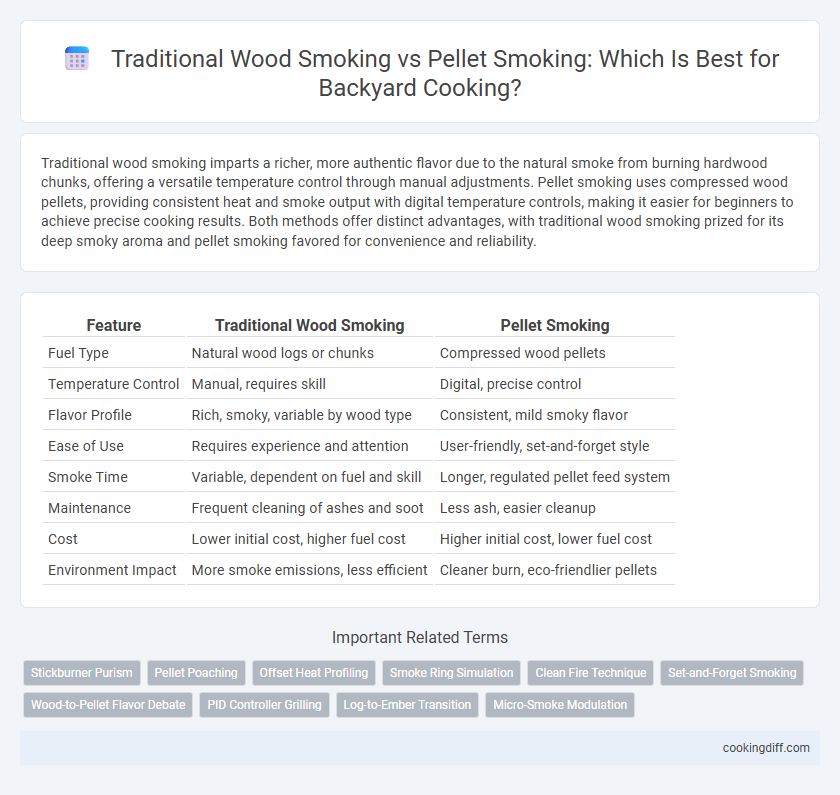
Traditional wood smoking imparts a richer, more authentic flavor due to the natural smoke from burning hardwood chunks, offering a versatile temperature control through manual adjustments. Pellet smoking uses compressed wood pellets, providing consistent heat and smoke output with digital temperature controls, making it easier for beginners to achieve precise cooking results. Both methods offer distinct advantages, with traditional wood smoking prized for its deep smoky aroma and pellet smoking favored for convenience and reliability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Wood Smoking | Pellet Smoking |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Type | Natural wood logs or chunks | Compressed wood pellets |
| Temperature Control | Manual, requires skill | Digital, precise control |
| Flavor Profile | Rich, smoky, variable by wood type | Consistent, mild smoky flavor |
| Ease of Use | Requires experience and attention | User-friendly, set-and-forget style |
| Smoke Time | Variable, dependent on fuel and skill | Longer, regulated pellet feed system |
| Maintenance | Frequent cleaning of ashes and soot | Less ash, easier cleanup |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, higher fuel cost | Higher initial cost, lower fuel cost |
| Environment Impact | More smoke emissions, less efficient | Cleaner burn, eco-friendlier pellets |
Introduction to Traditional Wood Smoking and Pellet Smoking
What are the differences between traditional wood smoking and pellet smoking for backyard cooking? Traditional wood smoking uses natural hardwood chunks or logs to impart a rich, smoky flavor but requires more skill to maintain consistent temperatures. Pellet smoking relies on compressed wood pellets and an electric feed system, offering ease of temperature control and convenience for even cooking results.
The Basics: How Traditional Wood Smoking Works
Traditional wood smoking relies on burning hardwoods to generate smoke and heat, imparting rich flavors to meat. This method requires careful fire management and steady temperature control to ensure consistent cooking results.
