Poaching refers to the illegal hunting or capturing of wildlife, often threatening endangered species and disrupting ecosystems. Tea poaching, in contrast, involves gently simmering tea leaves in hot water to extract aromatic liquids without boiling, preserving delicate flavors and enhancing the beverage's quality. Understanding the distinction between wildlife poaching and tea poaching highlights the importance of context in terminology related to sustainability and culinary arts.
Table of Comparison
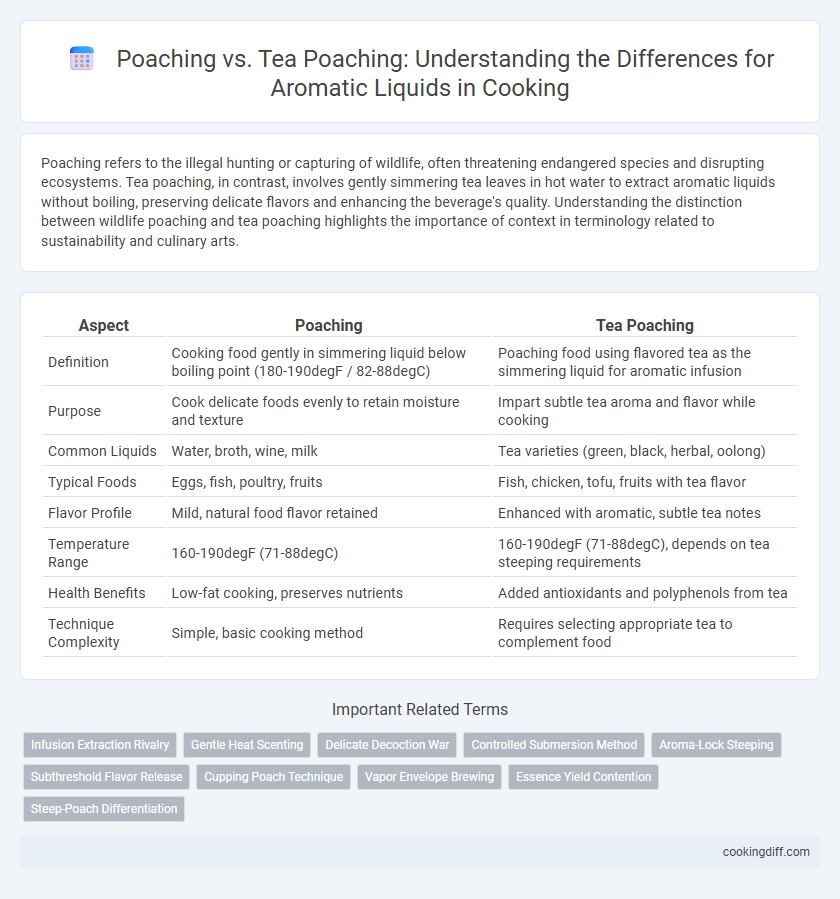
| Aspect | Poaching | Tea Poaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cooking food gently in simmering liquid below boiling point (180-190degF / 82-88degC) | Poaching food using flavored tea as the simmering liquid for aromatic infusion |
| Purpose | Cook delicate foods evenly to retain moisture and texture | Impart subtle tea aroma and flavor while cooking |
| Common Liquids | Water, broth, wine, milk | Tea varieties (green, black, herbal, oolong) |
| Typical Foods | Eggs, fish, poultry, fruits | Fish, chicken, tofu, fruits with tea flavor |
| Flavor Profile | Mild, natural food flavor retained | Enhanced with aromatic, subtle tea notes |
| Temperature Range | 160-190degF (71-88degC) | 160-190degF (71-88degC), depends on tea steeping requirements |
| Health Benefits | Low-fat cooking, preserves nutrients | Added antioxidants and polyphenols from tea |
| Technique Complexity | Simple, basic cooking method | Requires selecting appropriate tea to complement food |
Understanding Traditional Poaching: Classic Techniques
Traditional poaching involves gently cooking delicate foods like fish or eggs in simmering liquid, preserving their texture and flavor through controlled, low-temperature heat. This classic technique relies on water, broth, or wine as the cooking medium, ensuring even heat distribution without boiling.
