Porcelain inner pots offer a non-reactive, easy-to-clean surface that resists staining and imparts no metallic taste to pressure-cooked food, making them ideal for delicate recipes. Stainless steel inner pots provide superior durability, excellent heat conduction, and withstand high pressure without warping or corrosion, ensuring long-term reliability. Choosing between porcelain and stainless steel depends on priorities like flavor preservation versus robust performance under constant pressure cooking.
Table of Comparison
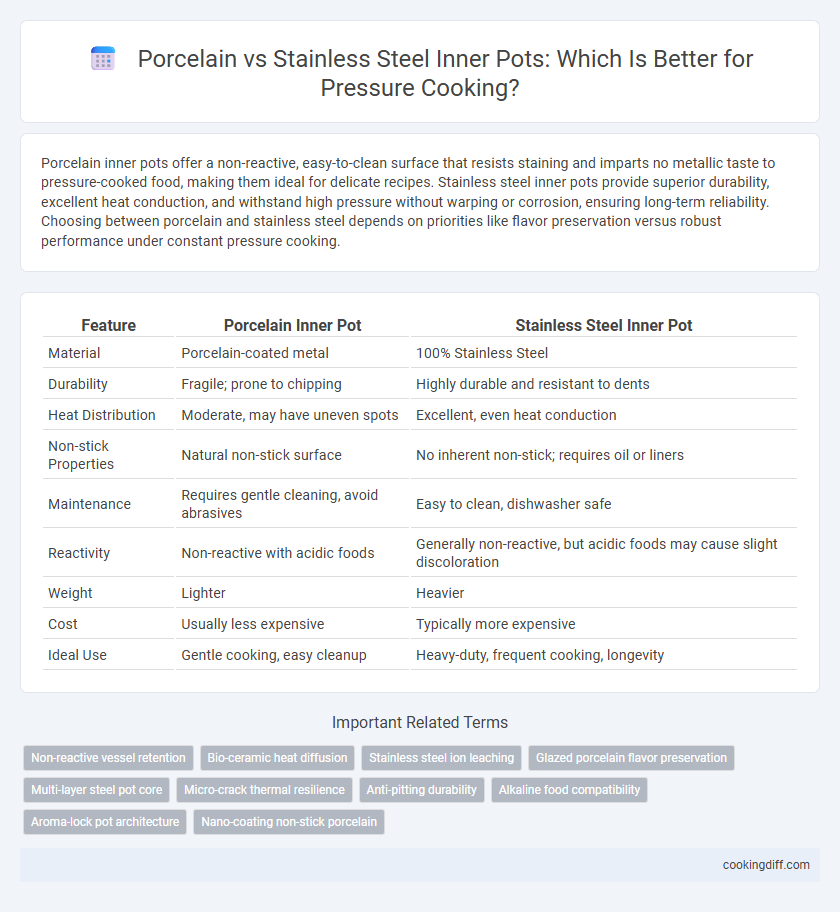
| Feature | Porcelain Inner Pot | Stainless Steel Inner Pot |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Porcelain-coated metal | 100% Stainless Steel |
| Durability | Fragile; prone to chipping | Highly durable and resistant to dents |
| Heat Distribution | Moderate, may have uneven spots | Excellent, even heat conduction |
| Non-stick Properties | Natural non-stick surface | No inherent non-stick; requires oil or liners |
| Maintenance | Requires gentle cleaning, avoid abrasives | Easy to clean, dishwasher safe |
| Reactivity | Non-reactive with acidic foods | Generally non-reactive, but acidic foods may cause slight discoloration |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Cost | Usually less expensive | Typically more expensive |
| Ideal Use | Gentle cooking, easy cleanup | Heavy-duty, frequent cooking, longevity |
Introduction: The Role of the Inner Pot in Pressure-Cooking
The inner pot is a crucial component of a pressure cooker, directly affecting heat distribution and cooking efficiency. Its material influences durability, maintenance, and food safety during pressure-cooking.
