Pickling techniques vary greatly, with traditional methods relying on vinegar-based brines and Sandor Katz's approach emphasizing natural fermentation using wild lactobacillus bacteria. Katz's method enhances probiotic benefits and complex flavors by allowing pickles to ferment at room temperature without added vinegar or salt substitutes. This artisanal approach often results in tangier, more nutritious pickles that nurture gut health compared to conventional vinegar pickling.
Table of Comparison
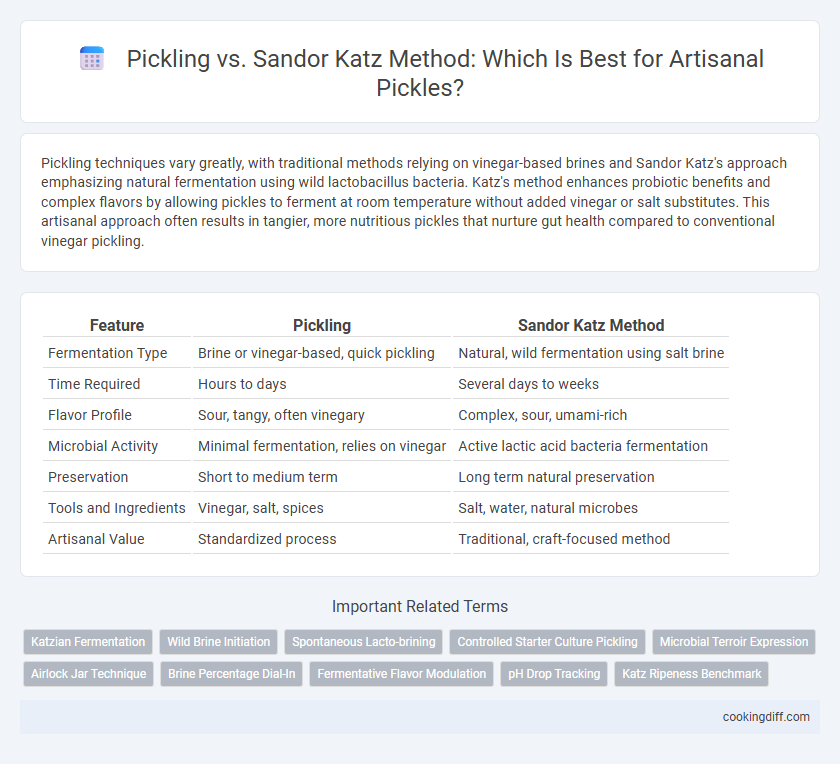
| Feature | Pickling | Sandor Katz Method |
|---|---|---|
| Fermentation Type | Brine or vinegar-based, quick pickling | Natural, wild fermentation using salt brine |
| Time Required | Hours to days | Several days to weeks |
| Flavor Profile | Sour, tangy, often vinegary | Complex, sour, umami-rich |
| Microbial Activity | Minimal fermentation, relies on vinegar | Active lactic acid bacteria fermentation |
| Preservation | Short to medium term | Long term natural preservation |
| Tools and Ingredients | Vinegar, salt, spices | Salt, water, natural microbes |
| Artisanal Value | Standardized process | Traditional, craft-focused method |
Introduction to Pickling: Traditional vs. Artisanal Methods
What distinguishes traditional pickling methods from Sandor Katz's artisanal approach? Traditional pickling relies on established preservation techniques using vinegar or brine to ferment vegetables, preserving flavor and texture. Sandor Katz's method emphasizes natural fermentation processes, harnessing wild microbes to create complex, probiotic-rich pickles with unique taste profiles.
Who is Sandor Katz? The Pioneer of Fermentation
Sandor Katz is a renowned fermentation expert celebrated for popularizing artisanal pickling through his influential books and workshops. His approach emphasizes natural fermentation using wild microbes, contrasting with traditional pickling methods that rely on vinegar or brine.
