Stewing relies on long, gentle simmering to break down tougher cuts of meat, creating rich, flavorful dishes through gradual flavor melding. Precision slow-cooking uses controlled temperatures and timing, often with modern appliances like sous vide, to ensure consistent texture and optimal tenderness without overcooking. This method enhances flavor retention and nutritional value while reducing the risk of drying or uneven cooking compared to traditional stewing.
Table of Comparison
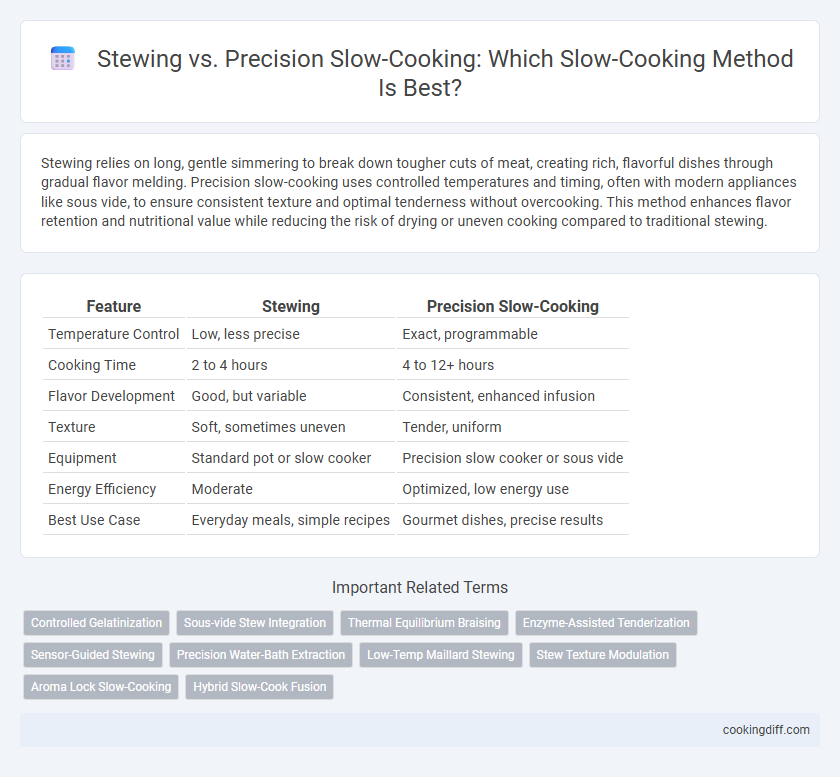
| Feature | Stewing | Precision Slow-Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Low, less precise | Exact, programmable |
| Cooking Time | 2 to 4 hours | 4 to 12+ hours |
| Flavor Development | Good, but variable | Consistent, enhanced infusion |
| Texture | Soft, sometimes uneven | Tender, uniform |
| Equipment | Standard pot or slow cooker | Precision slow cooker or sous vide |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate | Optimized, low energy use |
| Best Use Case | Everyday meals, simple recipes | Gourmet dishes, precise results |
Introduction: Understanding Traditional Stewing and Precision Slow-Cooking
Stewing is a traditional slow-cooking method that involves simmering ingredients in liquid over low heat for an extended period, resulting in tender textures and rich flavors. Precision slow-cooking uses technology such as sous vide to maintain exact temperatures, enhancing consistency and nutrient retention.
- Stewing - Combines meat and vegetables cooked slowly in a pot with liquid to develop deep flavors and tenderize tough cuts.
- Precision slow-cooking - Utilizes controlled temperature devices ensuring optimal cooking conditions for consistent results every time.
- Comparison - Stewing emphasizes traditional flavor development while precision slow-cooking prioritizes accuracy, texture preservation, and nutrient conservation.
Core Principles: What Sets Stewing Apart from Precision Slow-Cooking
Stewing involves cooking food slowly in liquid at low temperatures, allowing flavors to meld and ingredients to tenderize through gentle simmering. Precision slow-cooking, however, uses controlled temperature settings to ensure consistent heat distribution and exact timing for optimal texture and flavor extraction.
Stewing emphasizes traditional techniques with open or covered pots, often requiring manual adjustments to heat, while precision slow-cooking relies on technology such as programmable slow cookers or sous-vide systems. The core difference lies in precision slow-cooking's ability to maintain exact, steady temperatures, minimizing overcooking and enhancing ingredient consistency.
Equipment Essentials for Stewing and Precision Slow-Cooking
What are the essential equipment differences between stewing and precision slow-cooking? Stewing requires a heavy-bottomed pot or Dutch oven that retains heat evenly for consistent simmering. Precision slow-cooking relies on devices like slow cookers or sous-vide machines that maintain exact temperature control for optimal texture and flavor development.
Temperature Control: Comparing Heat Methods
Stewing relies on maintaining a consistent low simmer, typically around 85-95degC (185-203degF), which allows flavors to meld but can risk uneven heat distribution. Precision slow-cooking employs advanced temperature control technology, often precise to within 1degC, ensuring uniform cooking and optimal tenderness. This regulated heat method preserves nutrients and texture better than traditional stewing techniques.
Flavor Development: Stews Versus Sous Vide Results
| Stewing enhances flavor development through prolonged simmering at moderate temperatures, allowing natural juices to blend and intensify, resulting in a rich and hearty taste. |
| Precision slow-cooking methods like sous vide maintain exact low temperatures, preserving delicate flavors and ensuring even seasoning penetration for a more nuanced and consistent profile. |
| While stewing creates robust, melded flavors due to longer cooking durations, sous vide offers superior control over texture and flavor retention, delivering a refined culinary experience. |
Texture Transformation: Meat and Vegetables in Each Technique
Stewing breaks down collagen in meat through prolonged, moist heat, resulting in tender, flavorful chunks with a soft texture that melds well with vegetables. Vegetables in stews often become very soft, sometimes melting into the broth, enhancing the stew's richness and depth.
