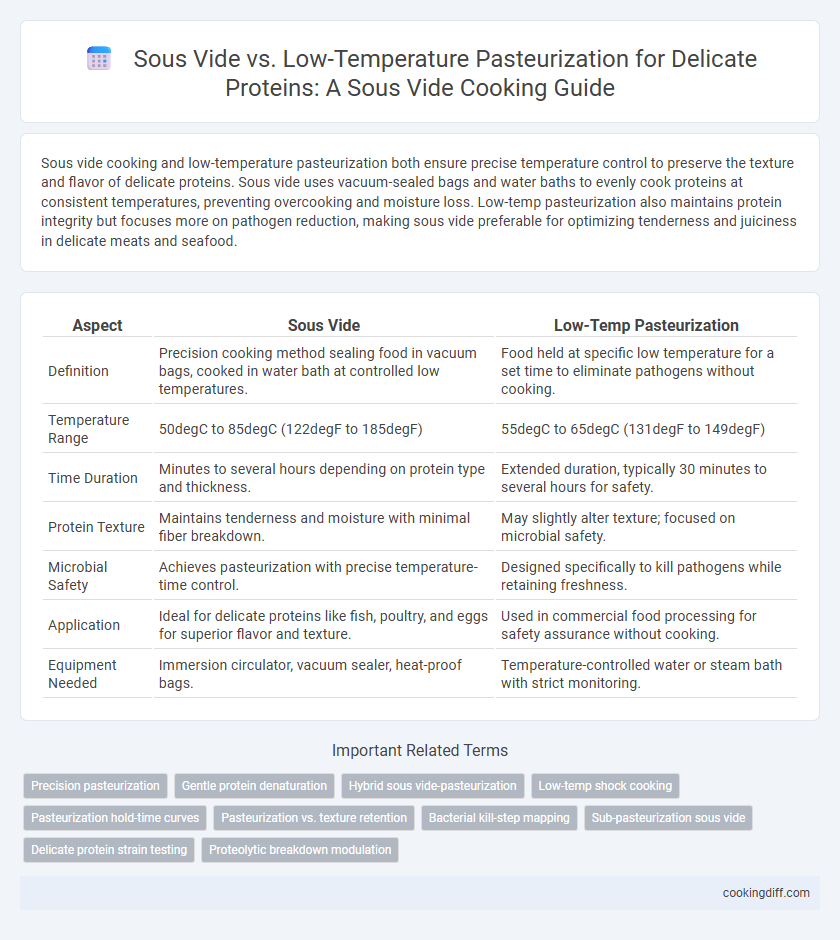
Sous vide cooking and low-temperature pasteurization both ensure precise temperature control to preserve the texture and flavor of delicate proteins. Sous vide uses vacuum-sealed bags and water baths to evenly cook proteins at consistent temperatures, preventing overcooking and moisture loss. Low-temp pasteurization also maintains protein integrity but focuses more on pathogen reduction, making sous vide preferable for optimizing tenderness and juiciness in delicate meats and seafood.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sous Vide | Low-Temp Pasteurization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Precision cooking method sealing food in vacuum bags, cooked in water bath at controlled low temperatures. | Food held at specific low temperature for a set time to eliminate pathogens without cooking. |
| Temperature Range | 50degC to 85degC (122degF to 185degF) | 55degC to 65degC (131degF to 149degF) |
| Time Duration | Minutes to several hours depending on protein type and thickness. | Extended duration, typically 30 minutes to several hours for safety. |
| Protein Texture | Maintains tenderness and moisture with minimal fiber breakdown. | May slightly alter texture; focused on microbial safety. |
| Microbial Safety | Achieves pasteurization with precise temperature-time control. | Designed specifically to kill pathogens while retaining freshness. |
| Application | Ideal for delicate proteins like fish, poultry, and eggs for superior flavor and texture. | Used in commercial food processing for safety assurance without cooking. |
| Equipment Needed | Immersion circulator, vacuum sealer, heat-proof bags. | Temperature-controlled water or steam bath with strict monitoring. |
Introduction to Sous Vide and Low-Temp Pasteurization
Sous vide cooking involves vacuum-sealing food and cooking it in a water bath at precise, controlled temperatures, preserving texture and moisture in delicate proteins. Low-temp pasteurization uses carefully monitored heat to reduce pathogens while maintaining protein integrity without overcooking.
