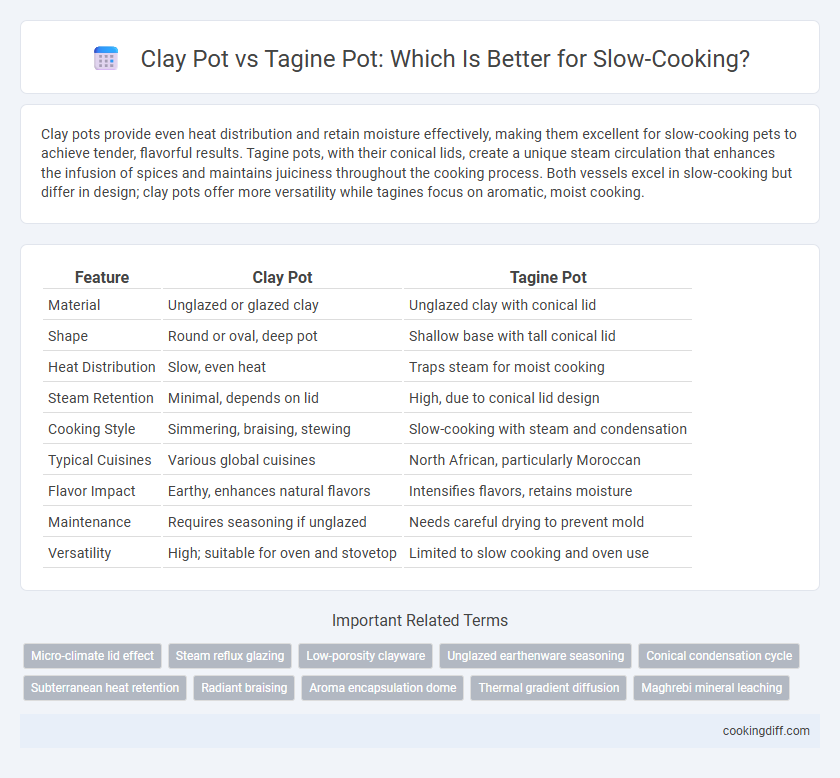
Clay pots provide even heat distribution and retain moisture effectively, making them excellent for slow-cooking pets to achieve tender, flavorful results. Tagine pots, with their conical lids, create a unique steam circulation that enhances the infusion of spices and maintains juiciness throughout the cooking process. Both vessels excel in slow-cooking but differ in design; clay pots offer more versatility while tagines focus on aromatic, moist cooking.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Clay Pot | Tagine Pot |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Unglazed or glazed clay | Unglazed clay with conical lid |
| Shape | Round or oval, deep pot | Shallow base with tall conical lid |
| Heat Distribution | Slow, even heat | Traps steam for moist cooking |
| Steam Retention | Minimal, depends on lid | High, due to conical lid design |
| Cooking Style | Simmering, braising, stewing | Slow-cooking with steam and condensation |
| Typical Cuisines | Various global cuisines | North African, particularly Moroccan |
| Flavor Impact | Earthy, enhances natural flavors | Intensifies flavors, retains moisture |
| Maintenance | Requires seasoning if unglazed | Needs careful drying to prevent mold |
| Versatility | High; suitable for oven and stovetop | Limited to slow cooking and oven use |
Introduction: Clay Pot vs Tagine Pot for Slow-Cooking
Clay pots and tagine pots are both traditional vessels designed to enhance the slow-cooking process by retaining moisture and distributing heat evenly. Clay pots are typically round with a tight-fitting lid, ideal for simmering stews and soups over low heat.
Tagine pots feature a distinctive conical lid that promotes steam circulation, concentrating flavors and tenderizing meats efficiently. The unique shape of a tagine is especially favored in North African cuisine for slow-cooked dishes like lamb and vegetable tagines.
