effectively.
- Dielectric Heating - The vibration of polar molecules creates internal heat, enabling rapid cooking compared to surface heat methods.
- Heat Distribution - Microwaves penetrate food unevenly, often requiring turntables or stirring to ensure even cooking.
Combi Ovens: Functions and Technology
Combi ovens combine convection, steam, and microwave technologies to enhance cooking versatility and precision. These ovens allow for programmable cooking cycles, ensuring consistent temperature and moisture control for optimal food texture and flavor. Advanced sensors in combi ovens adjust humidity and cooking time, reducing energy consumption while improving overall efficiency compared to traditional microwaving.
Cooking Speed: Microwaving vs. Combi Oven Efficiency
| Cooking Method | Speed | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Microwaving | Rapid heating, typically 1-5 minutes for common dishes | High energy efficiency due to direct molecular agitation, minimal heat loss |
| Combi Oven | Moderate speed, usually 10-30 minutes depending on food type | Offers versatile cooking modes with efficient steam and convection heat but higher energy consumption compared to microwaves |
Food Quality and Texture Comparison
Microwaving cooks food quickly by agitating water molecules, often resulting in uneven heating and a softer texture that can sacrifice crispness or browning. This rapid process can lead to moisture retention but may compromise the development of complex flavors and textures typically achieved with dry heat.
Combi ovens combine steam and convection heat, providing precise temperature control that enhances food texture by creating crispy exteriors and tender interiors. The dual cooking method preserves moisture while promoting caramelization and Maillard reactions, delivering superior overall food quality compared to microwaving.
Versatility in Cooking Techniques
Microwaving excels in rapid heating but is limited to basic cooking techniques like reheating and defrosting. Combi ovens offer versatility by combining steam, convection, and microwave cooking methods for a wide range of dishes.
Combi ovens provide precise control over temperature and humidity, enabling baking, roasting, steaming, and grilling in one unit. The ability to switch between cooking modes or combine them ensures consistent quality and texture. This flexibility makes combi ovens ideal for commercial kitchens seeking efficiency and diverse menu options.
Energy Consumption and Cost Analysis
Microwaving uses electromagnetic waves to heat food quickly, consuming significantly less energy than combi ovens, which operate by combining steam and convection heat. Energy consumption for microwaving typically ranges from 600 to 1200 watts, whereas combi ovens can use 3000 to 6000 watts during operation.
Cost analysis reveals that microwaves have lower initial purchase prices and reduced operational costs due to shorter cooking times and lower electricity usage. Combi ovens, while more expensive upfront, offer versatility in cooking methods but result in higher ongoing energy expenses and maintenance costs.
Space and Maintenance: Practical Considerations
How do microwaving and combi ovens compare in terms of space and maintenance? Microwaves require significantly less kitchen space and are easier to maintain due to fewer mechanical components. Combi ovens, while offering versatile cooking options, demand more room and regular professional servicing to ensure optimal performance.
Health and Nutrient Retention in Both Methods
Microwaving generally preserves more nutrients in vegetables due to shorter cooking times and reduced exposure to heat. Combi ovens, which use a combination of steam and convection heat, offer balanced cooking but may lead to slight nutrient loss depending on temperature and duration.
- Microwaving retains vitamins - Microwaving limits nutrient degradation by rapidly heating food and minimizing water use, which helps preserve vitamin C and B vitamins.
- Combi ovens provide even cooking - The steam function in combi ovens helps retain moisture and certain nutrients, but extended cooking times can cause some vitamin loss.
- Health impact varies by food type - Leafy greens and delicate vegetables benefit more from microwaving, while proteins maintain texture and juiciness better in combi ovens.
Related Important Terms
Inverter Microwave Cooking
Inverter microwave cooking delivers consistent power levels for even heating and precise temperature control, enhancing the taste and texture of foods compared to traditional microwaving methods. Combi ovens combine microwave and convection cooking, but inverter technology in microwaves offers faster cooking times and greater energy efficiency, making it ideal for quick meal preparation without sacrificing quality.
Steam Convection Hybrid
Steam convection hybrid ovens combine microwave speed with convection heat and steam, delivering faster cooking times and enhanced moisture retention compared to traditional microwaves. This technology ensures even heat distribution, preserving food texture and flavor while accelerating cooking processes in commercial and home kitchens.
Dual Heat Transfer Efficiency
Microwaving utilizes electromagnetic waves to heat food quickly by agitating water molecules, offering rapid energy transfer but often resulting in uneven cooking. Combi ovens combine convection heat and steam, providing dual heat transfer that ensures uniform cooking and moisture retention while balancing speed and quality.
Multi-stage Microwave Programming
Multi-stage microwave programming enhances precision cooking by allowing varied power levels and time sequences, optimizing texture and flavor compared to combi ovens that rely on combining steam and convection heat. This technology streamlines complex recipes, reducing cooking time while maintaining quality in microwave-prepared meals.
Sensor-driven Cooking Automation
Sensor-driven cooking automation in microwaving utilizes precise moisture and temperature sensors to adjust cooking times, ensuring consistent results while preserving food texture. Combi ovens integrate advanced sensor feedback with steam and convection heat control, offering greater versatility and accuracy for complex recipes requiring precise humidity and temperature management.
Crisp Plate Technology
Crisp Plate Technology in microwaving enhances browning and crispiness by evenly distributing microwaves and infusing heat from a specialized plate, outperforming conventional combi ovens that rely on steam and hot air. This technology enables faster cooking times while delivering a texture similar to traditionally fried or baked foods.
Combination Oven Power Levels
Combination ovens offer precise control over power levels by blending microwave energy with convection heat, allowing cooks to adjust settings for optimal texture and even cooking. This dual-power approach achieves faster cooking times than traditional ovens while preserving food quality better than standard microwaving alone.
Moisture Retention Algorithm
Microwaving utilizes electromagnetic waves that excite water molecules, promoting rapid heating while preserving moisture through minimal cooking time, whereas combi ovens combine steam and convection heat controlled by advanced moisture retention algorithms to optimize texture and juiciness by dynamically adjusting humidity levels throughout the cooking process. The moisture retention algorithm in combi ovens senses internal food humidity and modulates steam injection to prevent drying, resulting in more consistent moisture preservation compared to standard microwave cooking.
Pre-programmed Multi-mode Recipes
Microwaves offer quick cooking with pre-programmed multi-mode recipes that combine microwave energy with convection or grilling for efficient meal preparation. Combi ovens provide advanced control over humidity and temperature, enabling precise execution of multi-mode cooking programs for consistent restaurant-quality results.
Microwaving vs Combi Oven for cooking Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com