Microwaving cooks vegetables quickly by using electromagnetic waves that agitate water molecules, preserving most nutrients and maintaining a tender texture. Sous vide involves vacuum-sealing vegetables and cooking them in a temperature-controlled water bath for precise doneness and enhanced flavor retention. While microwaving offers convenience and speed, sous vide provides consistent results and better nutrient preservation through gentle, even cooking.
Table of Comparison
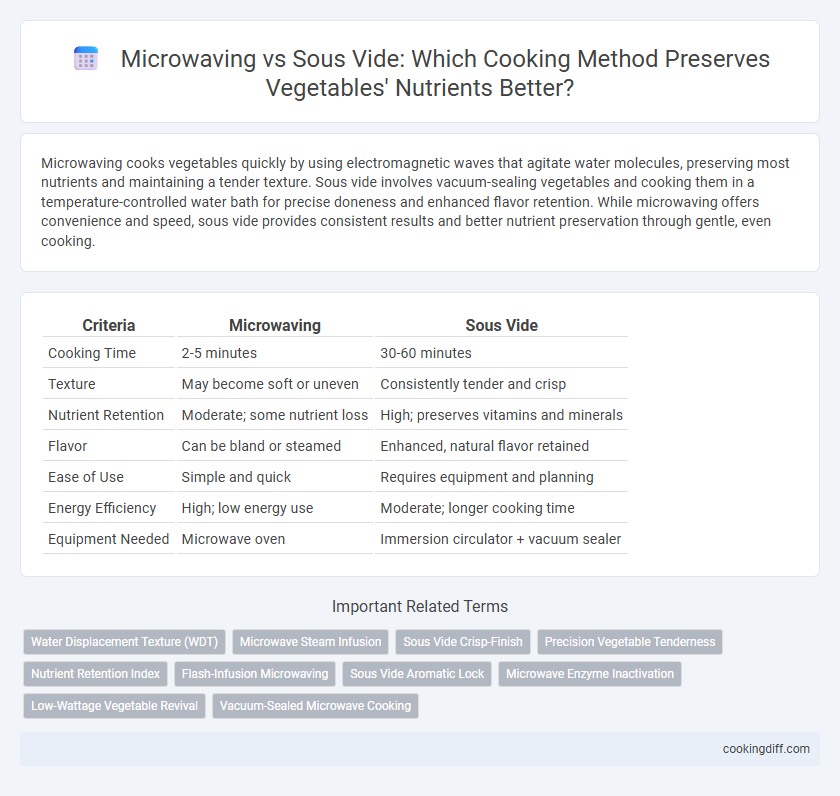
| Criteria | Microwaving | Sous Vide |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Time | 2-5 minutes | 30-60 minutes |
| Texture | May become soft or uneven | Consistently tender and crisp |
| Nutrient Retention | Moderate; some nutrient loss | High; preserves vitamins and minerals |
| Flavor | Can be bland or steamed | Enhanced, natural flavor retained |
| Ease of Use | Simple and quick | Requires equipment and planning |
| Energy Efficiency | High; low energy use | Moderate; longer cooking time |
| Equipment Needed | Microwave oven | Immersion circulator + vacuum sealer |
Introduction to Microwaving and Sous Vide Cooking Methods
Microwaving is a rapid cooking method that uses electromagnetic waves to heat water molecules in vegetables, ensuring quick and efficient cooking. Sous vide involves vacuum-sealing vegetables and cooking them in temperature-controlled water baths to maintain flavor and texture.
Microwaving preserves nutrients by reducing cooking time but can sometimes cause uneven heating. Sous vide offers precise temperature control, resulting in consistent texture and enhanced nutrient retention. Both methods provide convenient alternatives to traditional cooking, with microwaving excelling in speed and sous vide in quality.
How Microwaving Cooks Vegetables: Science and Process
Microwaving cooks vegetables by emitting electromagnetic waves that excite water molecules, generating heat internally and rapidly. This method preserves nutrients by reducing cooking time and minimizing exposure to high temperatures compared to traditional boiling. The process effectively softens cell walls while retaining color and texture, making it a quick and nutrient-efficient cooking technique.