Origins and Cultural Background
| Clay Pot Origins and Cultural Background |
| Clay pots have been used for thousands of years across various cultures worldwide, particularly in Asia, Africa, and Latin America, where they serve as essential cookware for slow-cooking techniques due to their ability to distribute heat evenly. Traditional clay pots, often unglazed, retain moisture and enhance the flavor of stews, soups, and braised dishes, reflecting culinary practices deeply rooted in indigenous and rural communities. These pots are celebrated for preserving nutrients and creating tender, flavorful meals through low, consistent heat over extended cooking periods. |
| Tagine Pot Origins and Cultural Background |
| The tagine pot originates from North African Berber culture, particularly Morocco, and is specifically designed for slow-cooking stews by combining a conical lid with a wide, shallow base that promotes steam circulation. This unique shape allows slow condensation of steam back into the dish, intensifying flavors typical of Moroccan cuisine, including spices, preserved lemons, and dried fruits. Tagines hold cultural significance as both a cooking vessel and symbol of hospitality, traditionally used in communal meals and celebrations. |
Material Composition and Design Features
Clay pots and Tagine pots are both excellent for slow-cooking due to their heat retention properties, but their material composition varies slightly, with traditional clay pots made from natural, porous clay, while Tagines often include a ceramic glaze that enhances moisture retention. The design of Tagine pots features a conical lid that promotes steam circulation, whereas clay pots usually have a simple, rounded lid to evenly distribute heat.
- Material Composition - Clay pots are unglazed and porous, allowing slow evaporation which enhances flavor concentration.
- Design Features - The Tagine's conical lid facilitates steam condensation and continuous basting of the food.
- Heat Retention - Both pots excel at retaining and evenly distributing heat for tender, slow-cooked results.
Choosing between a clay pot and a Tagine depends on the desired cooking style and moisture management in slow-cooking recipes.
Heat Distribution: Efficiency in Slow-Cooking
Clay pots offer uniform heat distribution, making them ideal for slow-cooking dishes as they retain moisture and enhance flavor development. Tagine pots, with their conical lids, promote efficient steam circulation, which intensifies heat retention and tenderness of slow-cooked ingredients.
The heat efficiency of clay pots minimizes hot spots, allowing for consistent cooking temperatures over extended periods. Tagine pots excel in slow-cooking by trapping steam inside the cone-shaped lid, ensuring juices are recycled back into the dish. This design supports a gentle, even cooking process that preserves nutrients and deepens taste profiles.
Moisture Retention and Flavor Development
Clay pots excel in moisture retention due to their porous material, allowing slow evaporation and continuous basting of the food, which enhances tenderness and depth of flavor. Tagine pots, with their distinctive conical lids, trap steam efficiently, promoting condensation that drips back onto the dish, intensifying aromatic spices and natural juices. Both vessels optimize slow-cooking by maintaining a humid environment that amplifies flavor development and prevents dryness in slow-cooked meals.
Versatility in Slow-Cooked Recipes
Clay pots offer exceptional heat retention and a neutral cooking environment, ideal for a wide range of slow-cooked dishes. Tagine pots, with their conical lids, excel in moisture circulation, enhancing flavors in Moroccan-style recipes.
- Clay pot versatility - Suitable for soups, stews, and braised meats across various cuisines due to even heat distribution.
- Tagine pot specialization - Designed primarily for North African slow-cooked dishes, promoting tender textures and aromatic blends.
- Flavor profile impact - Clay pots maintain pure ingredient flavors, while tagines infuse dishes with intensified, steam-circulated spices.
Ease of Use and Maintenance
Clay pots are generally heavier and require soaking before use to prevent cracking, making preparation slightly more time-consuming. Cleaning clay pots demands gentle hand washing without harsh detergents to maintain their porous surface and durability.
Tagine pots often feature a glazed surface that simplifies cleaning and reduces the need for soaking, enhancing ease of use. Their conical lids help condense steam efficiently but require careful handling to avoid chipping and preserve slow-cooking performance.