Tea poaching, on the other hand, infuses aromatic liquids with delicate tea flavors, using brewed tea as the poaching liquid to impart subtle herbal notes to the food. This method enhances the sensory profile of dishes by combining gentle cooking with unique tea aromas.
What Is Tea Poaching? An Aromatic Alternative
What is tea poaching and how does it differ from traditional poaching methods? Tea poaching involves gently simmering ingredients in aromatic teas, infusing dishes with unique flavors and subtle fragrances. This method provides a delicate alternative to conventional poaching liquids like water or broth, enhancing the taste profile without overpowering the natural ingredients.
Comparing Aromatic Bases: Broths, Stocks, and Teas
| Poaching Type | Aromatic Base | Flavor Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Poaching (broths & stocks) | Broths and stocks made from simmered bones, vegetables, and herbs | Rich, savory, layered with umami and depth from slow extraction of gelatin and minerals |
| Tea Poaching | Infused aromatic teas, including green, black, and herbal varieties | Light, fragrant, and nuanced with floral, earthy, or grassy notes dependent on tea type |
Flavor Infusion: How Poaching and Tea Poaching Differ
Poaching involves gently cooking food in a flavorful liquid to infuse moisture and subtle taste, while tea poaching specifically uses brewed tea as the poaching medium, imparting unique aromatic compounds. The choice between water-based poaching liquids and tea affects the depth and type of flavor penetration in the food.
- Flavor source - Poaching uses broths or seasoned liquids, whereas tea poaching utilizes the distinct aromas and tannins from brewed tea leaves.
- Infusion intensity - Tea poaching typically imparts a more delicate, nuanced flavor profile compared to traditional poaching liquids.
- Application - Tea poaching is ideal for light proteins and desserts, enhancing complexity without overwhelming natural tastes.
Ingredients Best Suited for Poaching vs Tea Poaching
Poaching typically involves gently cooking ingredients like fruits, poultry, or fish in a simmering liquid composed of water, wine, stock, or aromatic herbs to enhance flavor without overpowering the main ingredient. Tea poaching uses brewed tea as the cooking liquid, imparting subtle tannins and nuanced flavors ideal for delicate proteins and fruits that benefit from a fragrant, slightly bitter infusion.
Ingredients best suited for traditional poaching include chicken breasts, pears, and salmon, as their mild flavors absorb complements from stocks, wine, or herbal infusions. Black teas, green teas, and flavored blends infused with spices such as cinnamon or star anise excel for tea poaching, pairing well with ingredients like duck, tofu, or citrus fruits. Both methods rely on low-temperature cooking to maintain texture while infusing complex aromas specific to the chosen liquid.
Health Benefits: Nutrient Retention in Each Method
Poaching food gently in water preserves water-soluble vitamins like B and C better than high-heat cooking methods, supporting nutrient retention and overall health benefits. This method minimizes nutrient loss, making it ideal for delicate proteins and vegetables.
Tea poaching, using aromatic liquids infused with herbs and spices, not only enhances flavor but also contributes antioxidants and phytochemicals beneficial for wellness. The combined nutrient retention from low heat and infusion of health-promoting compounds makes tea poaching a flavorful and nutritious cooking technique.
Texture and Appearance: Effects of Each Poaching Approach
Poaching food in water or broth produces a tender texture while maintaining a moist appearance. Tea poaching with aromatic liquids imparts subtle flavors and can create a more delicate, slightly glazed surface on the food.
- Moisture retention - Traditional poaching preserves natural juiciness without altering the food's external texture significantly.
- Flavor infusion - Tea poaching allows aromatic compounds to penetrate, enhancing complexity and surface sheen.
- Visual appeal - Poaching results in a uniform matte finish, while tea poaching often leaves a gentle gloss and faint color tint.
Choosing between methods depends on desired texture and appearance tailored by the cooking liquid's characteristics.
Pairing Proteins and Produce: Choosing the Right Method
Poaching, a gentle cooking technique using simmering liquid, is ideal for delicate proteins like fish and chicken, preserving moisture and tenderness. Tea poaching infuses aromatic compounds from tea leaves, enhancing subtle flavors and complementing produce such as citrus or ginger for a unique taste profile. Selecting the right poaching method depends on the interplay between protein texture and desired aromatics, ensuring a balanced pairing with complementary fruits or vegetables.
