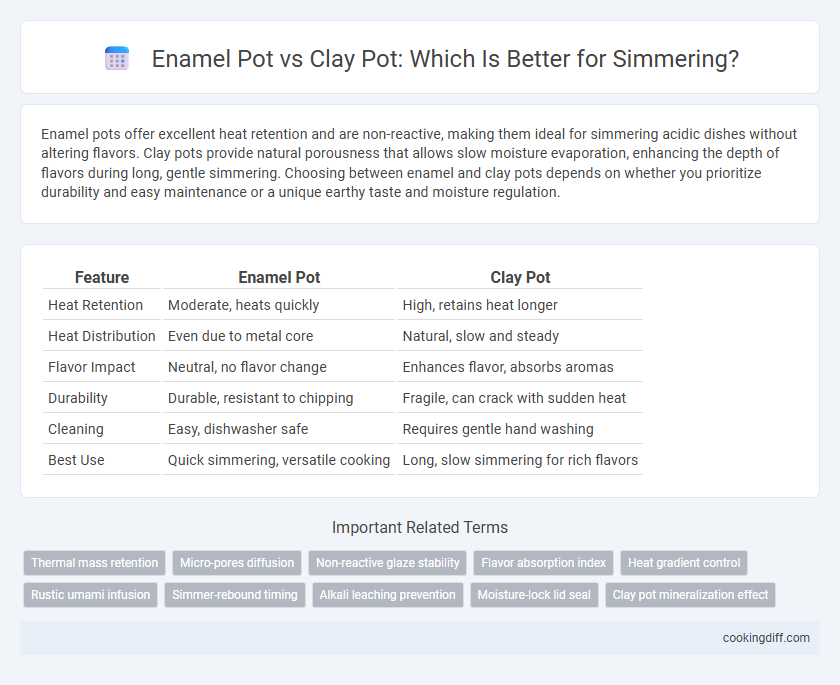
Enamel pots offer excellent heat retention and are non-reactive, making them ideal for simmering acidic dishes without altering flavors. Clay pots provide natural porousness that allows slow moisture evaporation, enhancing the depth of flavors during long, gentle simmering. Choosing between enamel and clay pots depends on whether you prioritize durability and easy maintenance or a unique earthy taste and moisture regulation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Enamel Pot | Clay Pot |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Retention | Moderate, heats quickly | High, retains heat longer |
| Heat Distribution | Even due to metal core | Natural, slow and steady |
| Flavor Impact | Neutral, no flavor change | Enhances flavor, absorbs aromas |
| Durability | Durable, resistant to chipping | Fragile, can crack with sudden heat |
| Cleaning | Easy, dishwasher safe | Requires gentle hand washing |
| Best Use | Quick simmering, versatile cooking | Long, slow simmering for rich flavors |
Introduction to Simmering: Why Cookware Matters
Simmering requires consistent, gentle heat to cook ingredients evenly without boiling. Choosing the right cookware, such as an enamel pot or a clay pot, significantly impacts temperature control and flavor retention.
An enamel pot offers excellent heat distribution and durability, making it ideal for maintaining steady simmering temperatures. Clay pots provide natural heat insulation and moisture retention, enhancing the depth of flavors in slow-cooked dishes. Understanding these properties ensures optimal results in simmering recipes.
Enamel Pots: Key Features for Simmering
What makes enamel pots ideal for simmering? Enamel pots offer excellent heat retention and even distribution, which helps maintain a consistent low temperature ideal for simmering. Their non-reactive surface prevents food from absorbing metallic flavors, making them perfect for slow-cooked dishes.
Clay Pots: Unique Benefits in Simmering
Clay pots excel in simmering due to their porous nature, which allows slow and even heat distribution, enhancing flavor infusion. Their ability to retain moisture prevents food from drying out, resulting in tender and rich dishes.
- Porous material - Clay pots absorb and release moisture gradually, creating a natural steaming effect during simmering.
- Even heat distribution - The thick walls of clay pots provide consistent heat, reducing hotspots that can cause uneven cooking.
- Enhanced flavor - Slow simmering in clay pots intensifies flavors by preserving aromatic compounds and blending ingredients thoroughly.
Heat Distribution: Enamel vs Clay Pots
Enamel pots offer consistent heat distribution due to their metal core, which ensures even simmering without hot spots. Clay pots retain heat longer but often heat unevenly, requiring careful temperature control to avoid burning. For precise simmering, enamel pots provide superior temperature stability compared to clay pots.
Moisture Retention: Comparing Pot Materials
Enamel pots excel in moisture retention due to their non-porous surfaces, which prevent liquid evaporation during simmering. Clay pots, being porous, absorb and slowly release moisture, creating a unique steaming effect that enhances flavor infusion.
- Enamel pots maintain consistent moisture levels - their sealed surfaces minimize evaporation, ensuring ingredients remain juicy and tender.
- Clay pots absorb moisture - allowing gradual redistribution, which aids in even cooking and adds subtle earthiness to dishes.
