Poaching poultry involves gently simmering meat in water or broth to maintain tenderness and moisture, whereas tea poaching uses brewed tea as the cooking liquid, infusing subtle flavors and antioxidants into the meat. Tea poaching imparts unique aromatic notes and can enhance the poultry's taste profile while keeping it juicy and tender. This method is a flavorful alternative to traditional water-based poaching, combining culinary technique with aromatic infusion.
Table of Comparison
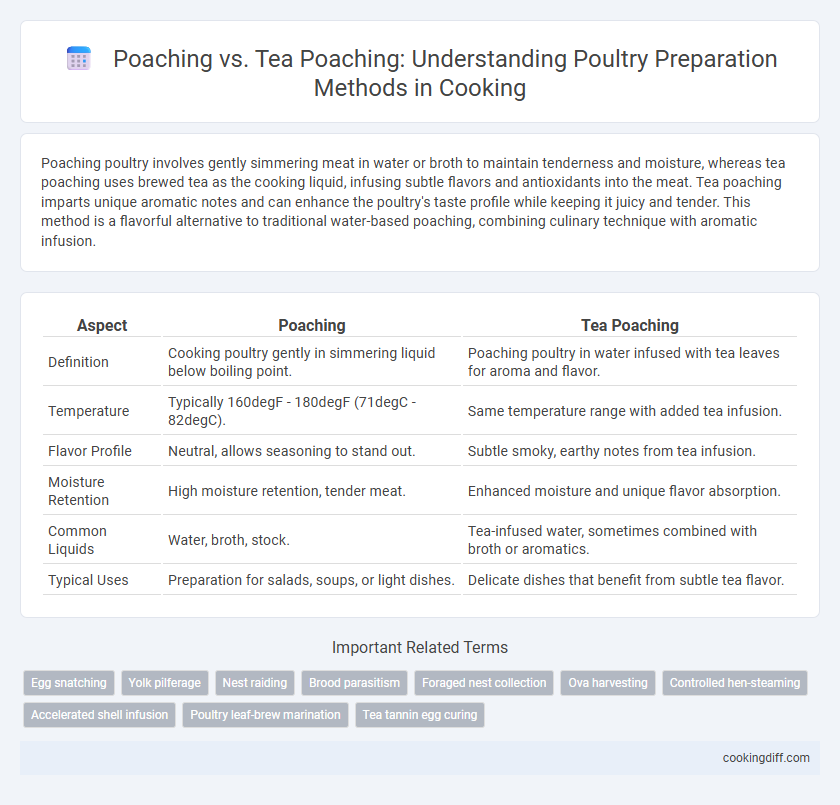
| Aspect | Poaching | Tea Poaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cooking poultry gently in simmering liquid below boiling point. | Poaching poultry in water infused with tea leaves for aroma and flavor. |
| Temperature | Typically 160degF - 180degF (71degC - 82degC). | Same temperature range with added tea infusion. |
| Flavor Profile | Neutral, allows seasoning to stand out. | Subtle smoky, earthy notes from tea infusion. |
| Moisture Retention | High moisture retention, tender meat. | Enhanced moisture and unique flavor absorption. |
| Common Liquids | Water, broth, stock. | Tea-infused water, sometimes combined with broth or aromatics. |
| Typical Uses | Preparation for salads, soups, or light dishes. | Delicate dishes that benefit from subtle tea flavor. |
Understanding Traditional Poaching for Poultry
Traditional poaching for poultry involves gently cooking the bird in simmering water to retain moisture and tenderness without overcooking. This method differs from tea poaching, which infuses poultry with delicate flavors from tea leaves during the cooking process.
- Traditional Poaching - Uses water or broth at a low temperature to cook poultry evenly and preserve juiciness.
- Tea Poaching - Incorporates tea leaves or brewed tea to impart subtle aromatic flavors into the poultry.
