Slow cookers maintain a steady low temperature, perfect for tenderizing tougher cuts of meat over several hours with minimal supervision. Sous vide uses precise temperature control by cooking food in a water bath, preserving moisture and enhancing flavor with exact doneness. While slow cookers offer convenience and hands-off cooking, sous vide excels in consistency and texture precision for slow-cooked dishes.
Table of Comparison
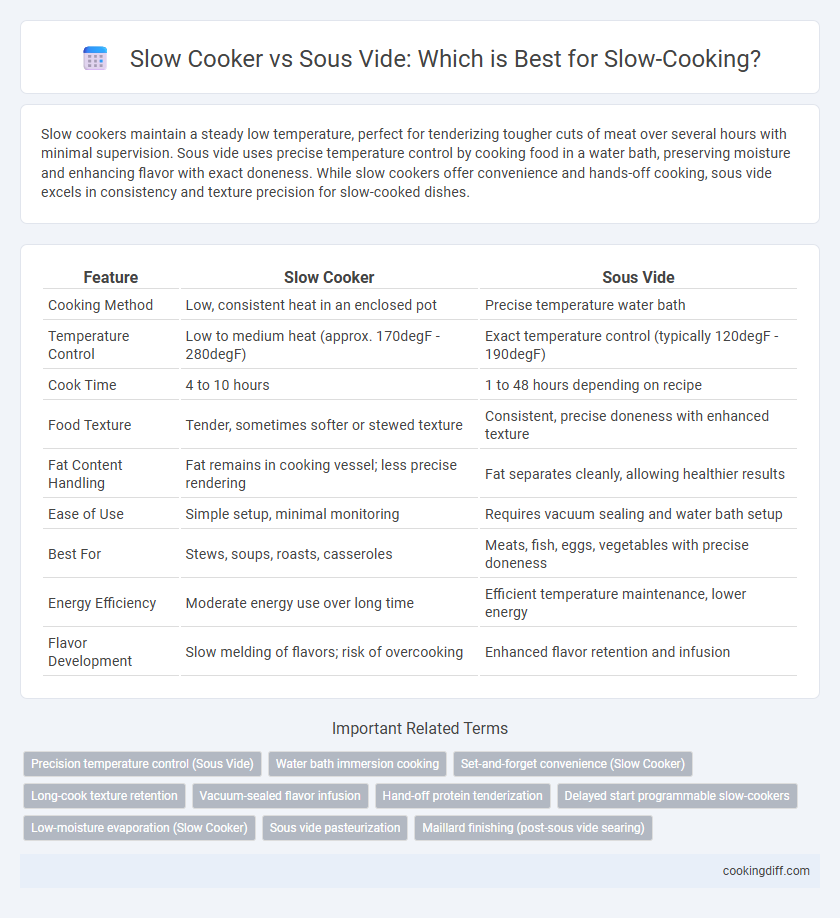
| Feature | Slow Cooker | Sous Vide |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Low, consistent heat in an enclosed pot | Precise temperature water bath |
| Temperature Control | Low to medium heat (approx. 170degF - 280degF) | Exact temperature control (typically 120degF - 190degF) |
| Cook Time | 4 to 10 hours | 1 to 48 hours depending on recipe |
| Food Texture | Tender, sometimes softer or stewed texture | Consistent, precise doneness with enhanced texture |
| Fat Content Handling | Fat remains in cooking vessel; less precise rendering | Fat separates cleanly, allowing healthier results |
| Ease of Use | Simple setup, minimal monitoring | Requires vacuum sealing and water bath setup |
| Best For | Stews, soups, roasts, casseroles | Meats, fish, eggs, vegetables with precise doneness |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate energy use over long time | Efficient temperature maintenance, lower energy |
| Flavor Development | Slow melding of flavors; risk of overcooking | Enhanced flavor retention and infusion |
Introduction to Slow Cooker and Sous Vide Methods
| The slow cooker uses consistent low heat for hours, ideal for tenderizing tough cuts of meat with minimal attention. Sous vide requires precise temperature control by immersing vacuum-sealed food in a water bath, ensuring even cooking and maintaining moisture. Both methods excel in slow-cooking but differ in technique, equipment, and texture outcomes. |
How Each Method Works: Slow Cooker vs Sous Vide
Slow cookers use low, consistent heat over several hours to gradually tenderize ingredients, while sous vide employs precise temperature control by immersing vacuum-sealed food in a water bath. Both methods excel at maintaining moisture but differ significantly in technique and temperature accuracy.
