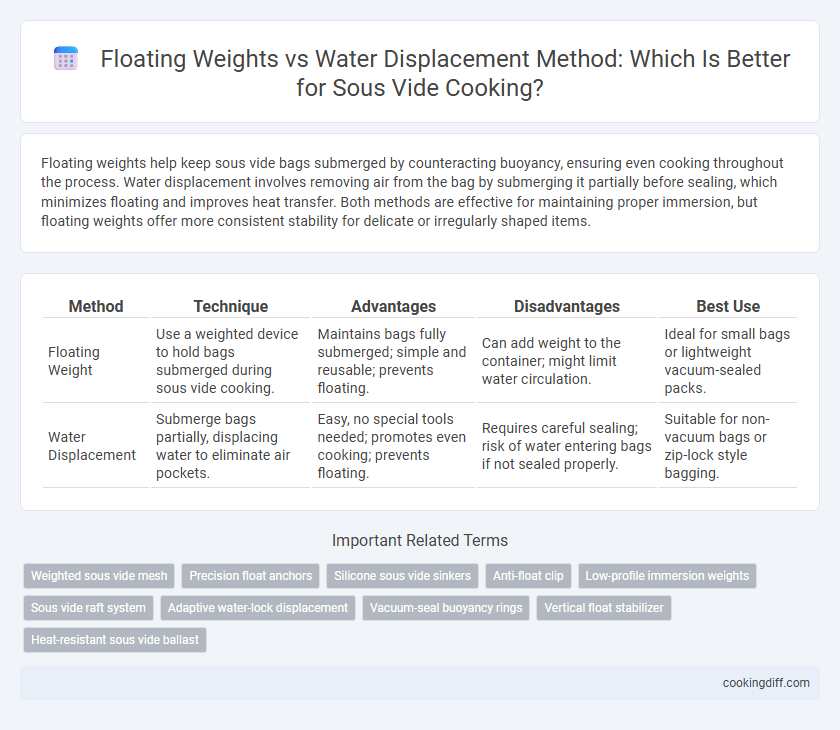
Floating weights help keep sous vide bags submerged by counteracting buoyancy, ensuring even cooking throughout the process. Water displacement involves removing air from the bag by submerging it partially before sealing, which minimizes floating and improves heat transfer. Both methods are effective for maintaining proper immersion, but floating weights offer more consistent stability for delicate or irregularly shaped items.
Table of Comparison
| Method | Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Floating Weight | Use a weighted device to hold bags submerged during sous vide cooking. | Maintains bags fully submerged; simple and reusable; prevents floating. | Can add weight to the container; might limit water circulation. | Ideal for small bags or lightweight vacuum-sealed packs. |
| Water Displacement | Submerge bags partially, displacing water to eliminate air pockets. | Easy, no special tools needed; promotes even cooking; prevents floating. | Requires careful sealing; risk of water entering bags if not sealed properly. | Suitable for non-vacuum bags or zip-lock style bagging. |
Introduction to Sous Vide Cooking
Sous vide cooking requires precise temperature control and proper sealing techniques to achieve perfect results. Floating weights and water displacement are common methods used to keep food bags submerged during the cooking process.
- Floating weight - A weighted device placed on top of the bag to prevent it from floating and ensure even cooking.
- Water displacement - A technique where air is removed by slowly lowering the food bag into water, allowing water pressure to push out air before sealing.
- Temperature consistency - Both methods help maintain consistent water contact and heat distribution, essential for sous vide precision.
Choosing between floating weight and water displacement depends on personal preference and the type of food being cooked.
The Challenge of Food Floating During Sous Vide
Floating food during sous vide cooking poses a challenge as it prevents even heat transfer and proper water circulation. Floating weights exert direct pressure on food, ensuring it stays submerged, while the water displacement method minimizes air pockets without adding weight. Choosing the right technique enhances cooking precision and results in evenly cooked, safely prepared dishes.
What Is a Floating Weight?
A floating weight is a device used in sous vide cooking to keep vacuum-sealed bags submerged during the cooking process. It prevents the bags from floating to the surface, ensuring even heat distribution and consistent cooking results.
Floating weights are typically made of heavy materials like stainless steel or silicone and are designed to rest on top of the bags without damaging them. Unlike the water displacement method, which relies on air removal by immersing the bag in water, floating weights provide a physical hold to maintain submersion. This method is especially useful for lightweight or irregularly shaped bags that tend to float during sous vide cooking.
Water Displacement: The Classic Sous Vide Method
Water displacement is the classic sous vide method that involves submerging food in a sealed plastic bag and gradually removing air by sinking the bag into water until the contents are fully immersed. This technique ensures airtight sealing to prevent water from contacting the food, which maintains flavor and texture during cooking. It is widely preferred for its simplicity and effectiveness in maintaining consistent temperature around the food.
Pros and Cons of Floating Weights
Floating weights provide consistent pressure to keep food submerged, ensuring even cooking during sous vide. They are simple to use but may shift or float away, impacting cooking precision.
- Consistent Pressure - Floating weights maintain steady submersion, promoting uniform heat distribution for optimal sous vide results.