- Cooking Temperature - Both methods rely on temperatures below boiling point to avoid toughening the meat.
What is Tea Poaching?
| Poaching | Poaching is a gentle cooking method using simmering liquid, preserving moisture and texture in poultry by cooking it just below boiling point at 160-180degF (71-82degC). |
| Tea Poaching | Tea poaching infuses poultry with subtle flavors by cooking it in a mixture of brewed tea, water, and aromatics, combining moisture retention with delicate, fragrant notes. |
| Difference | While traditional poaching uses plain water or broth, tea poaching introduces antioxidants and tannins from tea, enhancing the meat's flavor profile and tenderness uniquely. |
Flavor Profiles: Water vs Tea-Poached Poultry
Poaching poultry in water results in a delicate, natural flavor that highlights the meat's original taste. Tea-poaching infuses the poultry with subtle aromatic notes from the tea, adding complexity and depth to the flavor profile.
- Water-poached poultry maintains purity - The absence of additional flavor agents allows the natural taste of the poultry to shine through.
- Tea-poached poultry enhances aroma - Tea imparts floral, earthy, or smoky elements depending on the variety used.
- Flavor complexity differs significantly - Water poaching emphasizes simplicity, while tea poaching creates layered and nuanced taste experiences.
Health Benefits: Tea Poaching Compared to Standard Poaching
Tea poaching enhances poultry's flavor while infusing antioxidants and polyphenols from tea leaves, which standard poaching with water lacks. This method reduces fat absorption and preserves more nutrients, promoting a healthier protein option.
Tea poaching also imparts subtle antimicrobial properties that may reduce bacterial contamination risks compared to traditional water poaching. The presence of catechins in green or black tea supports immune health and may improve digestion when infused in poultry dishes. Choosing tea-poached poultry offers both a gourmet experience and potential health advantages over standard poaching techniques.
Step-by-Step Guide to Classic Poaching Poultry
What distinguishes classic poultry poaching from tea poaching techniques? Classic poaching involves gently simmering poultry in a clear, seasoned liquid to retain moisture and tenderness. In contrast, tea poaching infuses poultry with subtle floral and tannin flavors by simmering it in brewed tea, offering a unique taste experience.
How to Tea Poach Poultry: Essential Tips
Tea poaching poultry infuses the meat with delicate flavors while keeping it moist and tender, achieved by gently simmering the poultry in a brewed tea mixture. Use aromatic teas like green or jasmine combined with herbs and spices to enhance the flavor profile without overpowering the natural taste of the poultry. Maintain a low poaching temperature around 160-180degF (71-82degC) and avoid boiling to prevent toughening the meat and ensure a succulent result.
Ingredient Selection: Broths, Teas, and Aromatics
Poaching poultry typically involves simmering the meat in broths enriched with herbs and vegetables to enhance flavor and moisture. Tea poaching uses brewed teas as a flavorful, antioxidant-rich liquid that imparts subtle, aromatic notes to the poultry.
- Broth Selection - Broths often include chicken stock, vegetables, and aromatics like garlic and thyme to deepen the savory profile of the poultry.
- Tea Varieties - Common teas used include green, black, and oolong, each contributing unique flavors such as earthiness, floral tones, or slight bitterness.
- Aromatic Additions - Combining ingredients like ginger, star anise, and citrus peels enhances the complexity and fragrance of the poaching liquid.
Choosing the right combination of broths, teas, and aromatics defines the flavor character and tenderness of poached poultry.
Texture and Moisture: Comparing Results
Poaching poultry gently cooks the meat in simmering water, preserving moisture and resulting in a tender, juicy texture. Tea poaching uses brewed tea as the cooking liquid, infusing subtle flavors while maintaining similar moisture retention and tenderness. Both methods prevent drying out poultry, but tea poaching adds unique aromatic nuances without compromising the soft texture achieved through traditional poaching.