The Sous Vide Technique: Precision and Consistency for Vegetables
The sous vide technique uses precise temperature control to cook vegetables evenly, preserving nutrients and texture better than microwaving. By sealing vegetables in airtight bags and cooking them in a water bath, it ensures consistent doneness without overcooking or drying out. This method enhances flavor retention and offers a reliable way to achieve perfect vegetable textures every time.
Nutrient Retention: Microwaving vs Sous Vide Compared
Microwaving vegetables preserves water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B vitamins more effectively than boiling due to shorter cooking times and minimal water usage. Studies indicate microwaving can retain up to 90% of nutrients compared to traditional methods.
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control, which helps maintain nutrient integrity by avoiding overcooking and nutrient degradation. However, longer cooking times in sous vide may result in slight nutrient loss, making microwaving a faster option for nutrient retention in vegetables.
Flavor and Texture Outcomes in Microwaved vs Sous Vide Vegetables
Microwaving vegetables often results in a quicker cooking time but can lead to uneven texture and slightly diminished flavor depth. Sous vide cooking preserves vibrant flavors and ensures consistent, tender texture by cooking vegetables slowly in a controlled temperature environment.
- Flavor preservation - Sous vide maintains natural vegetable flavors better than microwaving, which can sometimes mute taste due to rapid heating.
- Texture control - Sous vide provides precise temperature control, resulting in uniformly tender vegetables, while microwaving may cause some parts to be overcooked or mushy.
- Cooking speed - Microwaving offers a significant time advantage but at the expense of the subtle flavor and texture benefits associated with sous vide.
Cooking Time and Convenience: Which Method Wins?
| Microwaving | Microwaving drastically reduces cooking time for vegetables to just a few minutes, offering unmatched speed and ease for busy kitchens. This method requires minimal preparation and cleanup, enhancing overall convenience. Its rapid heat application preserves nutrients effectively compared to longer cooking processes. |
| Sous Vide | Sous vide involves extended cooking times, often ranging from 30 minutes to over an hour, which limits its practicality for quick meals. While it provides precise temperature control and consistent texture, the need for specialized equipment and water baths reduces convenience. This method excels in flavor enhancement but is less time-efficient than microwaving. |
| Conclusion | For cooking vegetables with optimal convenience and speed, microwaving outperforms sous vide by significantly reducing cooking time and simplifying kitchen operations. Sous vide remains ideal for precise texture and flavor when time is not a constraint. Microwaving suits everyday meal prep demanding swift and nutritious results. |
Equipment and Cost Considerations for Home Cooks
Microwaving requires minimal equipment, typically just a microwave-safe container and the microwave itself, making it a cost-effective choice for home cooks. Sous vide cooking demands specialized equipment such as a precision immersion circulator and vacuum sealer, resulting in a higher initial investment.
- Microwave Oven Cost - Basic microwave ovens are affordable and widely available, with prices often under $100.
- Sous Vide Equipment Expense - Sous vide setups can range from $100 to $300 or more, factoring in the immersion circulator and sealing devices.
- Long-Term Investment - While microwaves serve multiple functions in the kitchen, sous vide equipment is more specialized, influencing overall cost considerations for home cooks.
Energy Efficiency: Microwaving Versus Sous Vide
Microwaving vegetables uses significantly less energy compared to sous vide cooking due to shorter cooking times and direct heat application. Sous vide requires prolonged use of a water bath and precise temperature control, leading to higher energy consumption.
- Microwaving Efficiency - Microwaves heat food quickly by agitating water molecules, reducing energy waste and cook time.
- Sous Vide Energy Use - Sous vide immersion circulators maintain consistent water temperature for extended periods, increasing electricity usage.
- Energy Cost Impact - Lower energy consumption in microwaving results in reduced electricity bills compared to sous vide methods.
Choosing microwaving over sous vide can contribute to more sustainable and cost-effective vegetable preparation.