- Fuel Source - Uses natural hardwood logs or chunks for authentic smoke flavor generation.
- Heat Control - Adjusted by regulating airflow through vents and managing wood placement.
- Smoke Production - Achieved by smoldering wood rather than open flames for ideal smoke density and flavor.
Pellet Smoking Explained: Technology Meets Flavor
| Pellet Smoking | Utilizes compressed hardwood pellets fed automatically by an electric auger to maintain consistent temperatures and smoke output, enhancing flavor precision in backyard cooking. |
| Technology | Equipped with digital controllers and temperature sensors, pellet smokers allow for precise heat regulation and longer, unattended cook times compared to traditional wood smokers. |
| Flavor Profile | Pellet smoking produces a clean, steady smoke infused with natural wood flavors such as hickory, mesquite, or apple, offering a balanced and customizable taste experience. |
Flavor Profile Differences: Wood vs. Pellet
Traditional wood smoking imparts a rich, deep smokiness with complex flavor notes that vary depending on the type of wood, such as hickory, mesquite, or apple. Pellet smoking offers a more consistent and controlled flavor, often milder and less intense, due to the compressed wood pellets made from hardwood sawdust. Enthusiasts often prefer wood for its bold, authentic taste, while pellet smokers appreciate ease of use and steady heat for balanced cooking results.
Temperature Control and Consistency Compared
Traditional wood smoking offers a rich, smoky flavor but often struggles with maintaining consistent temperature due to variable wood quality and airflow. Pellet smoking uses compressed wood pellets combined with digital controllers to provide precise temperature regulation and consistent heat output.
- Temperature Stability - Pellet smokers maintain steady heat through automated feed systems, minimizing temperature fluctuations common in traditional wood smokers.
- Ease of Control - Digital thermostats in pellet smokers allow users to set exact temperatures, whereas traditional wood smokers require manual adjustments and closer monitoring.
- Flavor Consistency - Traditional wood smoking can produce varying flavors based on wood type and burn rate, while pellet smoking delivers reliable, uniform smoke flavor over time.
Ease of Use: Manual vs. Automated Smoking
Traditional wood smoking requires manual control of temperature and smoke levels, demanding constant attention to maintain the desired cooking environment. Pellet smoking offers automated temperature regulation through digital controllers, simplifying the cooking process.
Manual wood smokers need frequent adjustments to fuel and airflow, which can challenge beginners and extend cooking times. Pellet smokers use compressed wood pellets fed by an electric auger, ensuring consistent heat and smoke output without constant supervision. This automation allows backyard cooks to focus more on preparing food and less on managing the smoker.
Equipment and Cost Considerations
Traditional wood smoking requires a smoker box or barrel, firewood, and charcoal, often making the initial equipment investment moderate but with ongoing costs for wood. Pellet smokers rely on electric-powered pellet feeders and require wood pellets, which can be more expensive upfront but offer consistent temperature control.
Maintenance costs differ as wood smokers often need frequent cleaning from ash buildup, while pellet smokers require occasional pellet replacement and electrical upkeep. Wood smokers lack automated temperature controls, potentially increasing fuel consumption, whereas pellet smokers optimize fuel efficiency through precise digital controllers.
Versatility and Recipe Options
Traditional wood smoking offers a wide range of flavor profiles by using different hardwoods like hickory, mesquite, and apple, making it ideal for authentic barbecue recipes requiring intense smoky aromas. Pellet smoking provides precise temperature control and consistency, allowing backyard cooks to experiment with diverse recipes from low-and-slow brisket to quick grilled vegetables with ease. Both methods enhance versatility, but pellet smokers streamline cooking processes and recipe adaptation for beginners and seasoned pitmasters alike.
Time Commitment: Setup and Cooking Duration
Traditional wood smoking requires lengthy preparation and monitoring, often extending total cook times significantly. Pellet smoking offers more consistent temperature control, reducing active time and simplifying setup for backyard cooking.
- Setup Complexity - Traditional wood smokers need manual fire tending and wood arrangement, increasing prep time.
