Pressure cookers deliver faster cook times and high heat pressure, breaking down tough pet food ingredients efficiently, while stoneware inserts provide gentle, even heat ideal for slow and steady cooking. Stoneware maintains moisture and flavor without risk of burning, making it suitable for delicate recipes. Selecting between these depends on whether speed or traditional slow-cooking texture and taste are priorities for your pet's meal preparation.
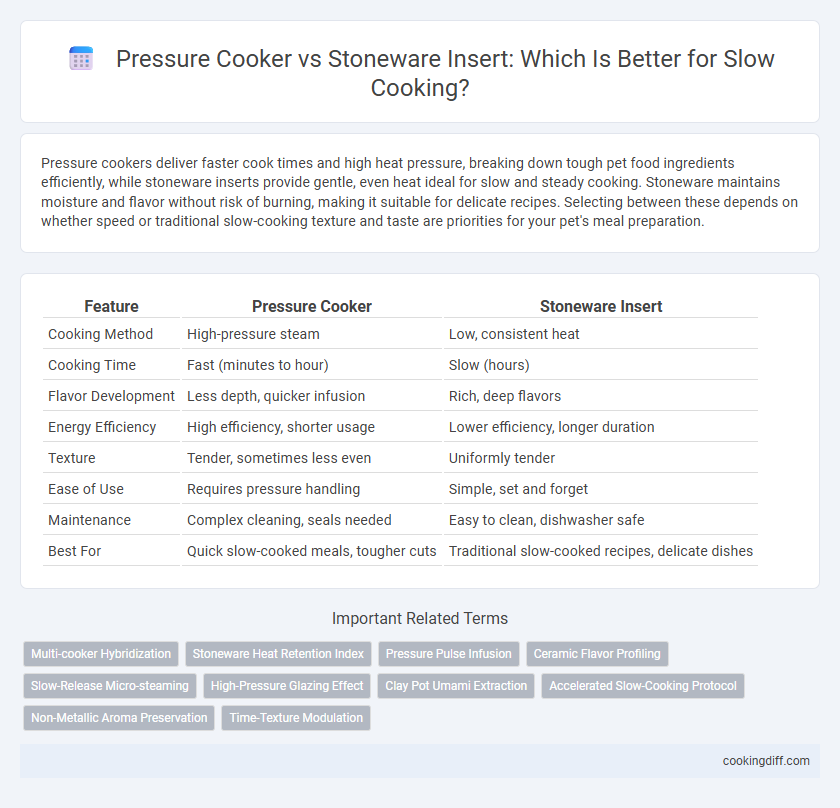
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pressure Cooker | Stoneware Insert |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | High-pressure steam | Low, consistent heat |
| Cooking Time | Fast (minutes to hour) | Slow (hours) |
| Flavor Development | Less depth, quicker infusion | Rich, deep flavors |
| Energy Efficiency | High efficiency, shorter usage | Lower efficiency, longer duration |
| Texture | Tender, sometimes less even | Uniformly tender |
| Ease of Use | Requires pressure handling | Simple, set and forget |
| Maintenance | Complex cleaning, seals needed | Easy to clean, dishwasher safe |
| Best For | Quick slow-cooked meals, tougher cuts | Traditional slow-cooked recipes, delicate dishes |
Introduction to Slow-Cooking Methods
Slow-cooking preserves flavors and tenderizes ingredients using low temperatures over extended periods. Pressure cookers and stoneware inserts represent two distinct methods for achieving slow-cooked meals with unique benefits.
- Pressure Cooker - Utilizes steam pressure to reduce cooking time while maintaining moisture and flavor.
- Stoneware Insert - Provides even heat distribution for gradual, consistent cooking in slow cookers or ovens.
- Slow-Cooking Benefits - Enhances texture and infuses spices deeply into dishes with minimal active supervision.
Choosing between pressure cookers and stoneware inserts depends on desired cooking speed and flavor development.
What Is a Pressure Cooker?
A pressure cooker is a sealed pot that cooks food quickly by trapping steam and increasing internal pressure, which raises the boiling point of water. It significantly reduces cooking time compared to traditional slow-cooking methods, while retaining nutrients and flavors. Ideal for tenderizing tough cuts of meat, it offers a versatile alternative to stoneware inserts in slow-cooking recipes.
Understanding Stoneware Inserts
Stoneware inserts provide even heat distribution, making them ideal for slow-cooking stews, casseroles, and braises. Their porous nature helps retain moisture, resulting in tender and flavorful dishes.
Unlike pressure cookers, stoneware inserts do not build pressure, allowing for gentle, consistent cooking over extended periods. They are compatible with most slow cookers and offer easy cleanup due to their non-stick surfaces.
Cooking Speeds: Pressure Cooker vs Stoneware Insert
Pressure cookers drastically reduce cooking times by using high-pressure steam, enabling meals to be ready in a fraction of the time compared to traditional slow-cooking methods. Stoneware inserts, designed for low and slow heat retention, deliver consistent, gentle cooking which enhances flavors over extended periods.
- Pressure Cooker Efficiency - Cooks foods in 20-30 minutes by raising boiling points and trapping steam.
- Stoneware Slow-cook Timing - Typically requires 4-8 hours for optimal tenderness and flavor development.
- Heat Distribution - Stoneware provides even slow heat, while pressure cookers rely on sealed high pressure for speed.
Flavor Development and Food Texture
Pressure cookers rapidly infuse flavors by sealing steam and maintaining high heat, while stoneware inserts slowly develop deeper, more nuanced flavors through gradual heat distribution. The texture of food cooked in a pressure cooker tends to be tender but can sometimes become overly soft, whereas stoneware ensures a consistent, tender texture without overcooking.
