Poaching in the context of wildlife refers to the illegal hunting or capturing of animals, often threatening endangered species and disrupting ecosystems. Wine poaching for fruits involves gently cooking fruits in simmering wine with spices to enhance flavor and texture, a culinary technique used in desserts. While both involve the term "poaching," one addresses unlawful environmental harm, whereas the other describes a harmless and traditional cooking method.
Table of Comparison
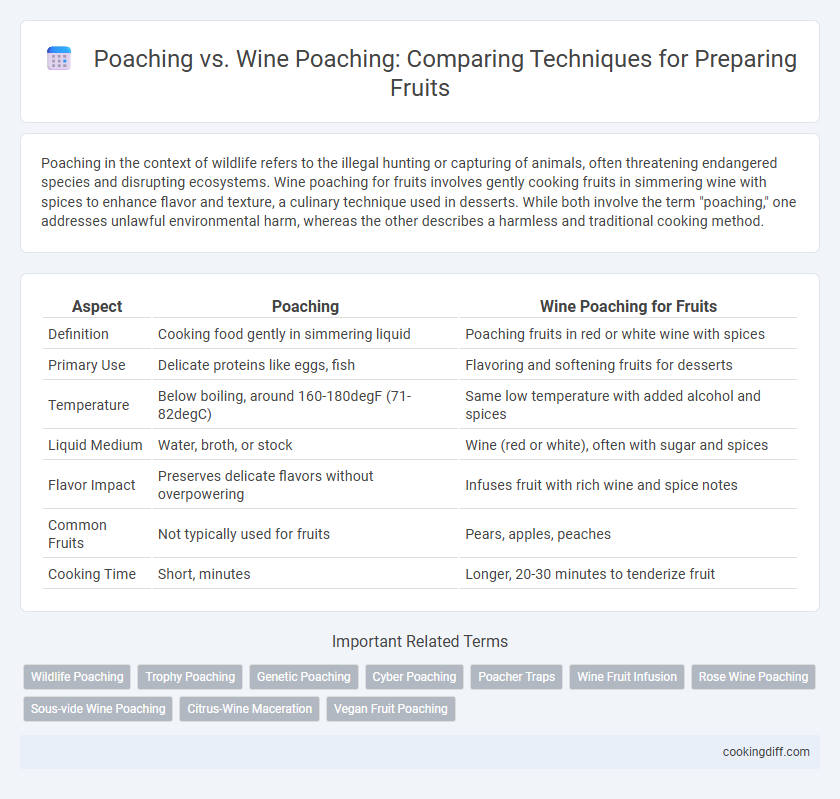
| Aspect | Poaching | Wine Poaching for Fruits |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cooking food gently in simmering liquid | Poaching fruits in red or white wine with spices |
| Primary Use | Delicate proteins like eggs, fish | Flavoring and softening fruits for desserts |
| Temperature | Below boiling, around 160-180degF (71-82degC) | Same low temperature with added alcohol and spices |
| Liquid Medium | Water, broth, or stock | Wine (red or white), often with sugar and spices |
| Flavor Impact | Preserves delicate flavors without overpowering | Infuses fruit with rich wine and spice notes |
| Common Fruits | Not typically used for fruits | Pears, apples, peaches |
| Cooking Time | Short, minutes | Longer, 20-30 minutes to tenderize fruit |
Introduction to Fruit Poaching Techniques
Fruit poaching is a gentle cooking technique that involves simmering fruits in flavored liquids such as wine, syrup, or juice to enhance their natural sweetness and texture. Unlike illegal wildlife poaching, which involves the unlawful hunting of protected animals, fruit poaching is a culinary method used to create delicate desserts. Key techniques include controlling temperature to prevent fruit from breaking down and infusing the fruit with aromatics like spices or citrus zest for added flavor complexity.
What is Traditional Fruit Poaching?
Traditional fruit poaching is a gentle cooking method where whole or sliced fruits are simmered in a flavored liquid, often water or syrup, to enhance their natural taste and texture. This contrasts with poaching in culinary terms, which typically involves cooking delicate proteins like eggs or fish in simmering liquid without boiling.
- Temperature Control - Traditional fruit poaching uses low heat to avoid breaking down the fruit's structure, preserving its shape and firmness.
- Poaching Liquid - The liquid can be simple syrup, spiced water, or wine, but the focus remains on infusing the fruit with subtle flavors.
- Purpose - The technique softens fruit gently while enhancing flavor and maintaining presentation, differing from other poaching applications centered on proteins.
Understanding Wine Poaching for Fruits
Poaching typically refers to illegal hunting or capturing of wild animals, posing significant threats to biodiversity and wildlife populations. Wine poaching for fruits, however, is a culinary technique where fruits are gently simmered in wine to infuse flavors and maintain texture.
Understanding wine poaching involves selecting suitable fruits like pears or peaches, combined with aromatic spices and quality wine such as red or white varieties. This method enhances the fruit's natural sweetness while creating a sophisticated dessert or garnish.
Key Differences Between Water and Wine Poaching
Water poaching involves submerging fruits in simmering water, preserving their natural flavors and textures without added sweetness or complexity. Wine poaching infuses fruits with the rich aromas and tannins of wine, enhancing taste while softening the fruit through slow cooking.
Water poaching is ideal for delicate fruits where subtlety is desired, maintaining a clean, pure flavor profile. Wine poaching introduces depth and warmth, often incorporating spices and sugar, making it suitable for desserts requiring richer, more robust flavors.
