Cheesecloth offers a breathable cover that allows gases to escape during pickling while keeping out dust and insects, making it ideal for short-term fermentation. Fermentation lids provide an airtight seal with built-in airlocks to prevent oxygen from entering, ensuring an anaerobic environment that enhances flavor development and preserves pickles longer. Choosing between cheesecloth and a fermentation lid depends on the desired fermentation control and duration.
Table of Comparison
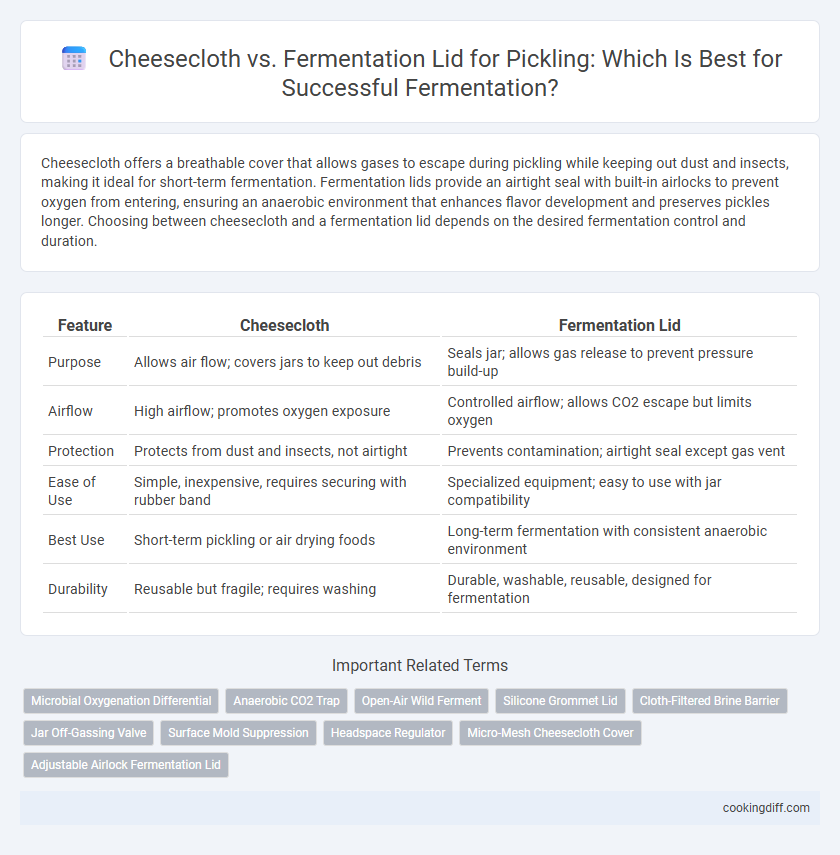
| Feature | Cheesecloth | Fermentation Lid |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Allows air flow; covers jars to keep out debris | Seals jar; allows gas release to prevent pressure build-up |
| Airflow | High airflow; promotes oxygen exposure | Controlled airflow; allows CO2 escape but limits oxygen |
| Protection | Protects from dust and insects, not airtight | Prevents contamination; airtight seal except gas vent |
| Ease of Use | Simple, inexpensive, requires securing with rubber band | Specialized equipment; easy to use with jar compatibility |
| Best Use | Short-term pickling or air drying foods | Long-term fermentation with consistent anaerobic environment |
| Durability | Reusable but fragile; requires washing | Durable, washable, reusable, designed for fermentation |
Introduction: Cheesecloth and Fermentation Lid in Pickling
Cheesecloth is a porous fabric that allows air circulation while preventing contaminants from entering the pickling vessel. It is commonly used in traditional pickling methods for fermenting vegetables and fruits.
Fermentation lids are specially designed with airlocks to release gases produced during fermentation while keeping the environment anaerobic. They provide a more controlled fermentation process compared to cheesecloth.
Understanding Cheesecloth: Uses in Pickling
Cheesecloth serves as an effective breathable barrier in the pickling process, allowing gases to escape while preventing contaminants from entering. Its loose weave supports natural fermentation by maintaining airflow essential for microbial activity.
- Breathability - Cheesecloth's open weave permits oxygen exchange crucial for lactic acid bacteria growth in fermentation.
- Protection - It acts as a shield against insects and airborne debris during the pickling period.
- Versatility - Cheesecloth can be used to cover jars or wrap pickled items directly, adapting to varied fermentation setups.
What is a Fermentation Lid? Key Features Explained
A fermentation lid is a specialized cover designed to fit airtight on jars, allowing gases produced during pickling to escape while preventing oxygen and contaminants from entering. Key features include an airlock system that releases carbon dioxide, a silicone seal to maintain an anaerobic environment, and compatibility with standard mason jars. This lid enhances fermentation efficiency by reducing the risk of mold and spoilage compared to traditional cheesecloth covers.
Airflow Control: Cheesecloth vs Fermentation Lid
Which method provides better airflow control for pickling: cheesecloth or a fermentation lid? Cheesecloth allows for natural airflow but offers less protection against contaminants and pests, making it ideal for short-term fermenting. Fermentation lids provide a controlled airflow environment with airlocks that minimize oxygen exposure and prevent unwanted bacteria, ensuring a more consistent and safe fermentation process.
Preventing Contamination: Which Offers Better Protection?
Cheesecloth allows for air circulation during pickling but can expose the brine to contaminants, increasing the risk of mold and unwanted bacteria. Fermentation lids create an airtight seal with an airlock system that releases gases while preventing external microorganisms from entering. Using a fermentation lid significantly reduces contamination risks, ensuring a safer and more controlled pickling environment compared to cheesecloth.