- Pressure Cooker Flavor Development - High-pressure steam accelerates chemical reactions, intensifying and merging flavors quickly.
- Stoneware Insert Flavor Development - Slow, even heat allows complex taste compounds to form, enhancing depth and richness.
- Food Texture Differences - Pressure cooking softens food swiftly but risks mushiness; stoneware maintains structure with gentle, steady cooking.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Which option, pressure cooker or stoneware insert, offers better energy efficiency for slow-cooking? Pressure cookers significantly reduce cooking time and energy consumption by cooking food at higher pressures and temperatures. Stoneware inserts retain heat well but require longer cooking durations, resulting in higher overall energy usage.
Convenience and Ease of Use
Pressure cookers offer rapid cooking times with straightforward controls, making them highly convenient for busy households. Stoneware inserts provide a simple setup and easy cleanup, enhancing overall ease of use during slow-cooking.
Pressure cookers require monitoring and release of pressure, which may add slight complexity compared to the plug-and-play nature of stoneware inserts. Stoneware inserts fit directly into slow cookers and maintain even heat distribution, reducing active cooking time. Both options deliver convenience but cater to different user preferences regarding time management and operational simplicity.
Safety Considerations for Each Appliance
Pressure cookers are designed with multiple safety mechanisms such as locking lids, pressure release valves, and gasket seals to prevent accidents caused by high pressure. Stoneware inserts, commonly used in slow cookers, operate at low temperatures and pose minimal risk, eliminating concerns about explosions or sudden pressure changes. Users should regularly inspect their pressure cookers for wear and ensure stoneware is free from cracks to maintain safe cooking conditions.
Cleaning and Maintenance Differences
Pressure cookers typically feature stainless steel or aluminum interiors that resist staining and are dishwasher safe, making cleaning quick and efficient. Stoneware inserts, although excellent for flavor retention, require gentle hand washing to prevent chipping and often need seasoning to maintain their surface.
Maintenance for pressure cookers involves regularly checking sealing rings and valves to ensure proper function and safety. Stoneware inserts demand careful handling to avoid cracks and may develop mineral deposits if not dried thoroughly after washing.
Related Important Terms
Multi-cooker Hybridization
Pressure cookers and stoneware inserts represent key components in the multi-cooker hybridization trend, combining rapid pressure cooking with the even heat distribution and moisture retention of stoneware for superior slow-cooking results. This fusion allows users to seamlessly switch between high-pressure cooking and gentle, consistent slow cooking, optimizing flavor development and tenderness in a single appliance.
Stoneware Heat Retention Index
Stoneware inserts offer superior heat retention due to their dense ceramic composition, maintaining consistent low temperatures essential for slow-cooking. In contrast, pressure cookers rapidly build and release steam but lack the prolonged, even heat distribution characteristic of stoneware's Heat Retention Index, making stoneware ideal for recipes requiring gentle, sustained heat.
Pressure Pulse Infusion
Pressure cooker slow-cooking utilizes Pressure Pulse Infusion technology to rapidly penetrate flavors and tenderize meats by cycling pressure and releasing steam, significantly reducing cooking time compared to traditional stoneware inserts. Stoneware slow-cooking allows for even heat distribution and gentle cooking but lacks the accelerated infusion process, resulting in longer cook times and less intense flavor permeation.
Ceramic Flavor Profiling
A stoneware insert enhances slow-cooked meals by evenly distributing heat and preserving moisture, which allows ceramic flavor profiling to develop rich, deep, and nuanced tastes in stews and braises. In contrast, a pressure cooker fast-tracks cooking but may limit the gradual flavor layering associated with ceramic stoneware, resulting in less complex aromatic profiles.
Slow-Release Micro-steaming
Pressure cookers utilize high-pressure steam to rapidly cook food, but their sealed environment limits slow-release micro-steaming essential for delicate slow-cooking processes. Stoneware inserts excel in slow-release micro-steaming by allowing gradual moisture evaporation and even heat distribution, enhancing flavor development and tenderizing ingredients over extended cooking times.
High-Pressure Glazing Effect
High-pressure glazing in stoneware inserts enhances flavor penetration by creating a semi-permeable barrier that retains moisture and nutrients during slow-cooking. Pressure cookers, while efficient in reducing cook time, lack this glazing effect, resulting in less depth of flavor and texture development compared to stoneware slow-cooking.
Clay Pot Umami Extraction
Pressure cookers use high heat and pressure to rapidly break down food fibers, whereas stoneware inserts, especially clay pots, enhance slow-cooked dishes by promoting gradual umami extraction through porous material that evenly retains moisture and heat. Clay pot slow-cooking preserves deep flavors and tender textures, maximizing natural umami compounds that pressure cookers often cannot replicate due to their accelerated cooking process.
Accelerated Slow-Cooking Protocol
Pressure cookers significantly reduce cooking time by increasing internal pressure and temperature, enabling an accelerated slow-cooking protocol that retains moisture and nutrients effectively. Stoneware inserts provide even heat distribution for traditional slow-cooking but lack the pressure cooker's speed and ability to tenderize tougher cuts efficiently.
Non-Metallic Aroma Preservation
Pressure cookers accelerate cooking by using high pressure and heat but may alter the natural aromas of ingredients, while stoneware inserts, made from non-metallic materials, excel in preserving the authentic flavors and scents during slow-cooking. Stoneware's porous surface absorbs and retains aromas, enhancing the overall taste profile without metallic interference, making it ideal for dishes where fragrance retention is paramount.
Pressure Cooker vs Stoneware Insert for slow-cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com