- Moisture control influences texture - enamel pots produce firmer textures while clay pots tend to yield softer, more aromatic results.
Choosing between enamel and clay depends on desired moisture retention and texture for simmered dishes.
Flavor Impact: How Pot Choice Affects Taste
Enamel pots retain heat evenly, allowing flavors to meld smoothly during simmering, resulting in rich and consistent taste profiles. Clay pots, being porous, absorb and release moisture slowly, enhancing depth and earthiness in dishes. The choice between enamel and clay pots significantly influences the flavor complexity and texture of simmered meals.
Durability and Maintenance: Enamel and Clay Compared
Enamel pots offer superior durability due to their non-porous, chip-resistant coating, making them less prone to cracking or absorbing flavors during simmering. Their maintenance is simplified as they are dishwasher safe and do not require seasoning, unlike clay pots.
Clay pots, while offering excellent heat retention, tend to be more fragile and can crack if handled roughly or subjected to thermal shock. They demand careful seasoning and thorough drying after use to prevent mold and prolong their lifespan.
Stove Compatibility: Which Pot Works Where?
| Pot Type | Stove Compatibility | Performance for Simmering |
|---|---|---|
| Enamel Pot | Compatible with gas, electric, induction, and ceramic stoves due to its metal core and durable enamel coating. | Maintains consistent low heat, making it ideal for gentle, controlled simmering without hotspots. |
| Clay Pot | Best suited for gas stoves; requires careful handling on electric or induction since it may crack without proper heat regulation. | Provides natural porous heat retention ideal for slow simmering but heats unevenly compared to enamel pots. |
Health and Safety Considerations
Enamel pots provide a non-reactive cooking surface that prevents metal leaching, making them safer for acidic simmering recipes, while clay pots require proper curing to avoid mold and bacteria growth. Both options offer health benefits, but safety depends on maintenance and the quality of materials used.
- Non-reactive Surface - Enamel coating prevents harmful chemical reactions during cooking and ensures safe food preparation.
- Porosity of Clay - Unglazed clay can absorb moisture and bacteria if not properly sealed or cured, posing potential health risks.
- Material Quality - High-quality, lead-free enamel and fired clay minimize health hazards during simmering.
Related Important Terms
Thermal mass retention
Enamel pots offer superior thermal mass retention due to their thick metal core, ensuring stable and even heat distribution during simmering, which prevents temperature fluctuations. In contrast, clay pots, while good at absorbing heat slowly, tend to lose heat faster once removed from the heat source, leading to less consistent simmering temperatures.
Micro-pores diffusion
Enamel pots have a smooth, non-porous surface that prevents liquid absorption, resulting in controlled, even heat distribution but limited micro-pore diffusion. Clay pots contain microscopic pores that enable slow diffusion of steam and moisture, enhancing flavor concentration and consistent simmering through natural breathability.
Non-reactive glaze stability
Enamel pots offer superior non-reactive glaze stability compared to clay pots, preventing metallic or off-flavors during long simmering processes and ensuring consistent heat distribution without chemical interaction. Clay pots, while porous and excellent for moisture retention, are more prone to absorb flavors and may leach minerals if not fully glazed or properly seasoned.
Flavor absorption index
Clay pots have a high flavor absorption index, allowing them to enhance the depth and richness of ingredients during simmering by retaining and redistributing flavors more effectively than enamel pots. Enamel pots, coated with a non-porous surface, prevent flavor absorption, maintaining the original taste but limiting the development of complex, infused flavors.
Heat gradient control
Enamel pots provide precise heat gradient control during simmering due to their thick metal base that distributes heat evenly, preventing hot spots and ensuring consistent cooking temperatures. Clay pots, while excellent at retaining moisture, offer less precise heat gradient control because their porous structure can cause uneven heat distribution and slower temperature adjustments.
Rustic umami infusion
Enamel pots retain consistent heat and provide a non-reactive surface, preserving the natural umami flavors while ensuring even simmering. Clay pots enhance rustic umami infusion by slowly absorbing and redistributing moisture, intensifying depth and earthiness in simmered dishes.
Simmer-rebound timing
Enamel pots feature superior heat retention and a quicker simmer-rebound timing compared to clay pots, allowing for more precise temperature control during slow cooking. Clay pots, while providing even heat distribution, have slower simmer-rebound times, which can result in longer periods to regain a consistent simmer after stirring or adding ingredients.
Alkali leaching prevention
Enamel pots provide a non-porous surface that prevents alkali leaching during simmering, ensuring food safety and preserving flavor integrity. Unlike clay pots, which can absorb liquids and release alkalis into the food, enamel-coated cookware maintains chemical stability under prolonged low heat.
Moisture-lock lid seal
Enamel pots with moisture-lock lid seals excel at retaining moisture during simmering, preventing evaporation and maintaining consistent heat for tender, flavorful dishes. Clay pots, while porous and able to absorb some moisture, lack an effective moisture-lock lid, resulting in more evaporation and slower cooking.
Enamel pot vs Clay pot for simmering. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com