- Slow Cooker Operation - Utilizes electric heating elements to maintain temperatures typically between 170degF and 280degF for extended periods.
- Sous Vide Mechanism - Circulates water at exact temperatures, often within 1degF of the target, to cook food uniformly and retain juices.
- Cooking Environment - Slow cookers expose food to air inside a sealed pot, whereas sous vide seals food in airtight bags submerged in water.
Flavor and Texture Results: A Comparative Analysis
Slow cookers tenderize meats by using consistent, low heat over several hours, resulting in rich, hearty flavors and soft textures. Sous vide precisely controls temperature with water circulation, enhancing flavor infusion and maintaining perfect texture without overcooking.
- Consistent Heat Distribution - Slow cookers apply steady heat that breaks down connective tissue, creating tender dishes with deep, robust flavors.
- Precise Temperature Control - Sous vide ensures precise temperature management, preserving moisture and achieving uniform textures throughout.
- Flavor Infusion - Sous vide cooking in vacuum-sealed bags intensifies flavor penetration compared to the prolonged, open-air slow cooking process.
Sous vide excels at maintaining exact textures and enhanced flavors while slow cookers offer convenience and classic slow-cooked taste.
Equipment Costs and Accessibility
Slow cookers generally have a lower initial cost, typically ranging from $30 to $100, making them an accessible option for most home cooks. Sous vide machines often start around $100 and can exceed $300 for advanced models, which may present a higher investment barrier.
Slow cookers are widely available in most retail stores and online platforms, making them easy to purchase and replace. Sous vide equipment requires a precision immersion circulator and vacuum sealers, which can be less common in local stores and more reliant on specialty or online shopping.
Cooking Time and Convenience
Slow cookers typically require 4 to 10 hours of cooking time, offering a hands-off approach ideal for busy schedules. Sous vide devices cook food at precise temperatures for extended periods, often ranging from 1 to 48 hours, ensuring consistent texture and flavor. Slow cookers provide greater convenience with simple settings, while sous vide requires additional equipment and food sealing but delivers exceptional precision.
Nutritional Impact of Both Techniques
Slow cookers maintain nutrients by cooking at lower temperatures for extended periods, preserving vitamins such as B-complex and minerals without significant degradation. The gentle heat reduces the loss of water-soluble nutrients often lost in high-temperature cooking methods.
Sous vide cooking precisely controls temperature, minimizing nutrient loss by sealing food in vacuum bags that prevent oxidation and leaching of vitamins and minerals. Research indicates sous vide retains more antioxidants and heat-sensitive nutrients compared to traditional slow cooking.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Slow cookers typically use less electricity than sous vide machines, operating at lower wattages around 100 to 250 watts. This makes slow cookers more energy-efficient for extended cooking times.
Sous vide devices rely on precise temperature control and water circulation, consuming about 800 to 1200 watts, which can increase energy usage over long periods. However, sous vide offers consistent heat distribution and reduces food waste by preserving nutrition and texture. Slow cookers excel in simplicity and lower power consumption, making them ideal for energy-conscious users.
Versatility: What Can You Cook in Each?
Slow cookers excel in versatility by handling a wide range of dishes including stews, soups, roasts, and even desserts like puddings and cakes. Sous vide offers precise temperature control, making it ideal for cooking proteins such as steak, chicken, and fish with consistent doneness, as well as vegetables and eggs. While slow cookers are perfect for one-pot meals with minimal supervision, sous vide shines in delivering restaurant-quality textures and flavors through vacuum-sealed cooking.
