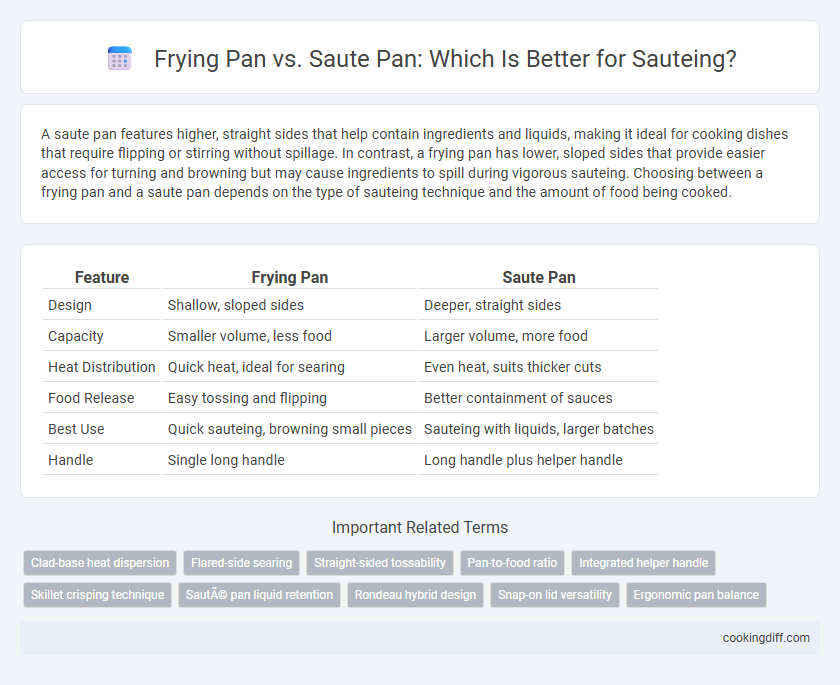
A saute pan features higher, straight sides that help contain ingredients and liquids, making it ideal for cooking dishes that require flipping or stirring without spillage. In contrast, a frying pan has lower, sloped sides that provide easier access for turning and browning but may cause ingredients to spill during vigorous sauteing. Choosing between a frying pan and a saute pan depends on the type of sauteing technique and the amount of food being cooked.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Frying Pan | Saute Pan |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Shallow, sloped sides | Deeper, straight sides |
| Capacity | Smaller volume, less food | Larger volume, more food |
| Heat Distribution | Quick heat, ideal for searing | Even heat, suits thicker cuts |
| Food Release | Easy tossing and flipping | Better containment of sauces |
| Best Use | Quick sauteing, browning small pieces | Sauteing with liquids, larger batches |
| Handle | Single long handle | Long handle plus helper handle |
Introduction to Sautéing: Why Pan Choice Matters
Sauteing requires quick, even cooking at high heat, making the right pan essential for optimal results. Choosing between a frying pan and a saute pan impacts heat distribution, surface area, and ease of tossing ingredients.
- Frying Pan - Features sloped sides for easy stirring and flipping of delicate foods during sauteing.
- Saute Pan - Has straight, higher sides to retain moisture and accommodate larger quantities of ingredients.
- Heat Distribution - Both pans offer quick heat transfer, but material and thickness affect cooking consistency in sauteing.
Defining Frying Pans and Sauté Pans
| Pan Type | Shape and Design | Typical Use in Sauteing |
|---|---|---|
| Frying Pan | Flat bottom with low, flared sides for easy flipping and stirring | Ideal for quick cooking and tossing food with minimal liquid; allows rapid evaporation |
| Saute Pan | Flat bottom with tall, straight sides to contain food and liquids | Preferred for sauteing larger quantities and cooking with sauces due to higher sides |
Key Differences in Design and Structure
The frying pan features low, flared sides and a wide surface area, ideal for quick evaporation and tossing ingredients while sauteing. In contrast, the saute pan has taller, straight sides to contain food and liquids, allowing for browning and simmering without spillage.
Frying pans typically offer better heat distribution for high-heat cooking, whereas saute pans provide more volume for cooking larger batches or dishes with sauces. The design differences impact cooking techniques, as saute pans facilitate stirring and flipping with less risk of food escaping the pan.
Heat Distribution and Cooking Performance
Saute pans typically offer better heat distribution due to their wider, flatter base and higher sides, ensuring even cooking and reducing hot spots. Frying pans, while versatile, may have uneven heat spread which can affect cooking performance during sauteing tasks.
- Heat Distribution - Saute pans provide more consistent heat across the surface, ideal for uniform browning.
- Cooking Performance - Frying pans may cause food to cook unevenly, especially with larger quantities.
- Design Impact - The high sides of saute pans help contain food, making stirring and tossing easier without spillage.
