Traditional smokers use charcoal or wood to create smoke at low temperatures, imparting a rich, smoky flavor to food but often requiring constant attention to maintain heat and smoke levels. Pellet smokers rely on compressed wood pellets and automated heating systems, offering precise temperature control and consistent smoke output for convenience and repeatable results. While traditional smokers excel in flavor complexity, pellet smokers provide ease of use and efficiency for both beginners and experienced cooks.
Table of Comparison
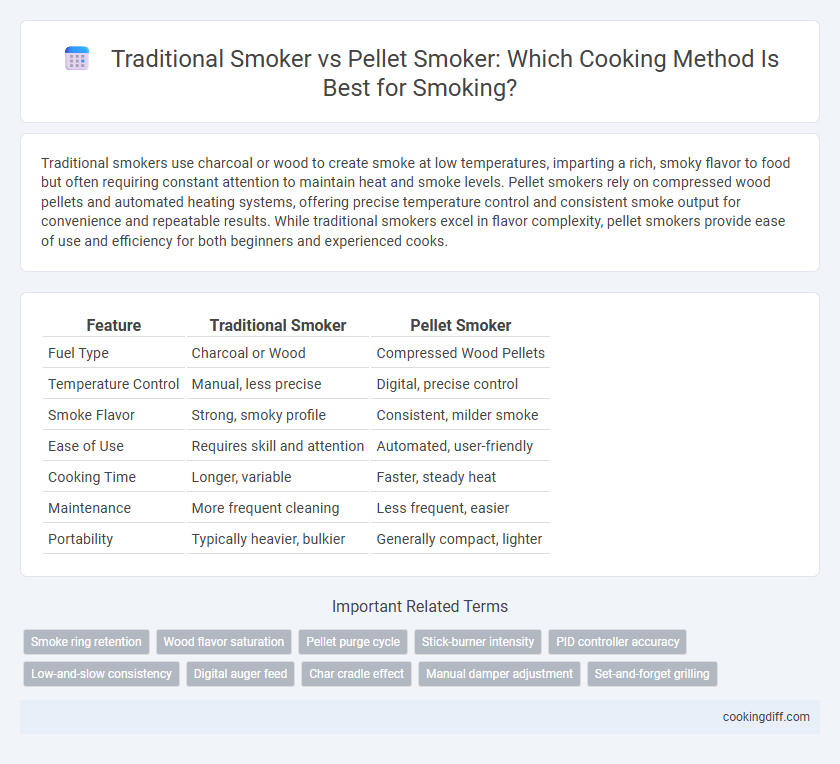
| Feature | Traditional Smoker | Pellet Smoker |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Type | Charcoal or Wood | Compressed Wood Pellets |
| Temperature Control | Manual, less precise | Digital, precise control |
| Smoke Flavor | Strong, smoky profile | Consistent, milder smoke |
| Ease of Use | Requires skill and attention | Automated, user-friendly |
| Cooking Time | Longer, variable | Faster, steady heat |
| Maintenance | More frequent cleaning | Less frequent, easier |
| Portability | Typically heavier, bulkier | Generally compact, lighter |
Introduction to Smoking: Traditional vs Pellet Smokers
Traditional smokers use wood or charcoal to generate heat and smoke, offering an authentic flavor with manual temperature control. Pellet smokers operate with compressed wood pellets, featuring automated temperature regulation for consistent cooking results.
Traditional smoking requires more attention and experience to maintain steady heat, while pellet smokers provide convenience through digital control systems. Both methods enhance food with smoky flavors but differ in user involvement and temperature precision.
Understanding Traditional Smokers: Key Features
Traditional smokers use wood or charcoal as the primary fuel source, imparting rich, smoky flavors to the food through slow, indirect heat. Their design typically includes a water pan, adjustable vents, and a firebox, allowing precise control over temperature and smoke levels during extended cooking sessions.
These smokers rely on manual monitoring, requiring skill to manage airflow and maintain consistent temperatures between 225degF and 275degF for optimal smoking results. The ability to customize wood types and charcoal blends is a key advantage, providing versatile flavor profiles for meats like brisket, ribs, and pulled pork.
Pellet Smokers Explained: Modern Cooking Innovation
| Pellet Smoker | Uses compressed wood pellets as fuel, offering precise temperature control through an automated feeding system that enhances smoke consistency and flavor infusion. |
| Traditional Smoker | Relies on wood or charcoal, requiring manual temperature adjustments, which can lead to inconsistent heat and smoke levels affecting the cooking outcome. |
| Cooking Innovation | Pellet smokers integrate digital controllers to maintain stable cooking environments, simplifying the smoking process and delivering uniform results with less user intervention. |
Flavor Profiles: Wood Chips vs Wood Pellets
Traditional smokers use wood chips that create a rich, intense smoke flavor, with variations depending on the type of wood such as hickory, mesquite, or apple. Pellet smokers utilize compressed wood pellets that offer consistent smoke output, delivering a milder and more controlled flavor profile tailored by the pellet type.
Wood chips in traditional smokers tend to produce a robust, smoky taste that can be adjusted by soaking or direct placement on coals. Pellet smokers provide an automated, steady burn of hardwood pellets, resulting in a cleaner, subtler smoke that enhances meat without overpowering it. This control appeals to cooks seeking precision and ease in flavor management during long smoking sessions.
Temperature Control: Manual vs Digital Precision
Traditional smokers rely on manual adjustments for temperature control, which can lead to fluctuations during cooking. Pellet smokers use digital precision to maintain consistent heat, enhancing cooking accuracy and flavor development.