Katz's method promotes health benefits by enhancing probiotic content and flavor complexity in pickles. He advocates for sustainable, small-batch fermentation practices that honor cultural traditions. His pioneering work has inspired a global resurgence in homemade fermented foods, making him a key figure in the fermentation movement.
Core Principles of Classic Pickling
Classic pickling relies on the core principles of salt concentration, temperature control, and anaerobic fermentation to preserve produce and develop complex flavors. This method uses lactic acid bacteria naturally present on the vegetables, which convert sugars into lactic acid, ensuring food safety and enhancing tanginess.
Sandor Katz's approach to artisanal pickles emphasizes experimentation with diverse fermenting agents and techniques while respecting these foundational principles. Both methods prioritize maintaining a balanced environment that fosters beneficial microbes and inhibits harmful pathogens to create rich, flavorful pickles.
The Sandor Katz Method Explained
The Sandor Katz method emphasizes natural fermentation using wild lactobacillus bacteria, resulting in unique flavors and probiotic benefits in artisanal pickles. This method differs from conventional pickling by avoiding vinegar and relying on salt and time for fermentation.
- Wild fermentation - Katz's approach harnesses naturally occurring bacteria to ferment vegetables without added vinegar.
- Probiotic richness - The method promotes the growth of beneficial microbes that enhance gut health.
- Time-dependent process - Unlike quick pickles, Katz's technique requires prolonged fermentation to develop complex flavors.
Ingredients: Comparing Spice and Brine Choices
Pickling and Sandor Katz's method both emphasize the importance of spices and brine composition but differ in their ingredient selection and fermentation approach. Katz often incorporates a broader range of wild and local spices, enhancing microbial diversity and flavor complexity.
- Traditional Pickling - Uses a consistent set of spices like dill, garlic, and mustard seeds in a simple saltwater brine.
- Sandor Katz's Method - Embraces diverse, regionally sourced spices and encourages experimentation with ingredient combinations for unique taste profiles.
- Brine Composition - Katz recommends adjusting salt concentration to balance microbial activity, whereas traditional pickling follows standard salinity levels.
Process Differences: Vinegar Pickling vs. Natural Fermentation
Vinegar pickling involves submerging vegetables in a solution of vinegar, salt, and spices, creating an acidic environment that preserves the produce quickly. The Sandor Katz method of artisanal pickling relies on natural fermentation, where wild lactobacillus bacteria convert sugars into lactic acid, developing complex flavors over time. Unlike vinegar pickling, natural fermentation enhances probiotic content and requires precise monitoring of salt concentration and fermentation duration for safety and taste.
Flavor Profiles: What Sets Each Method Apart
Pickling creates tangy and crisp flavors through vinegar or brine fermentation, while Sandor Katz's method emphasizes natural lacto-fermentation for complex, probiotic-rich taste. The Katz approach often results in deeper, earthier flavors due to wild microbial activity and extended fermentation times.
- Traditional Pickling - Uses vinegar or salt brine to quickly develop bright, sharp, and acidic flavors.
- Sandor Katz Method - Employs wild fermentation, producing nuanced, savory, and umami-rich profiles enhanced by beneficial bacteria.
- Flavor Complexity - Katz's approach deepens complexity over time, while standard pickling focuses on immediate, consistent sourness.
Both methods offer unique artisanal pickling experiences, with flavor preferences guiding choice.
Health Benefits: Probiotics and Nutritional Value
Pickling and Sandor Katz's fermentation method both enhance artisanal pickles with probiotics, promoting gut health by increasing beneficial bacteria. Katz's method emphasizes natural lacto-fermentation, which preserves nutrients such as vitamins C and K while improving digestibility. Compared to traditional vinegar pickling, Katz's approach yields higher probiotic content and enhanced nutritional value, supporting immune function and overall wellness.