Best Vegetables for Each Cooking Technique
Leafy greens like spinach and kale cook exceptionally well in a microwave, preserving their vibrant color and nutrients quickly due to the fast heating process. Root vegetables such as carrots and potatoes benefit more from sous vide cooking, which enhances their natural sweetness and ensures even texture through precise, low-temperature water bath cooking.
Microwaving is ideal for soft vegetables like broccoli and zucchini, maximizing convenience and nutrient retention in minimal time. Hardy vegetables including beets and fennel are best suited for sous vide, where slow cooking breaks down fibers gently, resulting in tender and flavorful dishes.
Related Important Terms
Water Displacement Texture (WDT)
Microwaving heats vegetables quickly by agitating water molecules, often resulting in varied texture due to uneven moisture distribution, while sous vide utilizes precise temperature control and Water Displacement Texture (WDT) techniques to maintain consistent firmness and prevent cellular breakdown. WDT in sous vide cooking preserves the vegetables' natural crunch by minimizing water loss and retaining cellular integrity, unlike microwaving which can cause sogginess or uneven texture.
Microwave Steam Infusion
Microwave Steam Infusion uses electromagnetic waves to rapidly heat water within vegetable cells, preserving nutrients and enhancing flavor by infusing steam directly into the food. Compared to sous vide, which relies on prolonged low-temperature water baths to cook vegetables evenly, microwaving with steam infusion offers faster cooking times and superior nutrient retention without sacrificing texture.
Sous Vide Crisp-Finish
Sous vide cooking preserves the nutrients and texture of vegetables by precisely controlling temperature, while the sous vide crisp-finish technique enhances their flavor and creates a desirable crispy exterior without overcooking. This method outperforms microwaving by maintaining optimal texture and taste, resulting in perfectly cooked vegetables with a satisfying crunch.
Precision Vegetable Tenderness
Microwaving vegetables offers rapid cooking but often results in uneven tenderness due to variable heat distribution, whereas sous vide provides precise temperature control that consistently achieves uniform, optimal vegetable tenderness. The sous vide method's ability to maintain exact heat levels preserves texture and nutrients, making it superior for achieving desired vegetable softness without overcooking.
Nutrient Retention Index
Microwaving vegetables typically achieves a higher Nutrient Retention Index compared to sous vide cooking due to shorter exposure to heat and water, which minimizes nutrient leaching. Studies indicate that microwaving preserves up to 85% of vitamins like vitamin C and folate, whereas sous vide methods retain around 70-75% depending on temperature and cooking duration.
Flash-Infusion Microwaving
Flash-Infusion Microwaving enhances vegetable cooking by rapidly penetrating heat, preserving nutrients and vibrant colors more effectively than traditional sous vide methods. Unlike sous vide, which requires extended cooking times and water immersion, flash-infusion microwaving achieves quick, uniform heating that maintains texture and maximizes flavor retention in vegetables.
Sous Vide Aromatic Lock
Sous vide cooking preserves the aromatic compounds and nutrients in vegetables by sealing them in vacuum bags, preventing evaporation and flavor loss during the cooking process. Microwaving, while faster, often leads to the escape of delicate aromas and nutrients due to uneven heating and exposure to air.
Microwave Enzyme Inactivation
Microwaving rapidly inactivates enzymes in vegetables by generating localized heat through dielectric heating, preserving color, texture, and nutrients more effectively than sous vide, which relies on slower, low-temperature water baths. Enzyme inactivation via microwaving minimizes degradation and extends shelf life while maintaining optimal cooking speed and energy efficiency.
Low-Wattage Vegetable Revival
Low-wattage microwaving preserves nutrients in vegetables by gently heating them at controlled power levels, preventing overcooking and nutrient loss often seen in high-temperature methods. Sous vide provides even temperature distribution and precise cooking, but low-wattage microwaving offers a faster, energy-efficient alternative for vegetable revival while maintaining texture and flavor.
Microwaving vs Sous Vide for cooking vegetables. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com