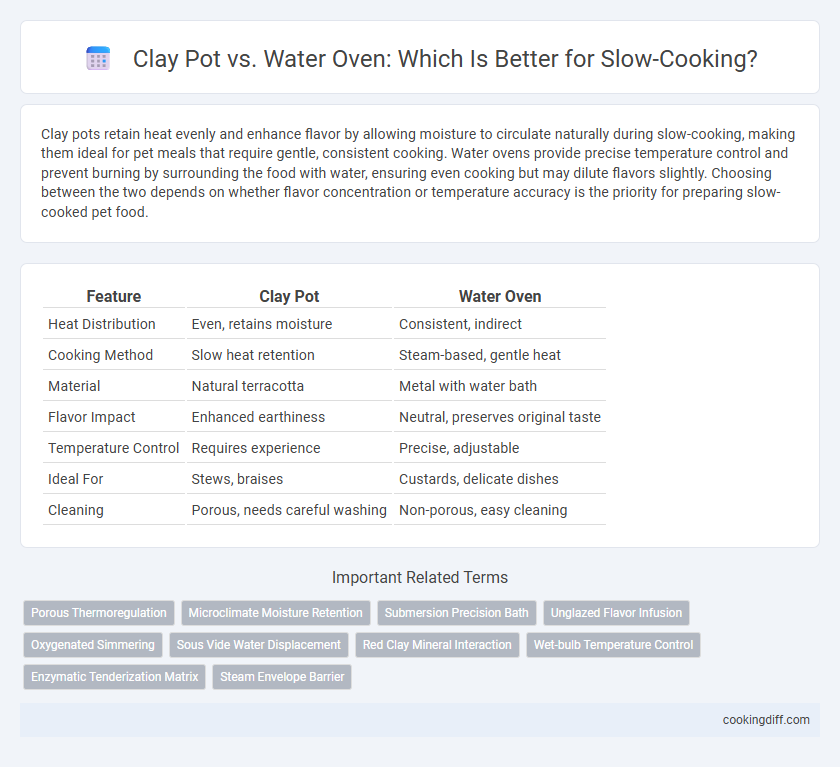
Clay pots retain heat evenly and enhance flavor by allowing moisture to circulate naturally during slow-cooking, making them ideal for pet meals that require gentle, consistent cooking. Water ovens provide precise temperature control and prevent burning by surrounding the food with water, ensuring even cooking but may dilute flavors slightly. Choosing between the two depends on whether flavor concentration or temperature accuracy is the priority for preparing slow-cooked pet food.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Clay Pot | Water Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Distribution | Even, retains moisture | Consistent, indirect |
| Cooking Method | Slow heat retention | Steam-based, gentle heat |
| Material | Natural terracotta | Metal with water bath |
| Flavor Impact | Enhanced earthiness | Neutral, preserves original taste |
| Temperature Control | Requires experience | Precise, adjustable |
| Ideal For | Stews, braises | Custards, delicate dishes |
| Cleaning | Porous, needs careful washing | Non-porous, easy cleaning |
Introduction: Clay Pot vs Water Oven for Slow-Cooking
Slow-cooking enhances flavors and tenderness by maintaining low, consistent heat over extended periods. Clay pots and water ovens offer distinct methods to achieve this, each impacting moisture retention and heat distribution differently.
- Clay Pot - Retains heat evenly and enhances moisture through its porous nature, enriching dishes with deep, earthy flavors.
- Water Oven - Uses steam to provide uniform heat, preventing drying and ensuring gentle cooking temperatures.
- Cooking Efficiency - Clay pots excel in gradual heat absorption, while water ovens offer precise temperature control for slow-cooking tasks.
Understanding Clay Pot Slow-Cooking Techniques
| Clay pot slow-cooking relies on porous earthenware that absorbs and evenly distributes moisture, enhancing flavor and tenderness of meats and vegetables. The unique heat retention properties of clay allow for low, consistent temperatures over long periods, ideal for braising and stewing. Unlike water ovens, clay pots do not require water baths, making them energy-efficient and preserving natural juices within the food. |
What Is a Water Oven and How Does It Work?
A water oven, also known as a bain-marie or water bath, uses gentle steam to cook food slowly and evenly. This method maintains consistent temperatures, making it ideal for delicate dishes and precise slow-cooking techniques.
Unlike a clay pot, which retains heat through its porous material, a water oven surrounds the food container with hot water, preventing direct heat contact. This eliminates the risk of burning and preserves moisture, enhancing flavor and texture during slow cooking.
Heat Distribution: Clay Pot vs Water Oven
Clay pots provide uneven heat distribution due to their porous material, which absorbs and slowly releases heat, creating a natural but variable cooking environment. This results in localized hot spots ideal for browning but requires careful monitoring to avoid burning.
Water ovens, or sous vide systems, offer precise and uniform heat distribution by circulating water at a consistent temperature around the food. This controlled environment ensures even cooking throughout, preventing overcooking and retaining moisture effectively.
Flavor Development in Clay Pot Cooking
How does flavor development in clay pot cooking compare to a water oven? Clay pot cooking enhances flavor by allowing moisture to circulate within the porous material, intensifying the natural taste of ingredients. This slow heat penetration in clay pots creates rich, well-rounded dishes that are often more aromatic than those prepared in a water oven.