- Porcelain Inner Pot - Offers a non-stick, aesthetic surface that resists corrosion but may be more fragile under high pressure.
- Stainless Steel Inner Pot - Provides superior durability and resistance to warping with excellent heat conduction for even cooking.
- Heat Retention - Stainless steel maintains consistent heat better than porcelain, impacting overall cooking times and results.
Choosing the right inner pot material enhances the pressure cooker's performance and longevity.
Material Overview: Porcelain vs Stainless Steel
Porcelain inner pots offer a non-reactive, scratch-resistant surface that maintains food flavor without metallic taste, ideal for acidic dishes. They provide even heat distribution but may be more fragile and prone to chipping compared to metals.
Stainless steel inner pots boast superior durability and resistance to corrosion, making them highly suitable for high-pressure cooking environments. Their polished surfaces facilitate easy cleaning and ensure compatibility with a wide range of heat sources.
Heat Conductivity and Cooking Performance
Porcelain inner pots offer moderate heat conductivity, distributing heat evenly but taking longer to reach cooking temperature. Stainless steel inner pots excel in rapid heat conduction and retention, enhancing overall cooking performance in pressure cookers.
- Porcelain Inner Pot Heat Conductivity - Provides consistent heat distribution but heats up slower compared to metal.
- Stainless Steel Inner Pot Heat Conductivity - Transfers heat quickly and maintains temperature effectively for efficient cooking.
- Cooking Performance Impact - Stainless steel pots reduce cooking time and improve pressure stability for better results.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Porcelain inner pots offer a non-reactive, scratch-resistant surface but tend to chip or crack over time, reducing their durability. Stainless steel inner pots are highly durable, resistant to dents, and maintain structural integrity through frequent high-pressure cooking cycles.
Stainless steel inner pots boast superior longevity due to their robust construction and resistance to thermal shock. While porcelain coatings provide an aesthetic appeal and easy cleaning, they are more prone to damage from sudden temperature changes or impacts. Pressure cookers with stainless steel pots typically outlast those with porcelain-lined pots, ensuring longer-term investment value.
Flavor Preservation and Food Safety
Porcelain inner pots excel at preserving the natural flavors of food by providing a non-reactive surface that prevents metallic taste transfer during pressure cooking. Stainless steel inner pots are renowned for their durability and resistance to corrosion, ensuring long-term food safety without leaching harmful substances. Both materials offer hygienic cooking environments, but porcelain's non-porous surface may better maintain the original taste and aroma of ingredients under high pressure.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Which inner pot offers easier cleaning and maintenance for pressure-cooking: porcelain or stainless steel? Porcelain inner pots feature a non-stick surface that resists food residue buildup, making them simpler to clean with just a soft sponge. Stainless steel pots require more effort to remove stuck-on food but offer superior durability and resistance to scratches during maintenance.
Reactivity with Ingredients
Porcelain inner pots are non-reactive, ensuring that acidic ingredients like tomatoes or citrus do not alter the flavor or color of the food during pressure cooking. Stainless steel inner pots may react slightly with highly acidic foods, potentially imparting a metallic taste or causing discoloration over time. Choosing a porcelain inner pot can preserve the natural taste and appearance of delicate ingredients while maintaining durability and easy cleaning.
Energy Efficiency in Pressure-Cooking
| Porcelain Inner Pot | Porcelain inner pots retain heat efficiently, reducing cooking time and energy consumption. Their excellent heat distribution allows for consistent pressure levels, enhancing energy efficiency during pressure-cooking cycles. Porcelain's thermal insulation properties minimize heat loss, contributing to lower electricity use. |
| Stainless Steel Inner Pot | Stainless steel inner pots heat up quickly but have lower heat retention compared to porcelain, which may lead to slightly increased energy use. Their rapid thermal conductivity supports faster pressure buildup, optimizing cooking duration. Durable and less prone to heat degradation, stainless steel pots maintain stable energy performance over time. |
Cost and Availability
Porcelain inner pots typically come at a higher cost due to their aesthetic appeal and delicate material, often making them less accessible for budget-conscious consumers. These pots are less commonly available in mainstream stores, requiring purchase through specialty retailers or online platforms.