Safety Considerations and Food Handling
Slow cookers maintain temperatures above 140degF (60degC), ensuring safe bacterial reduction when used properly. Sous vide cooking requires precise temperature control and vacuum sealing to prevent anaerobic bacterial growth and foodborne illnesses.
- Temperature control is critical - Slow cookers sustain consistent heat, while sous vide demands exact temperature settings to avoid unsafe zones.
- Proper food handling minimizes contamination risk - Vacuum sealing in sous vide limits exposure to oxygen, whereas slow cooking relies on sealed lids and timely food addition.
- Storage and reheating guidelines differ - Sous vide foods should be cooled rapidly and reheated safely, while slow cooker meals benefit from immediate consumption or proper refrigeration.
Related Important Terms
Precision temperature control (Sous Vide)
Sous vide offers unmatched precision temperature control by cooking food sealed in a water bath at exact, consistent temperatures, ensuring even doneness and perfect texture. In contrast, slow cookers rely on less precise heat settings that can result in variable cooking results and less control over outcome consistency.
Water bath immersion cooking
Water bath immersion cooking in sous vide offers precise temperature control, ensuring even cooking and retention of moisture in slow-cooked dishes, unlike slow cookers that rely on indirect heat and can result in varying temperature consistency. Sous vide's sealed environment minimizes flavor loss and prevents oxidation, making it ideal for delicate proteins and complex textures compared to the traditional slow cooker's convection-style heat.
Set-and-forget convenience (Slow Cooker)
Slow cookers offer unmatched set-and-forget convenience, allowing users to prepare meals with minimal supervision for hours, making them ideal for busy schedules and hands-off cooking. Unlike sous vide, which requires precise temperature control and equipment setup, slow cookers simplify the slow-cooking process by providing consistent heat in a single appliance.
Long-cook texture retention
Slow cookers maintain moisture over extended cooking times by using consistent low heat and sealed environments, resulting in tender, fall-apart textures ideal for stews and braises. Sous vide offers precise temperature control with vacuum-sealed bags, preserving texture and nutrients by cooking evenly without moisture loss, making it superior for delicate proteins requiring exact doneness and texture retention.
Vacuum-sealed flavor infusion
Vacuum-sealed flavor infusion in sous vide cooking enhances taste by locking in aromas and juices during precise, low-temperature slow-cooking, resulting in tender, evenly cooked dishes. Slow cookers rely on steady heat over hours, which softens ingredients but lacks the airtight seal that intensifies flavor concentration found in vacuum-sealed sous vide methods.
Hand-off protein tenderization
Slow cookers use low, consistent heat to break down collagen in proteins over several hours, resulting in tender, pull-apart textures ideal for tougher cuts like brisket or pork shoulder. Sous vide offers precise temperature control that gently tenderizes proteins by cooking them evenly in a water bath, preserving moisture and flavor while allowing for customized doneness levels.
Delayed start programmable slow-cookers
Delayed start programmable slow-cookers offer precise timing control, allowing meals to begin cooking hours after being set, which differs from sous vide that requires continuous temperature immersion from the start. This feature enhances convenience and energy efficiency in slow-cooking by enabling preparation flexibility without compromising food safety or texture.
Low-moisture evaporation (Slow Cooker)
Slow cookers minimize low-moisture evaporation by trapping steam and moisture within a sealed environment, ensuring food remains tender and flavorful over extended cooking periods. This contrasts with sous vide, which relies on precise temperature control in a water bath to prevent moisture loss but lacks the sealed steam environment characteristic of slow cookers.
Sous vide pasteurization
Sous vide pasteurization ensures precise temperature control to safely eliminate pathogens in slow-cooked foods, preserving moisture and texture better than traditional slow cookers. Unlike slow cookers, sous vide maintains consistent low temperatures through vacuum-sealed bags, delivering pasteurization that meets strict food safety standards without overcooking.
Slow cooker vs sous vide for slow-cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com