Culinary Uses for Poached vs Tea-Poached Poultry
Poaching poultry involves gently cooking the meat in simmering liquid, preserving its tenderness and moisture, making it ideal for delicate dishes and salads. This method allows for easy infusion of herbs and spices directly into the meat without overpowering its natural flavor.
Tea poaching infuses poultry with aromatic notes from brews like green or black tea, adding a subtle complexity suited for Asian-inspired recipes and light, fragrant meals. The antioxidants and tannins in tea also contribute to a unique taste profile and a tender texture distinct from traditional poaching liquids.
Related Important Terms
Egg snatching
Poaching, referring to illegal hunting or capturing of wildlife, contrasts sharply with tea poaching, a gentle cooking technique for poultry. Egg snatching, an illegal activity linked to wildlife poaching, threatens bird populations and biodiversity, unlike culinary tea poaching that preserves the quality and tenderness of poultry eggs during cooking.
Yolk pilferage
Yolk pilferage in poultry poaching occurs when eggs are incubated under conditions encouraging parasitic eggs to hatch, undermining primary breeders' success, while tea poaching, a cooking method involving gentle simmering of eggs in flavored water, poses no risk of yolk pilferage or reproductive interference. Understanding these distinctions clarifies that biological poaching disrupts poultry breeding cycles, whereas culinary tea poaching solely affects egg texture and flavor without impacting yolk integrity.
Nest raiding
Poaching in the context of wildlife involves illegal hunting and nest raiding, significantly threatening bird populations by destroying eggs and young chicks, whereas tea poaching refers to a cooking method for poultry that gently simmers meat to retain moisture and tenderness. Nest raiding, a critical aspect of wildlife poaching, disrupts breeding cycles and accelerates population decline, contrasting with poultry tea poaching, which is a culinary technique unrelated to ecological harm.
Brood parasitism
Poaching in the context of illegal wildlife hunting involves the unauthorized taking of animals, whereas tea poaching for poultry refers to a gentle cooking technique that preserves moisture and texture. Brood parasitism, a natural occurrence where certain bird species lay eggs in the nests of others, shares a conceptual link with poaching in that both involve exploitation--one by humans for illegal gain, the other by birds to outsource parental care.
Foraged nest collection
Poaching in wildlife refers to the illegal hunting or capturing of animals, often targeting species nesting in the wild, while tea poaching for poultry involves gently cooking birds in simmering water or broth to preserve moisture and tenderness. Foraged nest collection in poaching disrupts natural reproductive cycles by removing eggs or chicks, posing significant threats to biodiversity and species survival.
Ova harvesting
Poaching in the context of ova harvesting involves the illicit collection of eggs directly from wild birds, leading to severe declines in avian populations and biodiversity. Tea poaching for poultry, a culinary technique where eggs are gently cooked in flavored broth, has no connection to illegal wildlife activities and is a sustainable method for preparing eggs.
Controlled hen-steaming
Controlled hen-steaming in tea poaching gently cooks poultry by submerging it in hot, infused liquid at precise temperatures to retain moisture and enhance flavor. Unlike traditional poaching, this method prevents overcooking and maintains the poultry's delicate texture through regulated steam infusion.
Accelerated shell infusion
Poaching poultry in water enables accelerated shell infusion by allowing heat and flavors to penetrate the meat steadily, unlike tea poaching which infuses subtle tannins but at a slower rate. Accelerated shell infusion during traditional water poaching enhances moisture retention and tenderness more efficiently compared to the delicate, slower flavor absorption characteristic of tea poaching methods.
Poultry leaf-brew marination
Poaching poultry involves gently cooking meat in simmering liquid, preserving juiciness and tenderness, while tea poaching adds a unique flavor profile by infusing antioxidants and subtle tannins from tea leaves into the poultry. Utilizing poultry leaf-brew marination before tea poaching enhances moisture retention and imparts a delicate herbal aroma, elevating both taste and texture.
Poaching vs Tea poaching for poultry Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com