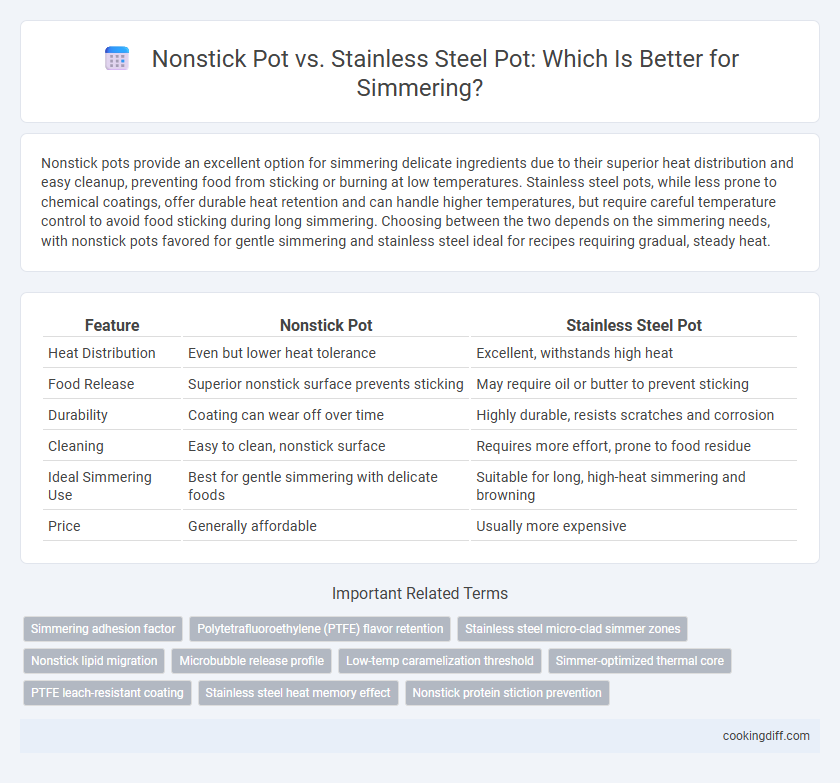
Nonstick pots provide an excellent option for simmering delicate ingredients due to their superior heat distribution and easy cleanup, preventing food from sticking or burning at low temperatures. Stainless steel pots, while less prone to chemical coatings, offer durable heat retention and can handle higher temperatures, but require careful temperature control to avoid food sticking during long simmering. Choosing between the two depends on the simmering needs, with nonstick pots favored for gentle simmering and stainless steel ideal for recipes requiring gradual, steady heat.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nonstick Pot | Stainless Steel Pot |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Distribution | Even but lower heat tolerance | Excellent, withstands high heat |
| Food Release | Superior nonstick surface prevents sticking | May require oil or butter to prevent sticking |
| Durability | Coating can wear off over time | Highly durable, resists scratches and corrosion |
| Cleaning | Easy to clean, nonstick surface | Requires more effort, prone to food residue |
| Ideal Simmering Use | Best for gentle simmering with delicate foods | Suitable for long, high-heat simmering and browning |
| Price | Generally affordable | Usually more expensive |
Introduction to Simmering: Why Pot Choice Matters
| Simmering requires precise temperature control, making the choice between nonstick and stainless steel pots crucial for optimal results. Nonstick pots offer even heat distribution and prevent food from sticking, ideal for delicate sauces or soups. Stainless steel pots provide superior heat retention and can withstand higher temperatures, enhancing flavor development during prolonged simmering. |
Overview: Nonstick vs Stainless Steel Pots
Nonstick pots provide even heat distribution with a smooth surface that prevents food from sticking, making them ideal for delicate simmering tasks. Stainless steel pots offer superior heat retention and durability, but they require more oil or liquid to avoid food adhering during the simmering process.
For simmering, nonstick pots ensure gentle, consistent heat that helps prevent scorching and allows for easy cleanup. Stainless steel pots excel in maintaining steady temperatures, especially for longer simmering sessions or when browning ingredients first. Choosing between the two depends on the simmering technique and dish requirements, with nonstick better suited for low-fat cooking and stainless steel preferred for high-heat versatility.
Heat Distribution: Performance in Simmering
Nonstick pots offer even heat distribution which prevents hot spots, making them ideal for gentle simmering. Stainless steel pots tend to have uneven heat distribution unless they feature an aluminum or copper core, affecting simmering performance.
- Nonstick Coating Enhances Heat Dispersion - The nonstick surface promotes uniform cooking temperatures essential for maintaining a steady simmer.
- Stainless Steel Conductivity Relies on Core Materials - Pure stainless steel has poor heat conduction, but tri-ply or multi-ply bases improve simmering control.
- Heat Retention Differences - Stainless steel retains heat longer, which may cause temperature fluctuations during simmering compared to nonstick pots.
Temperature Control and Consistency
Nonstick pots offer superior temperature control for simmering due to their even heat distribution and low heat retention, which prevents hot spots and burning. Stainless steel pots excel in heat consistency, maintaining steady temperatures over longer periods, ideal for slow simmering without temperature fluctuations. Choosing between the two depends on whether precise temperature regulation or sustained heat consistency is the priority in your simmering process.
Food Release and Sticking Issues
Nonstick pots excel in preventing food from sticking during simmering, ensuring effortless food release and easy cleanup. Stainless steel pots require proper preheating and adequate oil to minimize sticking, but they offer superior heat retention and durability.
