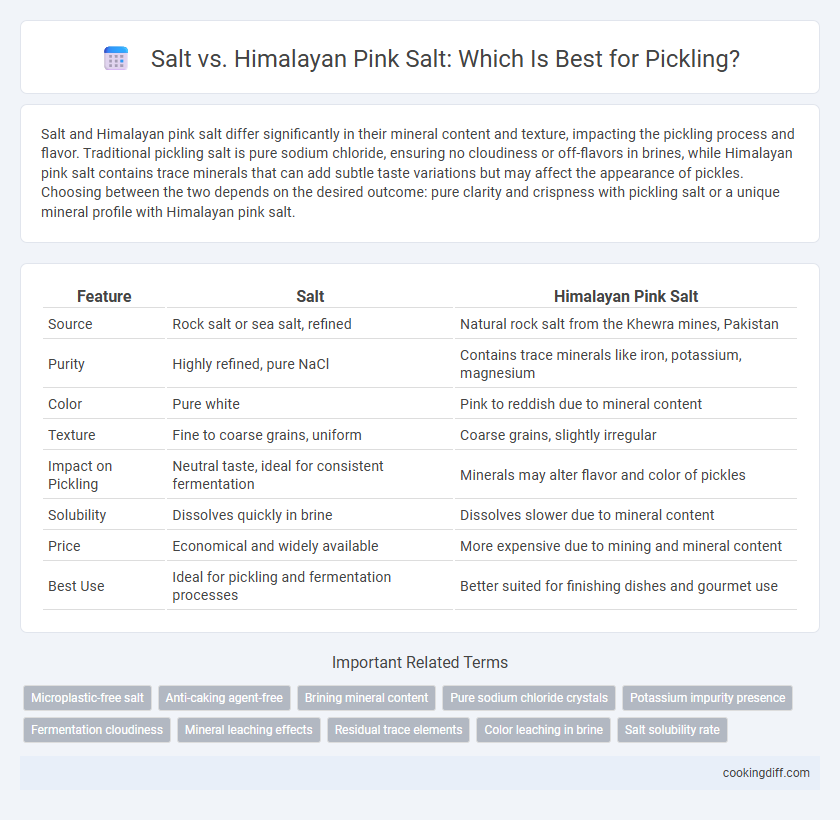
Salt and Himalayan pink salt differ significantly in their mineral content and texture, impacting the pickling process and flavor. Traditional pickling salt is pure sodium chloride, ensuring no cloudiness or off-flavors in brines, while Himalayan pink salt contains trace minerals that can add subtle taste variations but may affect the appearance of pickles. Choosing between the two depends on the desired outcome: pure clarity and crispness with pickling salt or a unique mineral profile with Himalayan pink salt.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Salt | Himalayan Pink Salt |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Rock salt or sea salt, refined | Natural rock salt from the Khewra mines, Pakistan |
| Purity | Highly refined, pure NaCl | Contains trace minerals like iron, potassium, magnesium |
| Color | Pure white | Pink to reddish due to mineral content |
| Texture | Fine to coarse grains, uniform | Coarse grains, slightly irregular |
| Impact on Pickling | Neutral taste, ideal for consistent fermentation | Minerals may alter flavor and color of pickles |
| Solubility | Dissolves quickly in brine | Dissolves slower due to mineral content |
| Price | Economical and widely available | More expensive due to mining and mineral content |
| Best Use | Ideal for pickling and fermentation processes | Better suited for finishing dishes and gourmet use |
Introduction: The Role of Salt in Pickling
| Salt is essential in pickling for its preservative qualities, inhibiting microbial growth and enhancing flavor. Regular pickling salt, typically pure sodium chloride, dissolves quickly, ensuring an even brine solution ideal for fermentation and preservation. Himalayan pink salt, while containing trace minerals like iron and magnesium, may affect the brine's clarity and flavor, making it less common for traditional pickling but still usable in artisanal recipes. |
What is Pickling Salt?
Pickling salt is a pure, fine-grained salt specifically designed for pickling and preserving foods without additives that can cloud brine or affect flavor. Unlike Himalayan pink salt, which contains trace minerals like iron oxide giving it a distinct color and taste, pickling salt is sodium chloride with no impurities, ensuring clear brine and consistent preservation results. Using pickling salt guarantees optimal texture and flavor retention in pickled vegetables because it dissolves quickly and evenly without introducing unwanted minerals.
Himalayan Pink Salt: Composition and Origins
Himalayan pink salt is primarily composed of sodium chloride with trace minerals such as iron oxide, which gives it its distinctive pink hue. Mined from ancient salt deposits in the Khewra Salt Mine of Pakistan, it is considered one of the purest forms of salt available.
Unlike regular pickling salt, Himalayan pink salt contains additional minerals like calcium, potassium, and magnesium that can influence the flavor and color of pickled foods. Its natural origin and mineral content make it a popular choice for artisanal pickling enthusiasts seeking unique taste profiles.
Key Differences Between Pickling Salt and Himalayan Pink Salt
Pickling salt is pure sodium chloride with no additives, ensuring it dissolves quickly and does not cloud the brine, making it ideal for preserving vegetables. Himalayan pink salt contains trace minerals like iron oxide, which can alter the flavor and color of pickled foods and may cause cloudiness in the brine. The key difference lies in purity and impact on pickling results, where pickling salt offers consistent preservation quality while Himalayan pink salt adds unique mineral content but with less predictable effects.
Purity and Additives: Why They Matter in Pickling
How does the purity of salt impact the quality of pickling?
Pickling requires salt free from additives to prevent cloudiness and off-flavors during fermentation. Himalayan pink salt contains trace minerals that may affect taste and color, while pure pickling salt ensures consistent preservation without impurities.
