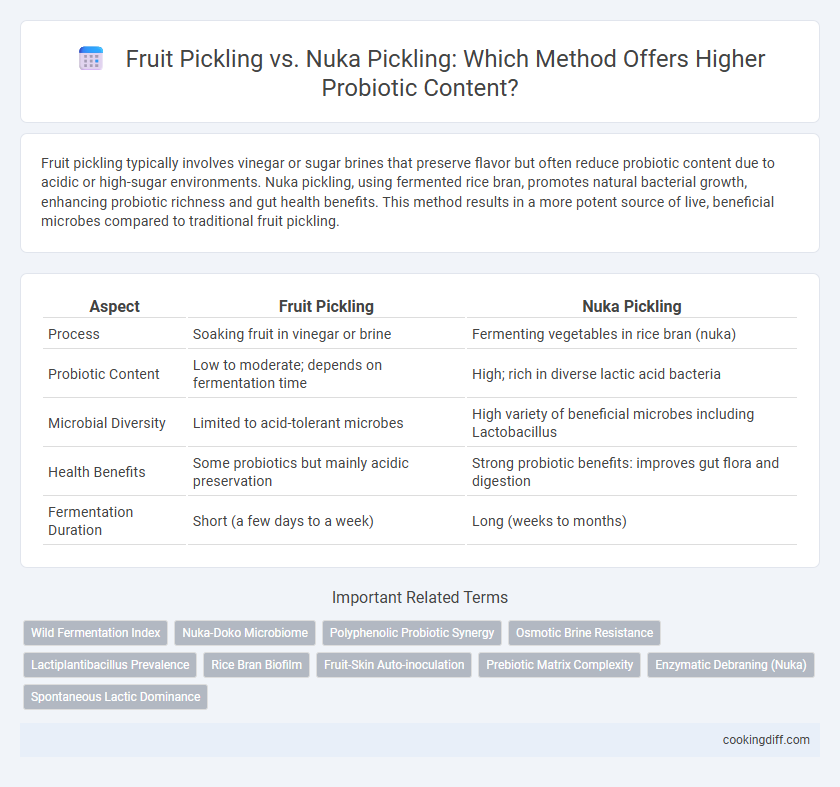
Fruit pickling typically involves vinegar or sugar brines that preserve flavor but often reduce probiotic content due to acidic or high-sugar environments. Nuka pickling, using fermented rice bran, promotes natural bacterial growth, enhancing probiotic richness and gut health benefits. This method results in a more potent source of live, beneficial microbes compared to traditional fruit pickling.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fruit Pickling | Nuka Pickling |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Soaking fruit in vinegar or brine | Fermenting vegetables in rice bran (nuka) |
| Probiotic Content | Low to moderate; depends on fermentation time | High; rich in diverse lactic acid bacteria |
| Microbial Diversity | Limited to acid-tolerant microbes | High variety of beneficial microbes including Lactobacillus |
| Health Benefits | Some probiotics but mainly acidic preservation | Strong probiotic benefits: improves gut flora and digestion |
| Fermentation Duration | Short (a few days to a week) | Long (weeks to months) |
Understanding Fruit Pickling and Nuka Pickling
Fruit pickling typically involves preserving fruits in a vinegar or sugar-based brine, which limits probiotic development due to the acidic environment. Nuka pickling, a traditional Japanese method using rice bran, fosters rich probiotic growth by encouraging beneficial bacteria during fermentation.
- Fruit Pickling Process - Involves immersion of fruits in acidic solutions, reducing the survival of probiotic microbes.
- Nuka Pickling Technique - Utilizes rice bran and salt to create an anaerobic environment ideal for lactic acid bacteria growth.
- Probiotic Content Comparison - Nuka pickling results in higher probiotic content compared to fruit pickling, enhancing gut health benefits.