Precision and Consistency in Water Oven Slow-Cooking
Water ovens provide exceptional precision by maintaining a consistent temperature throughout the slow-cooking process. This stability ensures even heat distribution, reducing the risk of overcooking or undercooking compared to clay pots.
- Temperature Control - Water ovens use digital thermostats for exact temperature regulation.
- Consistent Heat - The water bath evenly surrounds the cooking vessel, preventing hot spots.
- Reliable Results - Precision leads to predictable textures and flavors every time.
Water ovens are ideal for chefs seeking consistent and precise slow-cooking results beyond the variability of clay pot methods.
Energy Efficiency: Comparing Clay Pot and Water Oven
Clay pots retain heat effectively due to their porous material, allowing slow-cooking with minimal energy input. Water ovens provide consistent, gentle heat through water conduction but often require more energy to maintain temperature over time.
- Clay pots use residual heat - Their ability to absorb and slowly release heat reduces the need for continuous energy supply.
- Water ovens demand constant heating - Maintaining the water temperature requires ongoing energy, increasing overall consumption.
- Energy efficiency depends on cooking duration - Longer cooking periods favor clay pots for lower energy use, whereas shorter times may be more efficient with water ovens.
Suitability for Different Ingredients and Recipes
Clay pots retain heat evenly and enhance the flavor of ingredients like meats and vegetables through gradual moisture absorption, making them ideal for stews and braised dishes. Water ovens provide precise temperature control and gentle, consistent heat, perfect for delicate ingredients such as custards, fish, and slow-cooked eggs. Choosing between clay pots and water ovens depends on recipe complexity and ingredient sensitivity to moisture and temperature fluctuations.
Maintenance and Durability of Clay Pots vs Water Ovens
Clay pots require careful handling to prevent cracks and chipping, with regular seasoning to maintain their porous surface, ensuring optimal heat distribution. Water ovens, typically made from stainless steel or other durable materials, demand minimal maintenance and resist rust, offering longer-lasting reliability.
Maintaining clay pots involves gentle cleaning with non-abrasive materials to avoid damage and periodic re-seasoning to preserve their cooking properties. Water ovens feature sturdy construction that withstands high temperatures without warping and can be easily cleaned using standard detergents. Their durability and low upkeep make water ovens a practical choice for frequent slow-cooking enthusiasts.
Related Important Terms
Porous Thermoregulation
Clay pots enhance slow-cooking through their porous thermoregulation, allowing gradual moisture absorption and even heat distribution that tenderizes ingredients without drying them out. In contrast, water ovens maintain a consistent external temperature but lack the clay pot's natural breathability, resulting in less nuanced heat control and moisture retention.
Microclimate Moisture Retention
Clay pots create a microclimate that retains moisture by trapping steam within their porous walls, enhancing slow-cooked dishes with consistent hydration and tenderness. Water ovens maintain a humid environment through external water baths, ensuring even heat distribution and preventing drying, but lack the direct steam interaction unique to clay pot cooking.
Submersion Precision Bath
Clay pots offer natural heat retention and flavor enhancement for slow-cooking, while water ovens, specifically Submersion Precision Baths, provide precise temperature control critical for consistent results. The Submersion Precision Bath maintains exact cooking temperatures in a water-filled container, ensuring uniform heat distribution and preventing overcooking, which contrasts with the more variable heat environment of a clay pot.
Unglazed Flavor Infusion
Unglazed clay pots enhance slow-cooking by allowing porous surfaces to absorb and release moisture evenly, intensifying flavor infusion in dishes. Water ovens provide consistent heat but lack the natural breathability and subtle mineral contributions that unglazed clay imparts to slow-cooked meals.
Oxygenated Simmering
Clay pots enhance slow-cooking through oxygenated simmering, which allows small amounts of oxygen to permeate the porous material, enriching flavors and tenderizing ingredients more effectively than water ovens. Water ovens maintain a stable temperature via water bath but lack the subtle oxygen exchange that clay pots provide, resulting in less nuanced and less aromatic dishes.
Sous Vide Water Displacement
Clay pots provide even, gentle heat retention ideal for slow-cooking, whereas water ovens, particularly those using sous vide water displacement methods, maintain precise temperature control for consistent results. Sous vide water displacement ensures airtight sealing to preserve moisture and flavor by removing air bubbles, enhancing the slow-cooking process.
Red Clay Mineral Interaction
Red clay mineral in clay pots enhances slow-cooking by evenly distributing heat and retaining moisture, which intensifies flavors and tenderizes food better than a water oven's indirect steaming method. This natural mineral interaction also imparts subtle earthy notes to dishes, creating a unique taste profile not achievable with water ovens.
Wet-bulb Temperature Control
Clay pots naturally maintain stable wet-bulb temperatures through porous walls that allow moisture evaporation, creating a humid cooking environment ideal for slow-cooking. Water ovens precisely regulate wet-bulb temperature by circulating warm water, ensuring consistent heat and moisture levels for uniform slow-cooking results.
Enzymatic Tenderization Matrix
Clay pots create a porous environment that retains moisture and evenly distributes heat, enhancing enzymatic tenderization by maintaining optimal temperatures for collagen breakdown. Water ovens provide precise temperature control and consistent humidity, supporting enzymatic activity but lacking the natural breathability that characterizes the enzymatic tenderization matrix in clay pot cooking.
Clay pot vs water oven for slow-cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com