- Manual Temperature Control - Traditional smokers require physical manipulation of vents and fuel to regulate heat, often demanding constant monitoring.
- Digital Temperature Precision - Pellet smokers utilize automated systems with sensors and controllers to keep the temperature steady throughout the smoking process.
- Consistency and Convenience - Pellet smokers provide more reliable temperature consistency, reducing the risk of overcooking or undercooking compared to manual methods.
Cooking Consistency: Results with Each Method
Traditional smokers rely on wood or charcoal, offering rich, smoky flavors but often require careful temperature control, which can lead to inconsistent cooking results. Pellet smokers use wood pellets and a digital controller to maintain precise temperatures, providing consistent heat and predictable cooking outcomes. This reliable consistency makes pellet smokers ideal for recipes demanding steady, uniform heat throughout the cooking process.
Ease of Use: Setup and Maintenance Comparison
Traditional smokers require manual control of temperature and fuel, which can be time-consuming during setup and cooking. Pellet smokers feature automated temperature control and pellet feeding, simplifying both setup and maintenance.
- Fuel Management - Traditional smokers need constant monitoring and replenishing of charcoal or wood, while pellet smokers use an electric auger for steady pellet delivery.
- Temperature Control - Pellet smokers offer precise digital controls, whereas traditional smokers rely on manual adjustment of vents and dampers.
- Cleaning - Ash removal in traditional smokers is more labor-intensive compared to the relatively cleaner burn and ash trap systems in pellet smokers.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term Investment
Traditional smokers generally require a lower upfront investment compared to pellet smokers, which often cost more due to advanced technology and features. Long-term costs for traditional smokers may be higher because of increased fuel consumption and maintenance needs.
- Upfront Cost - Traditional smokers are typically more affordable initially, making them accessible for budget-conscious users.
- Fuel Efficiency - Pellet smokers use compressed wood pellets that burn more efficiently, reducing ongoing fuel expenses over time.
- Maintenance Expenses - Pellet smokers may have higher maintenance costs due to electronic components, whereas traditional smokers have simpler, often cheaper upkeep.
Choosing between the two depends on weighing the initial purchase price against long-term operational costs and personal cooking preferences.
Flexibility and Versatility in Smoking Techniques
Traditional smokers offer greater flexibility by allowing precise control over wood type, smoke intensity, and heat levels, enabling a range of smoking techniques like cold, hot, and wet smoking. Pellet smokers provide versatility with automated temperature controls and consistent smoke output, ideal for maintaining steady cooking conditions across different recipes. Both methods cater to distinct smoking styles, but traditional smokers excel in customization while pellet smokers prioritize convenience and consistency.
Related Important Terms
Smoke ring retention
Traditional smokers generate a thick, flavorful smoke ring by burning wood or charcoal, creating a chemical reaction that enhances the pink nitrite layer beneath the meat's surface. Pellet smokers, while offering precise temperature control and consistent smoke output, often produce a subtler smoke ring due to the cleaner combustion of compressed wood pellets.
Wood flavor saturation
Traditional smokers infuse food with a robust, deep wood flavor due to slow-burning charcoal and wood chunks creating dense smoke, while pellet smokers offer a more controlled, consistent smoke delivery using compressed wood pellets, resulting in a milder wood flavor saturation. The choice between them affects the intensity and authenticity of wood-smoked taste in dishes.
Pellet purge cycle
Pellet smokers use an automated pellet purge cycle to maintain consistent temperature and reduce ash buildup, offering more precise heat control compared to traditional smokers that rely on manual fuel adjustment. This purge cycle enhances flavor by promoting cleaner combustion and minimizing smoke contaminants during the cooking process.
Stick-burner intensity
Traditional stick-burner smokers use hardwood logs that produce a high-intensity smoke with rich, complex flavors derived from direct combustion, providing precise temperature control but requiring constant attention. Pellet smokers burn compressed wood pellets with a lower, more consistent heat and milder smoke intensity, offering ease of use and automated temperature regulation for steady cooking results.
PID controller accuracy
Traditional smokers rely on manual temperature adjustments, leading to fluctuations that can affect the consistency of cooking, while pellet smokers utilize a PID controller to maintain precise temperature control within +-1degF. This accuracy ensures even heat distribution and consistent smoke output, enhancing flavor profiles and reducing the risk of overcooking or undercooking.
Low-and-slow consistency
Pellet smokers offer precise temperature control and steady smoke output, ensuring consistent low-and-slow cooking that enhances flavor and tenderness. Traditional smokers rely on manual adjustments of charcoal or wood, often leading to fluctuating heat levels and less predictable results during extended cooking sessions.
Digital auger feed
Digital auger feed in pellet smokers offers precise temperature control and consistent smoke output, enhancing flavor uniformity compared to traditional smokers that rely on manual adjustments and indirect heat sources. This technology enables effortless operation by automatically regulating pellet delivery, reducing the risk of overheating or fluctuating smoke levels commonly experienced with traditional smoking methods.
Char cradle effect
The char cradle effect in traditional smokers enhances flavor by allowing slower, indirect heat distribution and steady smoke flow through wood chunks, producing a rich, smoky aroma. Pellet smokers use electrically controlled heat and compressed hardwood pellets, yielding consistent temperature control but less pronounced char cradle effect, resulting in milder smoke profiles.
Manual damper adjustment
Traditional smokers require manual damper adjustment to control airflow and temperature, demanding constant attention to maintain consistent heat levels. Pellet smokers automate airflow and temperature regulation through digital controllers, minimizing the need for manual damper adjustments and providing more precise cooking conditions.
Traditional smoker vs pellet smoker for cooking method. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com