Poaching in cooking involves gently simmering food in liquid to preserve texture and moisture, whereas oil poaching uses hot oil to lock in moisture more effectively due to its higher temperature stability and fat content. Oil poaching creates a protective barrier that prevents moisture loss, resulting in juicier and more tender dishes. The choice between water or oil poaching significantly impacts the flavor profile and moisture retention of the final dish.
Table of Comparison
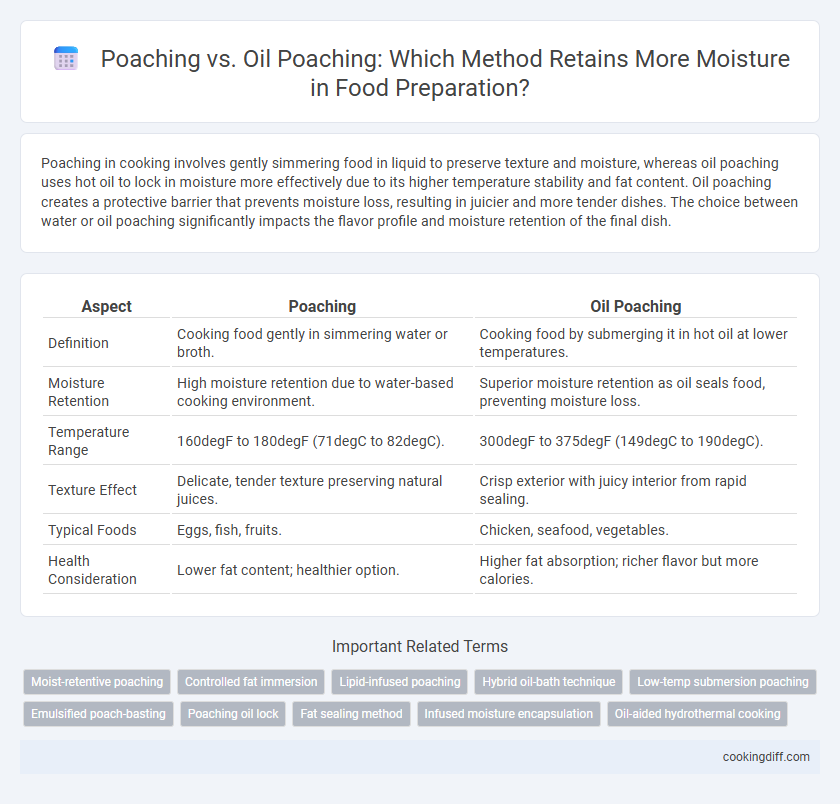
| Aspect | Poaching | Oil Poaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cooking food gently in simmering water or broth. | Cooking food by submerging it in hot oil at lower temperatures. |
| Moisture Retention | High moisture retention due to water-based cooking environment. | Superior moisture retention as oil seals food, preventing moisture loss. |
| Temperature Range | 160degF to 180degF (71degC to 82degC). | 300degF to 375degF (149degC to 190degC). |
| Texture Effect | Delicate, tender texture preserving natural juices. | Crisp exterior with juicy interior from rapid sealing. |
| Typical Foods | Eggs, fish, fruits. | Chicken, seafood, vegetables. |
| Health Consideration | Lower fat content; healthier option. | Higher fat absorption; richer flavor but more calories. |
Introduction to Poaching Methods
Poaching is a gentle cooking technique that uses low-temperature water or broth to retain moisture in delicate foods. Oil poaching involves submerging food in warm oil, which creates a different moisture retention dynamic due to oil's properties.
- Water Poaching - Uses simmering liquid to cook foods slowly while preserving natural juices and texture.
- Oil Poaching - Submerges food in oil at lower temperatures to maintain tenderness and enhance flavor without leaching moisture.
- Moisture Retention - Water poaching preserves moisture by cooking in a hydrated environment, whereas oil poaching forms a barrier that locks liquids inside the food.
Defining Classic Poaching
Classic poaching involves gently cooking food in a simmering liquid, usually water or broth, at low temperatures to preserve moisture and texture. Unlike oil poaching, which uses fats to retain moisture, classic poaching relies on the water-based environment to prevent drying out.
- Classic Poaching Definition - Cooking technique using simmering water or broth to gently cook food.
- Moisture Retention Method - Achieves moisture retention through slow, low-temperature cooking in liquid.
- Comparison to Oil Poaching - Oil poaching uses fats which can enhance flavor and moisture differently than water-based poaching.
What is Oil Poaching?
Oil poaching is a cooking technique where food is gently cooked in oil at low temperatures to preserve moisture and enhance texture. Unlike traditional poaching which uses water or broth, oil poaching uses fats to create a barrier, locking in natural juices and flavors.
- Moisture Retention - Oil poaching helps retain moisture by preventing evaporation during cooking.
- Temperature Control - The low temperature in oil poaching cooks food evenly without drying it out.
- Flavor Enhancement - The oil infuses food with rich flavors, improving overall taste compared to water-based poaching.
Oil poaching offers a superior method for moisture retention and flavor preservation in various culinary preparations.
Comparing Cooking Temperatures
Poaching typically involves cooking food gently in water or broth at temperatures between 160degF and 180degF, which helps retain moisture without breaking down delicate proteins. Oil poaching uses higher temperatures, generally ranging from 180degF to 210degF, allowing for better moisture retention due to the oil's ability to evenly surround and insulate the food. Comparing cooking temperatures, oil poaching maintains moisture more effectively by minimizing water loss and sealing in natural juices compared to traditional poaching methods.