Stainless steel inner pots offer a more affordable option with widespread availability, commonly found in most kitchen appliance stores and online markets. Their cost-effectiveness and durable material make them a popular choice for everyday pressure-cooking needs.
Related Important Terms
Non-reactive vessel retention
Porcelain inner pots offer superior non-reactive properties, preventing food from reacting with metal ions and preserving flavor integrity during pressure cooking. Stainless steel inner pots, while durable and resistant to corrosion, can sometimes interact with acidic or alkaline ingredients, slightly affecting taste and nutrient retention.
Bio-ceramic heat diffusion
Porcelain inner pots with bio-ceramic coating provide superior heat diffusion by evenly distributing pressure-cooking heat, enhancing food texture and preventing hot spots. Stainless steel inner pots lack bio-ceramic properties but offer durability and resistance to corrosion, although they may result in less uniform heat distribution compared to porcelain options.
Stainless steel ion leaching
Stainless steel inner pots for pressure cooking offer durability and resistance to corrosion but can release trace amounts of metal ions, such as nickel and chromium, under high heat and acidic conditions, potentially affecting food safety. Porcelain inner pots, being non-reactive, minimize ion leaching, ensuring a purer cooking environment ideal for sensitive ingredients.
Glazed porcelain flavor preservation
Porcelain inner pots for pressure cookers excel in preserving the natural flavors of food due to their non-reactive, glazed surface that prevents metallic taste transfer and maintains aroma integrity. In contrast, stainless steel inner pots, while durable and efficient in heat conduction, can sometimes impart a slight metallic flavor, affecting the overall taste profile of pressure-cooked meals.
Multi-layer steel pot core
Porcelain inner pots offer a non-stick surface and aesthetic appeal, but multi-layer stainless steel inner pots excel in heat distribution and durability, making them ideal for pressure cooking where consistent thermal conductivity is crucial. The multi-layer steel pot core, often combining aluminum and stainless steel layers, ensures even heat retention and resistance to warping, enhancing cooking efficiency and longevity.
Micro-crack thermal resilience
Porcelain inner pots offer a smooth, non-reactive surface that resists micro-cracking under rapid temperature changes, making them ideal for consistent thermal expansion during pressure cooking. Stainless steel inner pots excel in thermal resilience with superior durability, preventing micro-cracks through even heat distribution and robust structural integrity.
Anti-pitting durability
Porcelain inner pots offer superior anti-pitting durability due to their smooth, non-porous surface that resists corrosion and abrasion during pressure cooking. Stainless steel inner pots, while durable, are more prone to pitting corrosion over time when exposed to acidic foods and high-pressure steam.
Alkaline food compatibility
Porcelain inner pots offer excellent resistance to alkaline foods, preventing discoloration and maintaining flavor integrity during pressure-cooking, whereas stainless steel inner pots may react slightly with highly alkaline ingredients, potentially affecting taste. Porcelain's non-reactive surface ensures safer cooking for alkaline dishes like beans or vegetables, making it an optimal choice for preserving nutritional quality and avoiding metallic aftertastes.
Aroma-lock pot architecture
The Aroma-lock pot architecture in pressure cookers enhances heat distribution and retention, with porcelain inner pots offering superior non-stick properties and easy cleaning, while stainless steel inner pots provide exceptional durability and resistance to corrosion. Porcelain coatings prevent food from sticking and preserve flavors but may be less resistant to scratches compared to the highly resilient stainless steel, which excels in long-term performance and maintains consistent pressure cooking efficiency.
Porcelain inner pot vs Stainless steel inner pot for pressure-cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com