Precision slow-cooking carefully controls temperature and time to achieve uniform texture transformation, maintaining meat juiciness while preventing overcooking or falling apart. Vegetables retain more structure and distinct flavors, providing a balanced mouthfeel alongside perfectly tender meat.
Practical Applications: Ideal Dishes for Stewing and Precision Slow-Cooking
Stewing excels in creating rich, hearty dishes like beef bourguignon and coq au vin by slowly breaking down tougher cuts of meat with vegetables in a liquid base. Precision slow-cooking, utilizing devices like sous vide, ensures consistent temperature control, making it perfect for tender meats, delicate fish, and custards that require exact doneness without overcooking. Both methods enhance flavor development but suit different culinary goals: stewing for robust, rustic meals and precision slow-cooking for refined, evenly cooked dishes.
Time Efficiency: Cooking Durations and Planning
Stewing typically requires longer cooking durations, often several hours, to break down tough cuts of meat, making it less time-efficient compared to precision slow-cooking. Precision slow-cooking uses technology to maintain exact temperatures, optimizing cooking times and enhancing meal planning by reducing guesswork.
Precision slow-cooking significantly improves time efficiency by allowing cooks to set precise cooking durations tailored to specific recipes, which minimizes overcooking and energy consumption. Unlike traditional stewing, it offers consistent results by evenly distributing heat and maintaining stable temperatures throughout the process. This method supports better meal planning, helping home cooks and professionals synchronize cooking times with daily schedules or service demands.
Nutrient Retention: Health Impacts of Each Method
Stewing involves cooking ingredients submerged in liquid at low temperatures for long periods, which can lead to some nutrient loss, especially water-soluble vitamins. Precision slow-cooking utilizes controlled temperatures and timing to preserve maximum nutrients, enhancing the health benefits of meals.
- Stewing nutrient loss - Water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex diminish due to prolonged heat and liquid exposure.
- Precision slow-cooking retention - Maintains higher levels of heat-sensitive nutrients by minimizing overcooking through precise temperature control.
- Health impact - Precision slow-cooking promotes better nutrient density in foods, supporting improved overall nutritional intake.
Related Important Terms
Controlled Gelatinization
Stewing leverages prolonged simmering to naturally break down collagen into gelatin, enhancing meat tenderness through gradual collagen hydrolysis at moderate temperatures. Precision slow-cooking employs exact temperature control and timing to optimize gelatinization, ensuring consistent texture by preventing overcooking and maintaining moisture balance throughout the cooking process.
Sous-vide Stew Integration
Sous-vide stew integration enhances precision slow-cooking by maintaining a consistent low temperature that evenly breaks down collagen, resulting in tender, flavorful meat without overcooking. Unlike traditional stewing, sous-vide preserves nutrient integrity and intensifies flavor through controlled vacuum-sealed cooking, creating superior texture and depth in a slow-cooked dish.
Thermal Equilibrium Braising
Thermal equilibrium braising ensures the food is cooked evenly at a constant temperature, preserving moisture and enhancing flavor through precise heat control. Stewing combines smaller cuts submerged in liquid, resulting in a quicker cook time but less consistent texture compared to precision slow-cooking methods.
Enzyme-Assisted Tenderization
Stewing leverages prolonged heat to break down collagen but often risks overcooking and nutrient loss, whereas precision slow-cooking employs controlled low temperatures that optimize enzyme-assisted tenderization, preserving texture and flavor. Enzymes like proteases remain active during precise slow-cooking, enhancing meat tenderness more effectively than traditional stewing methods.
Sensor-Guided Stewing
Sensor-guided stewing leverages real-time temperature and moisture sensors to maintain precise cooking conditions, ensuring optimal tenderness and flavor extraction. This advanced slow-cooking method surpasses traditional stewing by minimizing overcooking risks and maximizing nutrient retention through continuous monitoring and adjustment.
Precision Water-Bath Extraction
Stewing involves cooking ingredients slowly in liquid over low heat, allowing flavors to meld but often resulting in variable texture and nutrient retention. Precision slow-cooking using water-bath extraction ensures consistent temperature control, preserving delicate flavors and maximizing nutrient extraction through uniform heat distribution and reduced oxidation.
Low-Temp Maillard Stewing
Low-temp Maillard stewing enhances flavor development by combining the slow-cooking benefits of prolonged heat with controlled browning reactions at temperatures typically between 140degF and 160degF. This method contrasts with precision slow-cooking devices that maintain strict temperature controls but may lack the complex flavor layers created by the gradual Maillard reaction during stewing.
Stew Texture Modulation
Stewing enhances flavor through prolonged simmering, producing tender, well-infused textures, while precision slow-cooking allows meticulous temperature control to achieve consistent, optimal tenderness and texture modulation. Precision slow-cooking minimizes overcooking risks, ensuring evenly cooked results with balanced moisture retention essential for ideal stew texture.
Aroma Lock Slow-Cooking
Stewing involves cooking ingredients slowly in liquid to enhance flavor through long simmering, while precision slow-cooking, such as Aroma Lock Slow-Cooking, uses controlled temperature settings to lock in aroma and nutrients for richer, more tender results. Aroma Lock technology minimizes evaporation and preserves volatile compounds, delivering superior taste and consistent texture compared to traditional stewing methods.
Stewing vs precision slow-cooking for slow-cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com