The Science Behind Probiotic Formation in Pickling
Fruit pickling primarily relies on vinegar or sugar brines, creating an acidic environment that inhibits most bacterial growth, resulting in minimal probiotic content. Nuka pickling, a traditional Japanese method using rice bran, fosters a rich lactobacillus population by promoting fermentation, which significantly enhances probiotic formation. The complex microbial activity in nuka pickling produces beneficial enzymes and organic acids that support gut health more effectively than the antimicrobial conditions found in fruit pickling.
Key Ingredients in Fruit Pickling vs Nuka Pickling
Fruit pickling primarily relies on natural sugars and organic acids found in fruits like apples, plums, and cherries, which ferment to produce beneficial probiotics. The process often includes salt and water, creating an environment for lactic acid bacteria to thrive, enhancing probiotic content.
Nuka pickling, a traditional Japanese method, uses a rice bran bed enriched with salt, kombu, and ginger, providing a unique medium rich in nutrients and fermentation-friendly microbes. The key ingredients in nuka pickling foster a diverse microbial ecosystem that can yield higher probiotic diversity compared to fruit pickling.
Fermentation Process: How Probiotics Develop
How do the fermentation processes in fruit pickling and nuka pickling differ in developing probiotics? Fruit pickling relies on natural sugars and lactic acid bacteria to ferment, promoting the growth of beneficial probiotics like Lactobacillus species. Nuka pickling uses rice bran rich in nutrients and microbes, creating a unique environment that enhances diverse probiotic strains for improved gut health.
Comparing Probiotic Strains in Fruits and Nuka Beds
Fruit pickling cultivates probiotic strains such as Lactobacillus plantarum and Leuconostoc mesenteroides, which thrive on the sugar content and natural pectins found in fruits. Nuka pickling, utilizing rice bran beds, encourages a broader diversity of microbes including Pediococcus and Bacillus species, enhancing the complexity of probiotic profiles.
The lactic acid bacteria in fruit pickling primarily aid in flavor development and preservation, producing moderate levels of beneficial metabolites. Nuka beds foster robust fermentation conditions that result in higher probiotic counts and a more varied enzymatic activity, potentially offering superior gut health benefits.
Nutritional Benefits: Fruit Pickles vs Nuka Pickles
| Pickling Method | Probiotic Content | Nutritional Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Fruit Pickling | Lower probiotic levels due to high sugar content inhibiting fermentation | Rich in vitamins like C and antioxidants but less effective in promoting gut health |
| Nuka Pickling | High probiotic content from fermentation in rice bran bed enhancing gut microbiota | Provides beneficial lactic acid bacteria, increases B vitamins, and supports digestion |
Factors Affecting Probiotic Levels in Each Method
Fruit pickling typically involves vinegar or sugar brines that inhibit probiotic growth, resulting in lower beneficial bacterial content compared to nuka pickling. Nuka pickling, using rice bran and salt, creates an anaerobic environment promoting Lactobacillus proliferation and higher probiotic levels.
Factors affecting probiotic levels in fruit pickling include acidity, sugar concentration, and temperature, which can limit microbial activity. In nuka pickling, the presence of nutrients in rice bran, optimal salt concentration, and fermentation time significantly enhance probiotic growth. Both methods require careful control of conditions to maximize the health benefits from probiotics.
Taste Profile and Texture Differences
Fruit pickling produces a tangy and sweet flavor with a crisp texture due to the high sugar content and natural acidity in fruits like apples and pears. Nuka pickling, a traditional Japanese method using rice bran, imparts a deeply umami, slightly nutty taste while preserving a firmer, more crunchy texture in vegetables. The probiotic content in nuka pickling is often richer because the fermentation environment promotes diverse beneficial bacteria, enhancing both flavor complexity and gut health benefits.
Health Impacts of Probiotic-rich Pickles
Fruit pickling and nuka pickling both generate probiotic-rich foods, but nuka pickling typically produces higher diversity and concentration of beneficial bacteria. These probiotics enhance gut health and boost the immune system more effectively than fruit pickles. The fermentation process in nuka pickling preserves essential nutrients while fostering a more robust microbial environment.