Sautéing Technique: How Each Pan Affects Results
Saute pans feature straight, tall sides that retain moisture and heat, making them ideal for evenly cooking ingredients without excessive evaporation. Frying pans have sloped sides, allowing for easier tossing and quick evaporation, which enhances browning and crisping during sauteing. The choice between these pans influences the texture and flavor profile, with saute pans providing more controlled cooking and frying pans promoting faster caramelization.
Versatility in the Kitchen: Frying Pan vs Sauté Pan
Frying pans feature a wide, flat base with gently sloping sides, making them ideal for quick, high-heat cooking and flipping ingredients. Saute pans offer higher, straight sides that provide better containment for stirring and prevent spillage during cooking with liquids or sauces. Versatility in the kitchen increases when using both pans, as frying pans excel in searing and browning while saute pans accommodate simmering and deglazing effectively.
Handles, Lids, and Ease of Use
Which pan offers better handles, lids, and ease of use for sauteing? A saute pan typically has a long handle plus a helper handle, providing better grip and control compared to the single handle on a frying pan. Frying pans often lack lids, while saute pans come with fitted lids that enhance moisture retention and cooking versatility.
Cleaning and Maintenance Comparison
Frying pans, with their flat shape and sloped sides, often require less effort to clean due to fewer crevices for food to get stuck. Saute pans, featuring higher sides and a larger surface area, may trap food particles, making maintenance slightly more involved.
Non-stick coatings on both frying pans and saute pans simplify cleanup, but durability varies depending on the quality of the pan. Stainless steel saute pans often need thorough scrubbing to remove browned bits, while frying pans with smooth surfaces typically resist buildup better. Regular seasoning of carbon steel pans enhances non-stick properties and eases cleaning for both pan types.
Which Pan Is Better for Sautéing?
A saute pan features straight sides and a larger surface area, which provides better heat distribution and prevents ingredients from spilling during the tossing motion. In contrast, a frying pan's sloped sides make flipping easier but reduce its capacity to hold liquids and evenly cook dense foods.
For sauteing, a saute pan is generally better due to its design that promotes even cooking and helps retain moisture in ingredients. However, for quick searing or tossing small portions, a frying pan can be more convenient and efficient.
Related Important Terms
Clad-base heat dispersion
A saute pan with a clad-base offers superior heat dispersion compared to a traditional frying pan, ensuring even cooking and reducing hot spots during sauteing. This enhanced thermal conductivity helps maintain consistent temperatures, which is crucial for achieving perfectly seared and evenly cooked ingredients.
Flared-side searing
Flared sides on a frying pan create a larger surface area for quick evaporation of moisture, enhancing caramelization and achieving a superior sear when sauteing. In contrast, saute pans with straight, higher sides retain moisture, making them less effective for achieving the optimal flared-side searing characteristic of classic saute techniques.
Straight-sided tossability
A saute pan with its straight sides enhances tossability by preventing food from spilling during vigorous stirring, unlike a frying pan whose sloped sides reduce control when tossing ingredients. Straight-sided designs increase surface contact and help maintain heat consistency, making saute pans more effective for tossing and evenly cooking smaller, delicate pieces.
Pan-to-food ratio
A saute pan's tall, straight sides and larger surface area reduce evaporative loss but can cause overcrowding when the pan-to-food ratio is too high, limiting effective browning. Frying pans with lower sides allow better moisture escape and more direct heat contact, ensuring even sauteing by keeping the pan-to-food ratio balanced for optimal Maillard reaction.
Integrated helper handle
A saute pan with an integrated helper handle offers better balance and easier maneuverability when tossing ingredients, especially during longer cooking sessions, compared to a frying pan that typically lacks this feature. The helper handle provides additional grip support, reducing wrist strain and allowing for safer, more precise sauteing techniques.
Skillet crisping technique
A frying pan, with its wide flat surface and low sides, excels at the skillet crisping technique by allowing maximum contact between the food and the heat source for even browning. In contrast, a saute pan's higher sides and smaller surface area limit moisture evaporation, making it less ideal for achieving the intense crispiness characteristic of skillet searing.
Sauté pan liquid retention
A saute pan features higher, straight sides compared to a frying pan, allowing it to better retain liquids, making it ideal for simmering sauces during sauteing. This design minimizes evaporation and spillage, enhancing flavor concentration and moisture retention in dishes.
Rondeau hybrid design
The Rondeau hybrid pan combines the deep, straight sides of a saute pan with the wide, flat base of a frying pan, optimizing heat distribution and allowing for efficient sauteing of larger quantities. This versatile design enhances browning and reduces splatter, making it ideal for searing and tossing ingredients with ease.
Snap-on lid versatility
A saute pan's snap-on lid enhances versatility by allowing food to be cooked with moisture retention and easy temperature control, ideal for simmering and finishing dishes. In contrast, a frying pan typically lacks a fitting lid, limiting its adaptability for recipes that require covered cooking during sauteing.
Frying pan vs Sauté pan for sautéing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com