Challenges and Troubleshooting in Both Methods
| Pickling traditionally requires precise salt concentrations and temperature control to prevent harmful bacteria growth; common issues include mold formation and off-flavors. Sandor Katz's fermentation method emphasizes natural microbial activity, posing challenges such as inconsistent fermentation times and maintaining anaerobic conditions. Both methods demand diligent monitoring to troubleshoot signs of spoilage, ensuring safe and high-quality artisanal pickles. |
Related Important Terms
Katzian Fermentation
Katzian fermentation emphasizes wild lactic acid bacteria in spontaneous fermentation, resulting in complex, naturally fermented flavors without added vinegar, unlike traditional pickling methods that use brine and vinegar for preservation. This artisanal technique fosters probiotic-rich pickles with enhanced nutritional benefits, aligning with Sandor Katz's philosophy of preserving microbial diversity and promoting gut health.
Wild Brine Initiation
Wild Brine Initiation relies on the naturally occurring lactic acid bacteria indigenous to the raw vegetables and environment, enabling a spontaneous fermentation process without added starter cultures. In contrast, Sandor Katz's artisanal pickling method emphasizes controlled fermentation by maintaining optimal salt concentrations and temperature to promote beneficial microbial growth, resulting in consistent flavor development and food preservation.
Spontaneous Lacto-brining
Spontaneous lacto-brining in artisanal pickling, as popularized by Sandor Katz, leverages naturally occurring lactic acid bacteria to ferment vegetables without added cultures, enhancing flavor complexity and probiotic benefits. This method contrasts with standard pickling that often relies on vinegar or controlled starter cultures, resulting in distinctive tangy profiles and unique microbial diversity critical for gut health.
Controlled Starter Culture Pickling
Controlled starter culture pickling uses specific, selected strains of bacteria to ensure consistent fermentation, resulting in predictable flavor profiles and improved safety compared to the wild fermentation method popularized by Sandor Katz. This approach allows artisanal pickle makers to achieve uniform texture and acidity levels while minimizing the risk of spoilage or harmful microbial growth.
Microbial Terroir Expression
Pickling techniques influence microbial terroir expression by fostering unique environmental microbiota that shape flavor profiles; the Sandor Katz method emphasizes wild fermentation, allowing indigenous microbes to dominate and reflect local microbial diversity. Traditional pickling often relies on controlled brine conditions, which can limit microbial variability and result in less complex terroir-driven flavor nuances.
Airlock Jar Technique
The Airlock Jar Technique enhances artisanal pickling by using a one-way valve that releases gases while preventing oxygen exposure, reducing spoilage and promoting anaerobic fermentation. Compared to Sandor Katz's traditional open-air fermentation, this method offers greater control over the environment, resulting in consistent flavor and texture in pickles.
Brine Percentage Dial-In
The Sandor Katz method for artisanal pickles emphasizes precise brine percentage dial-in, typically using a 2-5% salt concentration to balance fermentation speed and flavor development, which contrasts with traditional pickling methods that often rely on fixed or less variable salt ratios. Adjusting brine salinity based on ambient temperature and vegetable water content ensures optimal microbial activity, enhancing texture and preserving nutritional value in hand-crafted pickles.
Fermentative Flavor Modulation
Pickling using the Sandor Katz method emphasizes natural fermentation through wild lactobacilli, enhancing depth and complexity in artisanal pickles by developing nuanced lactic acid profiles and diverse flavor compounds. Traditional brine-based pickling techniques modulate fermentative flavors primarily through controlled salt concentrations and temperature, resulting in a more predictable but less dynamic flavor spectrum.
pH Drop Tracking
Pickling using traditional methods often relies on visual cues and timing, whereas Sandor Katz's artisanal approach emphasizes precise pH drop tracking to ensure optimal fermentation and food safety. Monitoring pH levels consistently during Katz's method allows for controlled sourness development and prevents spoilage, providing a reliable indicator of fermentation progress.
Pickling vs Sandor Katz method for artisanal pickles. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com