Moisture Retention: The Science Explained
| Poaching | Gently cooking food in liquid below boiling point, preserving cellular structure and moisture by preventing evaporation. |
| Oil Poaching | Cooking food submerged in oil at lower temperatures than frying, creating a barrier that minimizes moisture loss and enhances juiciness. |
| Moisture Retention | Both methods maintain moisture through heat control, but oil poaching provides superior retention due to oil's insulating properties that reduce water molecule escape. |
Flavor Impact: Oil vs. Water
How does poaching with oil compare to water-based poaching in terms of flavor impact? Oil poaching imparts a richer, more intense flavor due to the fat's ability to carry and enhance aromatic compounds, while water poaching preserves the natural taste of the food with a lighter, cleaner profile. The choice between oil and water poaching significantly influences the final dish's flavor complexity and moisture retention.
Nutritional Differences Between Methods
Poaching retains more water-soluble nutrients like vitamin B and folate due to its gentle cooking in water, preserving the natural moisture of foods. Oil poaching, while effective in moisture retention, enhances the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E, and K by cooking food in healthy oils like olive or avocado oil. The choice between poaching methods impacts the nutritional profile of the dish, with water poaching favoring hydrophilic nutrients and oil poaching benefiting lipophilic vitamins.
Best Foods for Each Poaching Technique
Traditional poaching involves gently cooking delicate foods like eggs, fish, and fruit in simmering water to retain moisture and subtle flavors. Oil poaching, using oils such as olive or grapeseed, is ideal for items like chicken or vegetables, providing a richer texture and enhanced moisture retention.
Best foods for water poaching include eggs, salmon, and stone fruits, as the method preserves their tender consistency without adding fat. Oil poaching suits denser foods such as chicken breasts, duck, or root vegetables, locking in moisture while infusing flavors from the oil. Both techniques offer distinct moisture benefits tailored to different types of foods and desired culinary outcomes.
Common Mistakes in Moisture Retention
Many individuals confuse poaching with oil poaching, leading to common mistakes in moisture retention during cooking. Poaching involves cooking food gently in water or broth, which helps preserve moisture through low-temperature steaming.
Oil poaching uses warm oil to cook food slowly, creating a moisture barrier that enhances juiciness but requires precise temperature control to avoid overcooking. Misunderstanding these methods often results in dry or greasy dishes, undermining the intended moisture retention benefits.
Related Important Terms
Moist-retentive poaching
Moist-retentive poaching utilizes steam or a tightly sealed environment to preserve the natural moisture and texture of foods, contrasting with oil poaching that relies on fat for moisture retention but may add caloric content. This technique enhances flavor without compromising nutrient density, making it ideal for delicate proteins and vegetables requiring gentle cooking.
Controlled fat immersion
Controlled fat immersion during oil poaching enhances moisture retention by creating a protective barrier around the food, preventing water loss and preserving texture more effectively than traditional dry poaching methods. This technique exploits the thermal stability of fats, optimizing heat transfer while maintaining juiciness and flavor.
Lipid-infused poaching
Lipid-infused poaching enhances moisture retention by incorporating oil-based fats that form a protective barrier around food, reducing water loss more effectively than traditional water-based poaching methods. This technique preserves texture and flavor by minimizing evaporation and preventing protein denaturation, making it superior for cooking delicate items such as fish and poultry.
Hybrid oil-bath technique
The hybrid oil-bath technique combines traditional poaching with controlled oil poaching to maximize moisture retention in foods, resulting in tender and flavorful outcomes. This method leverages the gentle heat transfer of poaching and the fat barrier of oil poaching, effectively minimizing water loss and enhancing texture.
Low-temp submersion poaching
Low-temp submersion poaching preserves moisture by gently cooking food in water or flavored liquid at temperatures below boiling, minimizing protein denaturation and moisture loss. Unlike oil poaching, which can impart additional fat and alter texture, water-based poaching maintains the natural juiciness and integrity of ingredients through controlled low-temperature heat transfer.
Emulsified poach-basting
Emulsified poach-basting enhances moisture retention by combining poaching's gentle heat with the rich fat of oil poaching, creating a protective barrier that minimizes moisture loss in proteins. This technique leverages the emulsified fat-water mixture to maintain juiciness and tenderness, outperforming traditional poaching methods in flavor infusion and texture preservation.
Poaching oil lock
Poaching locks moisture more effectively than oil poaching by gently cooking food at lower temperatures in a liquid, which prevents moisture loss and preserves texture. The oil used in poaching creates a protective barrier around the food, enhancing juiciness and nutrient retention compared to traditional dry cooking methods.
Fat sealing method
Poaching retains moisture by gently cooking food in liquid, while oil poaching uses fat sealing to create a protective barrier that prevents moisture loss and enhances texture. The fat sealing method in oil poaching locks in juices more effectively than water-based poaching, resulting in improved flavor and tenderness.
Infused moisture encapsulation
Infused moisture encapsulation in oil poaching enhances moisture retention by creating a protective lipid barrier that reduces water loss during cooking, unlike traditional poaching which relies solely on water-based heat transfer. This technique not only preserves texture and juiciness but also infuses additional nutrients and flavors, improving the overall sensory and nutritional profile of the food.
Poaching vs Oil Poaching for moisture retention. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com