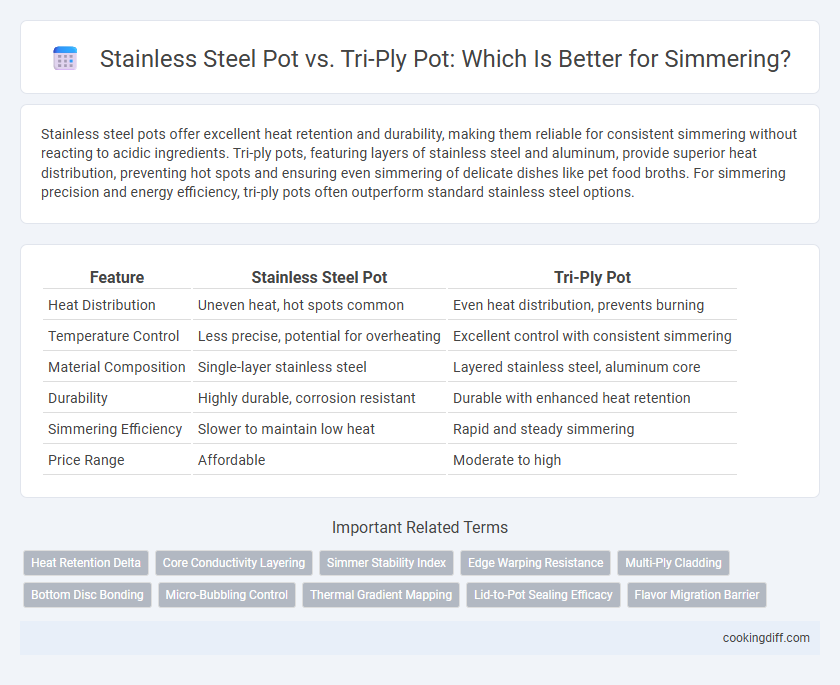
Stainless steel pots offer excellent heat retention and durability, making them reliable for consistent simmering without reacting to acidic ingredients. Tri-ply pots, featuring layers of stainless steel and aluminum, provide superior heat distribution, preventing hot spots and ensuring even simmering of delicate dishes like pet food broths. For simmering precision and energy efficiency, tri-ply pots often outperform standard stainless steel options.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stainless Steel Pot | Tri-Ply Pot |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Distribution | Uneven heat, hot spots common | Even heat distribution, prevents burning |
| Temperature Control | Less precise, potential for overheating | Excellent control with consistent simmering |
| Material Composition | Single-layer stainless steel | Layered stainless steel, aluminum core |
| Durability | Highly durable, corrosion resistant | Durable with enhanced heat retention |
| Simmering Efficiency | Slower to maintain low heat | Rapid and steady simmering |
| Price Range | Affordable | Moderate to high |
Introduction to Simmering: Why Pot Choice Matters
Simmering requires consistent, gentle heat to cook food evenly without boiling over or burning. The choice between stainless steel and tri-ply pots significantly impacts temperature control and cooking efficiency during this process.
- Heat Conductivity - Tri-ply pots feature an aluminum core sandwiched between stainless steel layers, providing superior heat distribution compared to standard stainless steel.
- Durability - Stainless steel pots are highly resistant to rust and corrosion, making them long-lasting choices for everyday simmering.
- Temperature Control - Tri-ply construction minimizes hot spots and allows for precise simmering, essential for delicate recipes requiring steady heat.
What Is a Stainless Steel Pot? Key Features
| Stainless Steel Pot | Constructed from durable stainless steel alloy, ensuring resistance to rust, corrosion, and staining. |
|---|---|
| Heat Distribution | Provides even heat conduction, although typically less efficient than tri-ply designs without a layered core. |
| Durability | Highly resistant to dents, scratches, and high temperatures, making it ideal for long-term use in simmering delicate sauces and soups. |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean and dishwasher safe, with non-reactive surfaces that prevent flavor alteration during simmering. |
Tri-Ply Pots Explained: Structure and Benefits
Tri-ply pots consist of three layers: an inner stainless steel core, a middle aluminum layer, and an outer stainless steel shell. This structure ensures even heat distribution and excellent temperature retention, crucial for consistent simmering.
The aluminum core accelerates heat conduction, eliminating hot spots that can cause food to burn or stick. As a result, tri-ply pots offer superior control over low, steady heat compared to stainless steel pots alone, making them ideal for delicate simmering tasks.
Heat Distribution: Stainless Steel vs Tri-Ply for Simmering
Tri-ply pots, composed of stainless steel layers sandwiching an aluminum core, provide superior heat distribution essential for consistent simmering. Stainless steel pots alone often cause uneven heat spots, risking food scorching during low, prolonged heat. Optimal simmering requires even heat transfer, making tri-ply cookware the preferred choice for precise temperature control in gentle cooking processes.
Temperature Control and Stability Comparison
Stainless steel pots provide even heat distribution but often lack in temperature control precision, which can cause fluctuations during simmering. Their single-layer construction tends to heat quickly but cool down slowly, reducing stability during low-heat cooking.