- Probiotic Diversity - Nuka pickling involves rice bran fermentation, resulting in a wider array of probiotic strains compared to fruit pickling.
- Gut Health Benefits - Probiotics in nuka pickles promote better digestion and improved microbiome balance, enhancing overall well-being.
- Nutrient Preservation - The nuka pickle fermentation maintains essential vitamins and minerals critical for immune support and metabolism.
Related Important Terms
Wild Fermentation Index
Fruit pickling using traditional brine fermentation generates a moderate Wild Fermentation Index (WFI), promoting beneficial lactobacilli growth with a balanced probiotic profile. Nuka pickling, leveraging rice bran's unique microbiota, results in a higher WFI, yielding richer probiotic diversity and enhanced gut microbiome support compared to fruit-based methods.
Nuka-Doko Microbiome
Nuka pickling, leveraging the Nuka-Doko microbiome, fosters a rich diversity of lactic acid bacteria, enhancing probiotic content more effectively than traditional fruit pickling methods. The dynamic microbial community in Nuka-Doko, dominated by Lactobacillus and Leuconostoc species, promotes superior fermentation, resulting in higher concentrations of beneficial probiotics and improved gut health benefits.
Polyphenolic Probiotic Synergy
Fruit pickling leverages the natural polyphenols in fruits to enhance probiotic growth, creating a synergy that boosts antioxidant properties and gut health benefits. Nuka pickling, using rice bran rich in polyphenols and prebiotics, fosters a robust probiotic community, intensifying polyphenolic-probiotic interactions for superior microbial diversity and functional efficacy.
Osmotic Brine Resistance
Fruit pickling typically involves high sugar concentrations that create an osmotic brine resistant environment favoring osmophilic yeast, which can limit probiotic bacterial growth. Nuka pickling uses a rice bran fermentation bed that maintains lower osmotic pressure, promoting robust proliferation of lactic acid bacteria with higher probiotic content.
Lactiplantibacillus Prevalence
Fruit pickling primarily encourages the growth of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum due to its natural sugars, creating a rich environment for this probiotic strain. Nuka pickling, relying on rice bran fermentation, often fosters a broader microbial diversity but generally shows lower Lactiplantibacillus prevalence compared to fruit pickling methods.
Rice Bran Biofilm
Fruit pickling typically relies on vinegar or salt brine fermentation, which produces fewer probiotics compared to Nuka pickling that uses rice bran biofilm rich in beneficial lactic acid bacteria. The rice bran biofilm in Nuka pickling creates a unique environment fostering high-density probiotic cultures, enhancing gut health and nutrient absorption.
Fruit-Skin Auto-inoculation
Fruit pickling enhances probiotic content through fruit-skin auto-inoculation, where natural yeasts and bacteria from the fruit's surface initiate fermentation, promoting beneficial lactobacilli growth. In contrast, nuka pickling relies on rice bran's microbial community, typically producing a different probiotic profile with less direct influence from fruit-skin microorganisms.
Prebiotic Matrix Complexity
Fruit pickling typically involves high sugar and acid content, which supports limited microbial diversity, resulting in a simpler prebiotic matrix and potentially lower probiotic complexity. Nuka pickling, using rice bran ferment, enriches the prebiotic matrix with complex carbohydrates and fibers, fostering a diverse microbial ecosystem that enhances probiotic richness and gut health benefits.
Enzymatic Debraning (Nuka)
Nuka pickling, centered on enzymatic debranning with rice bran, enhances probiotic content by fostering diverse lactic acid bacteria growth, unlike traditional fruit pickling which relies on natural fermentation but may yield less varied microbial populations. This enzymatic action in nuka pickling breaks down cell walls, increasing nutrient availability and promoting a richer probiotic environment beneficial for gut health.
Fruit Pickling vs Nuka Pickling for probiotic content. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com