Flavor Profiles: Water Poaching vs. Wine Poaching
Water poaching preserves the natural fruit flavors with a subtle sweetness, while wine poaching infuses complex, aromatic notes from the alcohol and spices. The choice between these methods significantly impacts the depth and intensity of the fruit's final flavor profile.
- Water Poaching - Enhances the fruit's inherent taste by gently cooking in a neutral liquid.
- Wine Poaching - Adds layers of rich, spiced flavors derived from red or white wine and complementary ingredients.
- Flavor Impact - Wine poaching creates a more robust and nuanced profile compared to the clean, delicate finish of water poaching.
Selecting between water or wine poaching depends on the desired complexity and character of the finished fruit dish.
Best Fruits for Each Poaching Method
| Poaching Method | Best Fruits | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Poaching | Pears, apples, quinces | Fruits maintain firm texture and absorb flavors from spiced syrup or wine |
| Wine Poaching | Peaches, plums, figs | Fruits develop deep color and enhanced complexity from red or white wine infusion |
Step-by-Step Guide: Water Poaching Fruits
Water poaching fruits involves gently simmering fruit in a flavored liquid below boiling point to maintain texture and enhance flavor without alcohol content. This method is distinct from wine poaching, which introduces wine to infuse the fruit with deeper, robust notes and a richer aroma.
- Preparation - Select ripe, firm fruits and prepare a water-based poaching liquid with sugar, spices, and citrus for balanced flavor.
- Simmering - Cook fruits gently in the simmering water, typically between 160degF and 185degF, to soften without disintegration.
- Serving - Cool the poached fruits in the liquid to retain moisture, then serve chilled or warm for a refreshing or comforting dessert.
Step-by-Step Guide: Wine Poaching Fruits
What is the step-by-step process for wine poaching fruits compared to traditional poaching methods? Wine poaching involves simmering fruits in a mixture of wine, sugar, and spices to infuse rich flavors and achieve a tender texture. This method differs from classic poaching as it uses alcohol and aromatics, enhancing the fruit's natural sweetness and complexity.
Tips for Enhancing Fruit Poaching Results
Poaching fruit requires gentle simmering in flavored liquid such as wine, juice, or spiced syrup to enhance natural sweetness and maintain texture. For optimal results, choose ripe but firm fruits like pears or peaches, and carefully control the cooking temperature to prevent over-softening. Adding complementary spices such as cinnamon, vanilla, or star anise boosts the aroma and depth of flavor in the poached fruit dish.
Related Important Terms
Wildlife Poaching
Wildlife poaching primarily targets animals for illegal trade in ivory, horns, and skins, severely threatening biodiversity and ecosystem balance. Unlike wine poaching, which gently infuses fruit flavors by simmering in alcohol, wildlife poaching devastates species populations and disrupts natural habitats.
Trophy Poaching
Trophy poaching involves illegally hunting and killing wildlife for valuable animal parts like tusks or antlers, driving endangered species toward extinction, unlike wine poaching which gently simmers fruits in wine to enhance flavor. The ecological impact of trophy poaching is devastating, threatening biodiversity and disrupting ecosystems, while wine poaching is a culinary technique with no harm to wildlife.
Genetic Poaching
Genetic poaching involves the unauthorized extraction and use of genetic material from wild plant populations, threatening biodiversity and conservation efforts, unlike wine poaching which refers to the gentle simmering of fruits to enhance flavor in culinary practices. The exploitation of wild fruit genetics without consent poses significant risks to ecosystems and agricultural sustainability.
Cyber Poaching
Cyber poaching involves the illegal harvesting or theft of digital data, often targeting sensitive information or intellectual property, contrasting with traditional fruit poaching in wine-making that gently infuses flavors by cooking fruits in wine. While fruit poaching enhances sensory qualities through controlled heat and alcohol, cyber poaching exploits technological vulnerabilities to unlawfully extract valuable digital assets, highlighting the critical need for cybersecurity measures.
Poacher Traps
Poacher traps are designed to capture illegal hunting activities targeting wildlife, utilizing camouflaged nets, cage traps, and motion sensors to catch and deter animals or human poachers. Unlike wine poaching, which involves gently heating fruit in simmering liquid to infuse flavor and preserve texture for culinary uses, poacher traps serve a protective and enforcement role in wildlife conservation rather than food preparation.
Wine Fruit Infusion
Poaching typically refers to illegal wildlife hunting, whereas wine poaching for fruits involves gently simmering fruits in wine to infuse rich flavors, enhancing desserts and beverages. Wine fruit infusion creates a harmonious blend of natural fruit sugars and wine tannins, elevating taste profiles for gourmet applications.
Rose Wine Poaching
Rose wine poaching enhances fruit flavors by gently infusing berries and stone fruits with delicate floral and fruity notes, preserving their natural texture while adding complexity. Unlike traditional poaching, which often uses plain water or simple syrups, rose wine imparts a subtle acidity and aromatic depth that elevates desserts and fruit presentations.
Sous-vide Wine Poaching
Sous-vide wine poaching uses precise temperature control to infuse fruits with rich flavors while preserving texture, unlike traditional poaching which often leads to overcooked, mushy results. This method enhances the natural sweetness and aroma of fruits such as pears and apples, creating gourmet dishes with consistent quality and vibrant taste.
Citrus-Wine Maceration
Poaching involves gently cooking fruits in liquid, preserving texture and infusing subtle flavors, whereas wine poaching, specifically citrus-wine maceration, combines the acidity of citrus fruits like oranges and lemons with wine to intensify aroma and create complex flavor profiles. This method enhances the natural sweetness and brightness of the fruit while allowing tannins and fruity notes from the wine to meld seamlessly during the maceration process.
Poaching vs Wine poaching for fruits Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com