Effects on Brine Clarity and Color
Regular pickling salt dissolves completely creating a clear brine, which is essential for visual appeal and monitoring fermentation. Himalayan pink salt contains trace minerals that can impart color and cloudiness to the brine, affecting the final appearance of pickled goods.
- Pickling Salt Ensures Clear Brine - Pure sodium chloride in pickling salt dissolves without residue, maintaining transparent brine clarity.
- Himalayan Pink Salt Adds Coloration - Trace minerals like iron oxide cause a reddish tint and haze in the brine, altering the expected appearance.
- Visual Monitoring Impact - Clear brine from pickling salt facilitates easy observation of fermentation progress, unlike the cloudiness introduced by Himalayan salt.
Flavor Impact: Does Salt Type Change Taste?
Salt type can subtly influence the flavor profile of pickled foods, with Himalayan pink salt imparting trace minerals that may add a mild complexity. Traditional pickling salt delivers a clean, pure saltiness without additional flavors, making it ideal for recipes where saltiness is the main goal.
- Himalayan pink salt contains trace minerals - These minerals can slightly alter the taste and color of pickled products, offering a subtle difference compared to pure sodium chloride.
- Pickling salt is pure and additive-free - This ensures consistent saltiness without introducing other flavors, preserving the intended taste of the pickled item.
- Flavor impact depends on recipe sensitivity - In strongly flavored pickles, the difference in salt type is less noticeable, while mild brines reveal more flavor variations.
Mineral Content and Its Influence on Fermentation
Salt used in pickling varies significantly in mineral content, affecting fermentation outcomes. Himalayan pink salt contains trace minerals like iron and calcium that can influence bacterial activity differently than pure sodium chloride in traditional pickling salt.
- Sodium Chloride Purity - Pickling salt is typically 99.9% sodium chloride, ensuring consistent fermentation without unwanted minerals.
- Trace Minerals - Himalayan pink salt includes minerals such as magnesium and potassium, which may alter the fermentation process and flavor profile.
- Fermentation Control - Higher purity salts provide predictable fermentation rates, while mineral-rich salts can introduce variability in microbial growth.
Choosing the right salt depends on desired fermentation consistency and flavor complexity.
Cost and Availability Comparison
Regular pickling salt is typically more affordable and widely available compared to Himalayan pink salt, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale or frequent pickling projects. Standard pickling salt dissolves quickly and contains no additives, ensuring consistent preservation quality without altering flavor.
Himalayan pink salt tends to be more expensive and less accessible in most grocery stores, often found in specialty or health food shops. Its unique mineral content may influence taste, but the higher cost and limited availability can be a barrier for everyday pickling needs.
Related Important Terms
Microplastic-free salt
Himalayan pink salt is naturally free from microplastics, making it a safer choice for pickling compared to some commercial pickling salts that may contain microplastic contaminants due to processing or packaging. Using microplastic-free Himalayan pink salt ensures a purer fermentation process and reduces the risk of introducing harmful pollutants into preserved foods.
Anti-caking agent-free
Pickling salt is typically preferred for pickling due to its purity and absence of anti-caking agents, which prevents cloudiness in brines and ensures a clear fermentation process. Himalayan pink salt, while containing trace minerals and a distinct flavor, often includes natural impurities that can affect the clarity and preservation qualities essential for optimal pickling results.
Brining mineral content
Salt for pickling should ideally have a high sodium chloride content with minimal impurities to ensure proper brining and fermentation; table salt and pickling salt meet these criteria, whereas Himalayan Pink Salt contains trace minerals like iron and calcium that can alter brine clarity and flavor. The mineral content in Himalayan Pink Salt may introduce unwanted cloudiness and off-tastes in pickled products, making pure, additive-free pickling salt preferable for consistent brining results.
Pure sodium chloride crystals
Pickling salt and Himalayan pink salt both primarily contain sodium chloride, but pickling salt is composed of pure, fine sodium chloride crystals without additives or trace minerals, ensuring clarity and optimal preservation in pickling. Himalayan pink salt contains trace minerals that may alter flavor and color, making pickling salt the preferred choice for consistent acidity and brine clarity.
Potassium impurity presence
Himalayan pink salt contains trace levels of potassium impurities that can affect the fermentation process in pickling, potentially leading to softer or less crisp vegetables. In contrast, pure pickling salt, which typically lacks potassium and other minerals, ensures consistent preservation and optimal texture in pickled foods.
Fermentation cloudiness
Salt quality directly affects fermentation cloudiness in pickling, with regular pickling salt producing clearer brines due to its purity and absence of minerals. Himalayan Pink Salt often introduces additional minerals that can cause increased cloudiness and unpredictable fermentation results.
Mineral leaching effects
Salt used in pickling influences mineral leaching, with traditional pickling salt primarily composed of pure sodium chloride, minimizing impurities that could alter pickling brine chemistry. Himalayan pink salt contains trace minerals like iron, calcium, and magnesium, which may leach during pickling, potentially affecting the brine's pH and flavor profile, making it less predictable for consistent fermentation results.
Residual trace elements
Salt used for pickling mainly comprises sodium chloride, but Himalayan pink salt contains residual trace elements such as iron, magnesium, and calcium, which can slightly influence the fermentation process and flavor profile. These trace minerals may affect the clarity and texture of pickled products compared to pure pickling salt, which is typically free from impurities and additives.
Color leaching in brine
Himalayan pink salt contains trace minerals like iron oxide that can cause color leaching in pickling brine, potentially altering the appearance of pickled vegetables. In contrast, pure pickling salt is free of additives and minerals, ensuring clear brine and consistent pickling results without unwanted discoloration.
Salt vs Himalayan Pink Salt for pickling salt. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com