- Cooking Duration - Wood smoking can take several hours longer due to temperature fluctuations and fuel adjustments.
- Temperature Control - Pellet smokers maintain steady heat via electronic feeds, minimizing time spent overseeing the process.
Choosing between wood and pellet smokers depends on the desired balance of hands-on involvement and time efficiency.
Related Important Terms
Stickburner Purism
Traditional wood smoking uses natural hardwoods that impart rich, smoky flavors and offers a hands-on experience with more control over smoke intensity, while pellet smoking with devices like the Stickburner Purism provides consistent temperature regulation, cleaner combustion, and ease of use through automated feed systems. Stickburner Purism combines the authentic taste of wood smoke with modern technology, allowing backyard chefs to achieve precise cooking results with less effort.
Pellet Poaching
Pellet poaching offers precise temperature control and consistent smoke infusion, enhancing flavor complexity compared to traditional wood smoking methods. Utilizing compressed hardwood pellets, pellet smokers provide efficient fuel use and reduced maintenance, making backyard cooking more convenient and environmentally friendly.
Offset Heat Profiling
Traditional wood smoking utilizes direct offset heat with variable temperature zones influenced by wood size and airflow, creating distinct flavor profiles through uneven heat distribution. Pellet smoking offers consistent offset heat control with computerized regulation, ensuring stable temperature profiling for uniform cooking and predictable smoke intensity.
Smoke Ring Simulation
Traditional wood smoking creates a natural smoke ring through the combustion of wood, releasing nitrogen oxides that react with the meat's myoglobin to produce the characteristic pink hue. Pellet smoking, while offering consistent temperature control and ease of use, often struggles to replicate this authentic smoke ring due to the lower levels of nitrogen oxides generated by compressed wood pellets.
Clean Fire Technique
Traditional wood smoking relies on burning hardwood logs that produce variable smoke quality and more creosote buildup, impacting flavor and requiring frequent fire management. Pellet smoking uses compressed wood pellets with controlled airflow and temperature, ensuring a cleaner fire technique that minimizes smoke impurities for consistent, healthier backyard cooking.
Set-and-Forget Smoking
Traditional wood smoking offers authentic smoky flavors by burning hardwood chunks or logs, requiring periodic attention to maintain temperature and smoke levels, whereas pellet smoking employs automated digital controllers and insulated pellet hoppers to deliver a precise, consistent heat for true set-and-forget smoking convenience, allowing backyard cooks to focus on other tasks without frequent monitoring. Pellet smokers efficiently burn compressed hardwood pellets, providing even smoke distribution and temperature stability that outperforms traditional wood smokers in user-friendliness and time management during long smoking sessions.
Wood-to-Pellet Flavor Debate
Traditional wood smoking infuses meats with a deep, smoky flavor rich in natural resin and organic compounds from burning hardwoods like hickory or mesquite, creating complex taste profiles prized by purists. Pellet smoking offers consistent heat and smoke production through compressed sawdust pellets, producing a milder, more uniform wood flavor that appeals to those seeking convenience without sacrificing the essence of wood smoke.
PID Controller Grilling
Traditional wood smoking relies on manual adjustments to control temperature and smoke levels, often resulting in inconsistent heat, while pellet smoking uses a PID controller to maintain precise temperature by regulating pellet feed rate and airflow, ensuring consistent cooking results. PID controller grilling optimizes fuel efficiency and smoke flavor extraction, making pellet smokers superior for backyard cooking enthusiasts seeking accuracy and convenience.
Log-to-Ember Transition
Traditional wood smoking relies on the natural log-to-ember transition, producing rich, complex smoky flavors through slower, uneven combustion of hardwood logs. Pellet smoking offers a more controlled burn with consistent heat output and steady smoke generation by automatically feeding compressed wood pellets into the firepot, ensuring a reliable log-to-ember conversion ideal for precision cooking.
Traditional Wood Smoking vs Pellet Smoking for backyard cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com