Health and Safety Considerations
How do health and safety considerations compare between clay pots and tagine pots for slow-cooking? Clay pots are generally made from natural, non-toxic materials free from harmful chemicals, making them safe for cooking at low temperatures. Tagine pots, traditionally glazed with lead-free finishes and designed for even heat distribution, minimize the risk of food contamination and ensure safer slow-cooking.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Clay pots are generally more affordable and widely available in many kitchenware stores worldwide, making them a cost-effective choice for slow-cooking enthusiasts. Tagine pots, while often pricier due to their unique design and cultural significance, can be harder to find, especially outside North Africa.
- Clay pot affordability - These pots typically cost less due to simpler manufacturing processes and broader market availability.
- Tagine pot pricing - The intricate design and traditional craftsmanship often result in higher prices for tagine pots.
- Availability differences - Clay pots are more accessible globally, whereas tagine pots are primarily available in specialty or ethnic stores.
Related Important Terms
Micro-climate lid effect
The tagine pot's conical lid creates a unique micro-climate by condensing steam and allowing it to drip back onto the food, preserving moisture and enhancing flavors during slow-cooking. In contrast, the clay pot's flat lid retains heat evenly but lacks the moisture circulation benefits of a tagine, resulting in a different slow-cooked texture.
Steam reflux glazing
Steam reflux glazing in clay pots enhances moisture retention, creating a self-basting environment ideal for slow-cooking meats and vegetables. Tagine pots feature a conical lid designed to condense steam, promoting continuous moisture circulation that intensifies flavors and tenderizes ingredients efficiently.
Low-porosity clayware
Low-porosity clayware, such as traditional tagine pots, excels in slow-cooking by retaining moisture and evenly distributing heat, which enhances flavor concentration and tenderness. Unlike general clay pots, low-porosity varieties minimize liquid absorption, preventing evaporation and preserving the integrity of stews and braises over extended cooking times.
Unglazed earthenware seasoning
Unglazed earthenware in both clay pots and tagine pots requires careful seasoning to enhance durability, prevent cracking, and improve non-stick properties during slow-cooking. Proper seasoning involves soaking, oiling, and gradual heating to seal the porous surface, ensuring optimal heat retention and moisture distribution.
Conical condensation cycle
The tagine pot's distinct conical lid creates a unique condensation cycle, directing steam to drip back onto the food, enhancing moisture retention and flavor infusion during slow-cooking. In contrast, a traditional clay pot, with its flat lid, allows less efficient condensation, resulting in a different slow-cooking dynamic that may require more frequent liquid additions.
Subterranean heat retention
Clay pots and tagine pots both excel in retaining subterranean heat, ensuring even slow-cooking by gradually distributing warmth throughout the vessel. The thick walls of clay pots absorb and radiate heat steadily, while tagines' conical lids trap steam and heat inside, enhancing moisture retention and flavor infusion during extended cooking.
Radiant braising
Clay pots and tagine pots excel in radiant braising by evenly distributing heat and retaining moisture during slow-cooking, enhancing the tenderness and flavor of meats and vegetables. The tagine's conical lid promotes condensation, cycling steam back to the food, while the traditional clay pot's porous material allows gradual heat penetration, both optimizing slow-cooked dishes.
Aroma encapsulation dome
Clay pots and tagine pots both excel in slow-cooking by trapping steam and aromas, but the tagine's conical dome uniquely channels condensation back onto the food, enhancing flavor infusion. This specialized shape ensures continuous moisture circulation, preserving the dish's aroma while tenderizing ingredients over low heat.
Thermal gradient diffusion
Clay pots and tagine pots both excel in slow-cooking by providing even heat distribution, but tagines feature a conical lid that promotes superior thermal gradient diffusion through steam condensation and circulation. This design enhances moisture retention and flavor concentration, making tagines particularly effective for slow-cooking stews and braised dishes compared to traditional clay pots.
Clay pot vs Tagine pot for slow-cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com