Ease of Use: Comparing Application and Maintenance
| Cheesecloth | Fermentation Lid |
|---|---|
| Cheesecloth is simple to apply over jars but requires securing with a rubber band, making setup slightly time-consuming. | Fermentation lids screw directly onto mason jars, providing a quick and airtight seal that simplifies the pickling process. |
| Maintenance involves frequent washing and replacement due to exposure to liquids and potential mold growth. | Fermentation lids are easily cleaned with soap and water, designed for repeated use without wear affecting performance. |
Cost and Availability: Cheesecloth vs Fermentation Lid
Cheesecloth is an inexpensive and widely available option for pickling, commonly found in grocery and craft stores. Fermentation lids, while slightly more costly, are specialized tools designed to create an airtight seal and are typically purchased online or in specialty kitchen shops.
- Cheesecloth cost-effectiveness - Cheesecloth is generally less expensive and can be bought in bulk, reducing overall costs.
- Fermentation lid availability - Fermentation lids are less commonly stocked and may require ordering from niche retailers.
- Durability comparison - Fermentation lids offer reusable durability, whereas cheesecloth is often single-use or requires frequent replacement.
Choosing between cheesecloth and fermentation lids depends on budget constraints and ease of access for pickling enthusiasts.
Impact on Flavor and Fermentation Results
Cheesecloth allows airflow and microbial exchange, promoting a more complex and tangy fermentation flavor. Fermentation lids create an anaerobic environment, resulting in cleaner, more consistent flavor profiles and reduced risk of contamination.
- Cheesecloth enhances natural yeast and bacteria interaction - This exposure develops rich, layered flavors but requires careful monitoring to avoid mold.
- Fermentation lids maintain anaerobic conditions - They prevent oxygen from entering, ensuring controlled fermentation and less spoilage.
- Flavor outcomes differ due to oxygen exposure and microbial control - Cheesecloth tends to produce more robust flavors, while lids yield milder, predictable results.
Cleaning and Reusability: Which is More Sustainable?
Cheesecloth is lightweight and easily washable, allowing for quick drying and repeated use, which reduces waste over time. Its porous fabric structure makes thorough cleaning simple, minimizing the risk of contamination in pickling processes.
Fermentation lids are typically made of durable plastics or stainless steel, designed to be cleaned with water and mild detergents, and can be reused for multiple fermentation cycles. Their robust construction often ensures longer lifespan, contributing to sustainability by limiting single-use waste.
Related Important Terms
Microbial Oxygenation Differential
Cheesecloth allows oxygen exchange, promoting aerobic microbial activity essential for certain fermentation processes, while fermentation lids create an anaerobic environment by limiting oxygen exposure, favoring the growth of lactic acid bacteria. The oxygenation differential impacts microbial diversity and fermentation speed, influencing flavor development and preservation quality in pickled foods.
Anaerobic CO2 Trap
Cheesecloth allows airflow but does not create an anaerobic environment, making it less effective at trapping CO2 during fermentation. Fermentation lids are designed with airlocks that maintain anaerobic conditions by releasing CO2 while preventing oxygen entry, ensuring optimal anaerobic fermentation and preventing spoilage.
Open-Air Wild Ferment
Cheesecloth allows natural airflow and prevents contaminants while enabling wild lacto-fermentation bacteria to thrive in open-air pickling. Fermentation lids create a sealed environment with controlled gas release, ideal for consistent anaerobic conditions but less effective at promoting wild microbial diversity.
Silicone Grommet Lid
Silicone grommet lids provide an airtight seal crucial for pickling, preventing contamination while allowing gas to escape, unlike traditional cheesecloth that exposes fermenting vegetables to airborne microbes. These fermentation lids enhance consistency and safety by maintaining optimal anaerobic conditions, which cheesecloth alone cannot ensure.
Cloth-Filtered Brine Barrier
Cheesecloth serves as an effective cloth-filtered brine barrier during pickling, allowing gases to escape while preventing contaminants from entering the fermentation vessel. Fermentation lids provide a more airtight seal with built-in airlocks, but lack the breathable, natural filtration that cheesecloth offers for brine exposure control.
Jar Off-Gassing Valve
Cheesecloth allows natural fermentation gases to escape while preventing contaminants, but it lacks a controlled off-gassing valve, risking inconsistent pressure buildup. Fermentation lids with built-in jar off-gassing valves precisely regulate air release, minimizing spoilage and ensuring optimal anaerobic conditions during pickling.
Surface Mold Suppression
Cheesecloth allows air circulation but may increase the risk of surface mold during pickling, requiring more frequent monitoring and removal of any mold growth. Fermentation lids create a sealed, anaerobic environment that effectively suppresses surface mold by limiting oxygen exposure, promoting a cleaner and more consistent fermentation process.
Headspace Regulator
Cheesecloth provides basic airflow for pickling but lacks precise headspace regulation, potentially leading to inconsistent fermentation outcomes. Fermentation lids are designed with airtight seals and airlocks that maintain optimal headspace pressure, preventing contamination while allowing gases to escape efficiently.
Micro-Mesh Cheesecloth Cover
Micro-mesh cheesecloth covers provide optimal airflow and prevent contaminants during pickling, ensuring proper fermentation without the risk of mold or pests. Unlike fermentation lids, cheesecloth offers a breathable yet protective barrier that promotes natural gas exchange essential for sauerkraut and kimchi preservation.
Cheesecloth vs Fermentation Lid for pickling. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com