Aromatic Liquids: Customizing Flavors in Poaching
Poaching aromatic liquids involves gently simmering ingredients in flavored broths to infuse delicate flavors into proteins or fruits without overpowering their natural taste. Tea poaching specifically utilizes brewed tea varieties as the poaching liquid, offering unique, customizable flavor profiles that can range from floral to smoky depending on the type of tea used. This method enhances dishes by marrying the subtle aromas of tea with the inherent qualities of the food, creating a layered and aromatic culinary experience.
Related Important Terms
Infusion Extraction Rivalry
Poaching involves simmering food gently in liquid below boiling point to infuse flavors without agitation, preserving delicate textures, while tea poaching specifically targets aromatic extraction by steeping tea leaves in hot water to release essential oils and compounds. The rivalry between these infusion techniques hinges on balancing temperature control and immersion time to optimize flavor extraction in culinary and beverage applications.
Gentle Heat Scenting
Poaching relies on submersion in hot water to cook ingredients gently, while tea poaching uses simmering aromatic liquids infused with tea leaves to impart delicate flavors through gentle heat scenting. This method preserves the integrity of flavors by slowly releasing fragrant compounds without the harshness of direct boiling, enhancing the aromatic profile of the dish.
Delicate Decoction War
Poaching, typically associated with illegal wildlife hunting, contrasts sharply with tea poaching, a culinary technique involving submersion of tea leaves in water below boiling point to preserve delicate flavors and aromatic compounds. The Delicate Decoction War highlights the precise temperature control in tea poaching, essential for extracting subtle essences without bitterness, unlike the aggressive methods implied by conventional poaching practices.
Controlled Submersion Method
The Controlled Submersion Method in tea poaching involves carefully regulating water temperature and immersion time to extract aromatic liquids without degrading delicate flavors, contrasting sharply with wildlife poaching's illegal and destructive exploitation of animal species. This precise technique enhances the infusion of essential oils and volatile compounds from tea leaves, ensuring a balanced and fragrant brew while maintaining the integrity of botanical materials.
Aroma-Lock Steeping
Poaching in culinary terms involves gently cooking ingredients in liquid, but Tea Poaching specifically targets the extraction of aromatic compounds, preserving delicate flavors through controlled temperature and immersion times. Aroma-Lock Steeping enhances this process by using specialized temperature regulation and infusion techniques, maximizing the retention of volatile aromatics essential for rich, fragrant teas and aromatic liquids.
Subthreshold Flavor Release
Poaching in culinary terms involves simmering ingredients gently to preserve texture and extract subtle flavors, while tea poaching specifically targets subthreshold flavor release by infusing aromatic compounds at controlled temperatures without bitterness. This method enhances delicate liquid aromas in tea-based infusions, optimizing flavor profiles through precise temperature regulation and extraction timing.
Cupping Poach Technique
The Cupping Poach Technique in tea preparation enhances the extraction of aromatic liquids by gently steeping tea leaves at controlled temperatures, preserving volatile oils and maximizing flavor profiles. Unlike wildlife poaching, tea poaching emphasizes precision and sensory evaluation, essential for quality cupping assessments in specialty tea tasting.
Vapor Envelope Brewing
Poaching and tea poaching differ fundamentally in application and technique, with tea poaching utilizing gentle vapor envelope brewing to preserve delicate aromatic liquids and enhance flavor extraction without direct contact with boiling water. Vapor envelope brewing creates a controlled steam infusion that maintains optimal temperature, preventing bitterness while maximizing the aromatic profile unique to high-quality teas and infusions.
Essence Yield Contention
Poaching in general often involves submerging materials at moderate temperatures to extract flavors, but tea poaching specifically targets aromatic liquids using delicate heat control to preserve volatile essences. The key contention lies in the essence yield; tea poaching typically achieves higher purity and concentration of aromatic compounds compared to traditional poaching methods, which may dilute or degrade these fragile essences due to broader temperature ranges and longer exposure times.
Poaching vs Tea Poaching for aromatic liquids. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com