- Nonstick Surface - Provides a smooth coating that reduces food adhesion, ideal for delicate sauces and slow cooking.
- Stainless Steel Heat Management - Retains heat evenly, but food can stick if the pot is not preheated or oiled correctly.
- Cleaning and Maintenance - Nonstick pots clean easily due to minimal sticking, whereas stainless steel may need more scrubbing to remove cooked-on residue.
Durability and Longevity for Simmering
Which pot offers better durability and longevity for simmering, nonstick or stainless steel? Stainless steel pots excel in durability with their resistance to scratches, high heat, and corrosion, making them ideal for long-term use in simmering processes. Nonstick pots, while convenient for easy cleaning, tend to degrade faster under prolonged high heat exposure common in simmering, reducing their lifespan significantly.
Reactivity with Ingredients During Simmering
Nonstick pots have a non-reactive coating that prevents food from interacting with the pot's surface, making them ideal for simmering acidic ingredients like tomatoes without altering flavor. Stainless steel pots are reactive to acidic foods, which can sometimes result in a metallic taste or discoloration during prolonged simmering. For dishes requiring long simmering times with delicate flavors, nonstick pots offer a more stable cooking environment free from ingredient reactivity concerns.
Cleaning and Maintenance Considerations
Nonstick pots require gentle cleaning with soft sponges to prevent damaging the coating, and they should never be scrubbed with abrasive materials. While stainless steel pots can withstand more aggressive scrubbing and dishwasher cycles, they may require regular polishing to maintain their shine and prevent discoloration.
Residue on nonstick surfaces is typically easier to wipe away, reducing cleanup time, whereas stainless steel pots might need soaking to loosen baked-on food. Proper care of both types involves drying thoroughly to avoid water spots or rust on stainless steel, and avoiding high heat that can degrade nonstick coatings.
Safety and Health Factors for Prolonged Simmering
Nonstick pots offer ease of cleaning and lower oil usage, but prolonged simmering at high heat risks releasing toxic fumes from degraded coatings. Stainless steel pots withstand high temperatures without chemical leaching, making them safer for extended cooking times despite potential sticking issues.
- Nonstick chemical stability - Prolonged heating above 500degF can break down PTFE coating, emitting harmful fumes harmful to respiratory health.
- Stainless steel durability - Resistant to corrosion and heat damage, it does not release toxins even during extended simmering.
- Potential metallic leaching - Low possibility of nickel or chromium leaching from stainless steel but generally considered safe within normal cooking parameters.
For health-conscious simmering, stainless steel pots provide superior safety over nonstick when cooking times are long and temperatures are maintained steadily.
Related Important Terms
Simmering adhesion factor
Nonstick pots minimize adhesion during simmering due to their smooth, coated surface, preventing food from sticking and allowing for effortless stirring and cleaning. Stainless steel pots, while durable and ideal for browning, often require precise temperature control and sufficient liquid to prevent food adhesion and burning during simmering.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) flavor retention
Nonstick pots coated with Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) excel at preventing food from sticking, but may retain subtle flavors from previous dishes, potentially affecting delicate simmered recipes. Stainless steel pots do not absorb flavors, providing a neutral cooking surface ideal for consistent and uncontaminated simmering results.
Stainless steel micro-clad simmer zones
Stainless steel pots with micro-clad simmer zones offer precise temperature control and even heat distribution, preventing hot spots and ensuring consistent simmering. Unlike nonstick pots that may degrade at low simmering temperatures, micro-clad stainless steel maintains durability and optimal thermal performance for delicate sauces and long cooking times.
Nonstick lipid migration
Nonstick pots reduce lipid migration during simmering due to their smooth, non-porous surfaces that prevent food from sticking and burning, preserving flavor and nutrients. In contrast, stainless steel pots may promote more lipid migration as food particles can adhere and degrade at high temperatures, altering the dish's taste and quality.
Microbubble release profile
Simmering with a nonstick pot produces a more consistent microbubble release profile due to its even heat distribution and reduced surface adhesion, enhancing gentle cooking without scorching. Stainless steel pots exhibit less uniform microbubble formation, often causing hotspots that can disrupt the delicate simmering process and lead to uneven heat transfer.
Low-temp caramelization threshold
Nonstick pots excel for simmering due to their low-temp caramelization threshold, allowing sugars and ingredients to brown gently without sticking or burning. Stainless steel pots require careful heat control since their higher caramelization point can lead to uneven cooking or scorching at low simmer temperatures.
Simmer-optimized thermal core
A nonstick pot with a simmer-optimized thermal core provides even heat distribution, preventing hotspots and ensuring delicate ingredients cook gently without sticking. In contrast, stainless steel pots often require higher heat adjustments and more stirring to maintain consistent simmering, as their thermal cores may not offer the same precise temperature control.
PTFE leach-resistant coating
Nonstick pots with PTFE leach-resistant coatings provide even heat distribution and easy cleanup while preventing food from sticking during simmering, ensuring safer cooking by minimizing potential chemical leaching. Stainless steel pots, although durable and resistant to corrosion, lack the nonstick surface, which can cause food to adhere and require more careful temperature control to avoid burning or uneven simmering.
Stainless steel heat memory effect
Stainless steel pots excel in simmering due to their superior heat memory effect, retaining and distributing heat evenly for precise temperature control and consistent cooking results. Unlike nonstick pots that can lose heat quickly, stainless steel maintain stable simmering temperatures, enhancing flavor development in slow-cooked dishes.
Nonstick pot vs Stainless steel pot for simmering. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com