Tri-ply pots, featuring an aluminum core sandwiched between stainless steel layers, offer superior temperature control by evenly distributing and retaining heat. This multi-layer design ensures consistent simmering temperatures, minimizing hot spots and improving cooking stability.
Cooking Performance: Flavor and Texture Impacts
Which pot offers better cooking performance for simmering, stainless steel or tri-ply? Tri-ply pots provide more even heat distribution due to their layered construction, preventing hotspots and ensuring consistent simmering. Stainless steel pots may struggle with uneven heat, potentially affecting the flavor depth and texture of delicate dishes.
Durability and Longevity in Daily Simmering
Stainless steel pots offer excellent durability, resisting rust and corrosion during daily simmering tasks. Their robust construction ensures long-lasting performance without warping under consistent heat.
Tri-ply pots combine stainless steel with aluminum layers, enhancing heat distribution and preventing hot spots for even simmering. The bonded layers improve the pot's resistance to wear and extend its lifespan in frequent use. This design supports consistent simmering while maintaining structural integrity over time.
Maintenance and Cleaning: Which Pot Is Easier?
Stainless steel pots are highly resistant to rust and staining, making them easier to maintain with regular dishwashing or hand washing. Tri-ply pots, composed of layers of stainless steel and aluminum, require careful cleaning to prevent damage to the bonding layers, often necessitating gentle scrubbing and avoidance of abrasive cleaners. Overall, stainless steel pots offer simpler maintenance and cleaning routines compared to tri-ply pots, enhancing their durability for simmering tasks.
Price and Value Analysis: Stainless Steel vs Tri-Ply
Stainless steel pots typically come at a lower price point compared to tri-ply pots, making them more accessible for budget-conscious cooks. However, tri-ply cookware offers enhanced heat distribution and durability, which can provide better value over time despite the higher initial cost.
- Cost Efficiency - Stainless steel pots are usually less expensive upfront, ideal for those prioritizing immediate affordability.
- Longevity and Performance - Tri-ply pots combine layers of stainless steel and aluminum for even heating, reducing hot spots during simmering and extending cookware lifespan.
- Investment Value - The higher price of tri-ply cookware is often offset by improved cooking results and durability, providing greater long-term value.
Related Important Terms
Heat Retention Delta
Stainless steel pots generally have lower heat retention Delta compared to tri-ply pots, causing more rapid temperature fluctuations during simmering. Tri-ply pots, with their layered construction of stainless steel and aluminum, provide superior heat retention Delta, ensuring consistent low heat essential for delicate simmering tasks.
Core Conductivity Layering
Stainless steel pots with a tri-ply core feature an aluminum or copper conductive layer sandwiched between stainless steel, ensuring even heat distribution crucial for maintaining consistent simmering temperatures. Pure stainless steel pots often have less effective heat conduction, leading to hot spots that can disrupt delicate simmering processes.
Simmer Stability Index
The Simmer Stability Index of a tri-ply pot surpasses that of a stainless steel pot due to its layered construction, which distributes heat more evenly and maintains consistent low temperatures for extended periods. This enhanced simmer stability prevents hot spots and ensures precise temperature control, making tri-ply pots ideal for delicate simmering tasks.
Edge Warping Resistance
Stainless steel pots offer excellent edge warping resistance due to their durable construction and high-quality metal alloys, ensuring long-lasting shape retention during simmering. Tri-ply pots combine stainless steel with an aluminum core, providing superior heat distribution but slightly less edge rigidity, which may result in minor warping over extended use at simmering temperatures.
Multi-Ply Cladding
Tri-ply pots, featuring a multi-ply cladding of stainless steel and aluminum layers, provide superior heat distribution and retention ideal for consistent simmering compared to single-layer stainless steel pots which may have hot spots. The layered construction ensures even low-temperature cooking, reducing the risk of scorching and promoting better flavor development for delicate simmered dishes.
Bottom Disc Bonding
Tri-ply pots feature a bonded bottom disc composed of layers including stainless steel and aluminum, ensuring even heat distribution and superior temperature control during simmering. Stainless steel pots with a single bonded bottom disc often exhibit slower heat response and uneven heating, making tri-ply pots more efficient for maintaining consistent low simmer temperatures.
Micro-Bubbling Control
Stainless steel pots offer consistent heat distribution but may struggle with precise micro-bubbling control during simmering due to lower thermal responsiveness. Tri-ply pots, featuring layers of stainless steel and aluminum, provide superior heat conductivity and even temperature regulation, enabling better micro-bubbling control essential for delicate simmering tasks.
Thermal Gradient Mapping
Stainless steel pots exhibit uneven thermal gradient mapping due to their single-layer construction, resulting in hot spots that can cause inconsistent simmering. Tri-ply pots, with their layered core of aluminum sandwiched between stainless steel, offer superior thermal conductivity and even heat distribution, ensuring a stable and precise simmering temperature.
Lid-to-Pot Sealing Efficacy
Stainless steel pots typically feature tightly fitted lids with robust sealing that minimizes steam escape during simmering, ensuring consistent heat and moisture retention. Tri-ply pots offer enhanced heat distribution but may have slightly less effective lid-to-pot sealing due to multi-layer construction, potentially allowing more steam to dissipate.
Stainless Steel Pot vs Tri-Ply Pot for simmering. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com