- Potential Movement - These weights can move or float, causing uneven cooking or requiring repositioning mid-process.
- Ease of Use - Floating weights are straightforward and reusable, making them a practical choice for everyday sous vide cooking.
Advantages and Limitations of Water Displacement
Water displacement is a popular method for sealing food in sous vide cooking by submerging the bag in water to remove air, ensuring even heat transfer and preventing floating. However, this technique may be less effective with certain plastic bags and can lead to water entering the bag if not sealed properly.
- Effective Air Removal - Water displacement efficiently removes air from flexible bags, improving heat conduction during cooking.
- Cost-Efficient - It requires no special equipment, making it an accessible option for home cooks without vacuum sealers.
- Risk of Water Leakage - Improperly sealed bags can allow water intrusion, potentially compromising food quality and safety.
Which Foods Are Prone to Floating?
Foods prone to floating during sous vide cooking often include leafy greens, delicate herbs, and foods with air pockets such as gnocchi or dumplings. These items tend to resist submersion even when using water displacement methods due to trapped air and low density.
Floating weight devices apply gentle pressure to keep foods fully submerged and ensure even cooking, making them ideal for delicate or buoyant ingredients. In contrast, water displacement works best for compact, dense foods like meats and vegetables that naturally sink.
Safety Considerations with Both Methods
| Floating Weight Method | Ensures food remains fully submerged, preventing exposure to air and reducing the risk of bacterial growth. Ideal for vacuum-sealed bags, as it maintains consistent temperature and water contact. |
| Water Displacement Method | Involves partially submerging food and pressing out air to avoid floating, but may risk slight water infiltration if bags are not properly sealed. Requires careful bag sealing to maintain food safety and avoid contamination. |
| Safety Considerations | Both methods demand airtight sealing to prevent water ingress and ensure proper pasteurization. Maintaining a stable sous vide bath temperature, typically between 130degF to 165degF (54degC to 74degC), is crucial to inhibit harmful bacterial growth during cooking. |
Tips for Securing Sous Vide Bags Effectively
How can one effectively secure sous vide bags using floating weight versus water displacement methods? Floating weight involves placing a heavy, food-safe object on the bag to keep it submerged, ensuring even cooking by preventing the bag from floating. Water displacement technique expels air by submerging the bag slowly, creating a vacuum seal that enhances heat transfer and prevents water from entering the bag.
Related Important Terms
Weighted sous vide mesh
Weighted sous vide mesh bags ensure consistent food submersion by preventing flotation, optimizing heat transfer and even cooking compared to water displacement methods that rely on removing air but may allow partial buoyancy. Using weighted meshes enhances precision in temperature control during sous vide cooking, maintaining full immersion without the need for constant monitoring or manual adjustments.
Precision float anchors
Precision float anchors provide stable and consistent submersion of food bags in sous vide cooking, ensuring even heat distribution and preventing floating without compressing delicate items. Unlike water displacement methods that rely on pushing air out by volume, float anchors maintain precise positioning, enhancing cooking accuracy and texture preservation.
Silicone sous vide sinkers
Silicone sous vide sinkers provide consistent weight and stability during cooking, preventing bags from floating, unlike the variable pressure and precision challenges faced with water displacement methods. Their flexible design resists slipping, ensuring optimal food submersion and even heat distribution in sous vide baths.
Anti-float clip
Anti-float clips offer a reliable solution to keep bags submerged during sous vide cooking, preventing floating weight issues that can lead to uneven heat distribution. Compared to the water displacement method, anti-float clips provide consistent pressure, ensuring precise temperature control and optimal food texture.
Low-profile immersion weights
Low-profile immersion weights maintain consistent pressure on sous vide bags, preventing floating and ensuring even cooking without obstructing water circulation. Compared to water displacement methods, these weights provide a stable, reusable solution that enhances precision and reduces the risk of bag leakage.
Sous vide raft system
The Sous Vide Raft System uses a floating weight to stabilize food bags during cooking, preventing them from drifting and ensuring even heat distribution compared to the water displacement method, which relies solely on pushing air out by immersion. This floating weight approach enhances precision and consistency in sous vide cooking by maintaining optimal contact between the bag and the circulating water bath.
Adaptive water-lock displacement
Adaptive water-lock displacement enhances sous vide precision by sealing bags securely, preventing water ingress and maintaining consistent buoyancy compared to traditional floating weights. This method optimizes heat transfer efficiency and ensures even cooking by eliminating bag movement and reducing the risk of water contamination.
Vacuum-seal buoyancy rings
Floating weight vacuum-seal buoyancy rings prevent food bags from rising during sous vide cooking by applying consistent pressure, ensuring even heat transfer and precise temperature control. This method outperforms water displacement techniques by reducing the risk of water infiltration and maintaining vacuum integrity throughout the cooking process.
Vertical float stabilizer
A vertical float stabilizer provides precise weight distribution to maintain consistent immersion levels during sous vide cooking, ensuring stable temperature and even heat transfer. Compared to water displacement methods that rely on volume reduction, the floating weight offers superior control and prevents bags from shifting or floating, enhancing cooking accuracy.
Floating weight vs water displacement for sous vide. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com