Both techniques prioritize temperature accuracy to enhance food safety and quality, but sous vide often offers greater control over texture development. Low-temp pasteurization is commonly applied in commercial settings for efficient microbial reduction in proteins like poultry and seafood.
Key Differences in Cooking Techniques
Sous vide cooking immerses food in a precisely controlled water bath at steady low temperatures, preserving texture and moisture in delicate proteins. Low-temp pasteurization applies heat consistently to eliminate pathogens but often involves slightly higher temperatures that can alter protein structure.
- Temperature Control - Sous vide maintains exact temperatures typically between 50degC and 65degC to protect protein integrity.
- Safety Focus - Low-temp pasteurization targets microbial safety with sustained exposure to temperatures around 60degC to 70degC.
- Texture Impact - Sous vide minimizes cellular damage, resulting in tender, evenly cooked proteins.
The primary distinction lies in sous vide's precision for culinary quality versus pasteurization's emphasis on food safety through pathogen reduction.
Temperature Control and Precision
Sous vide offers unparalleled temperature control, maintaining water baths within +-0.1degC, which preserves the texture and integrity of delicate proteins such as fish and eggs. This precise regulation prevents overcooking and ensures uniform pasteurization without compromising moisture content.
Low-temp pasteurization often operates at fixed temperatures with less precise control, increasing the risk of thermal gradients that can degrade sensitive proteins. Sous vide's consistent heat distribution allows exact time-temperature combinations to achieve both safety and optimal tenderness efficiently.
Impact on Protein Texture and Tenderness
Sous vide cooking maintains precise temperature control, preserving the delicate texture and tenderness of proteins by preventing overcooking and moisture loss. Low-temp pasteurization uses slightly higher temperatures that can cause subtle changes in protein structure, potentially leading to a firmer texture.
The gentle heat application in sous vide allows collagen in proteins like fish and poultry to break down slowly, enhancing tenderness and mouthfeel. Low-temp pasteurization primarily aims at food safety, which sometimes compromises the delicate protein matrix, resulting in less juicy outcomes. Overall, sous vide offers superior texture retention for delicate proteins compared to low-temp pasteurization methods.
Flavor Preservation in Delicate Proteins
Sous vide cooking preserves the natural flavors of delicate proteins by maintaining precise, consistent temperatures that prevent overcooking and moisture loss. Low-temp pasteurization achieves safety but often involves longer exposure times that can diminish subtle flavor compounds. The controlled environment of sous vide enhances tenderness and flavor retention, making it superior for delicate proteins like fish and shellfish.
Food Safety Considerations
Sous vide cooking and low-temp pasteurization both maintain temperature precision to ensure the safety of delicate proteins, but sous vide often allows longer cooking times at lower temperatures. Food safety hinges on reaching specific temperature-time combinations to effectively eliminate pathogens without compromising texture or flavor.
- Temperature Control - Sous vide provides consistent temperature regulation, reducing the risk of undercooking delicate proteins compared to traditional low-temp pasteurization.
- Pathogen Reduction - Both methods require precise time-temperature combinations to achieve pasteurization levels that inhibit harmful bacteria like Salmonella and Listeria.
- Packaging and Sealing - Vacuum-sealing in sous vide minimizes oxygen exposure, which helps prevent microbial growth and extends the safety of cooked proteins.
Time Efficiency and Workflow
Sous vide offers precise temperature control that accelerates cooking times for delicate proteins compared to traditional low-temp pasteurization methods. This method streamlines workflow by reducing the need for constant monitoring, allowing chefs to multitask efficiently. Time efficiency gained through sous vide enhances kitchen productivity while maintaining optimal protein texture and safety.
Equipment and Accessibility
Sous vide equipment offers precise temperature control ideal for delicately cooking proteins, ensuring consistent texture and safety. Low-temp pasteurization requires industrial-grade equipment that is often less accessible for home cooks.
- Sous vide devices - Compact immersion circulators provide accurate and affordable temperature regulation at home.
- Low-temp pasteurization systems - Typically large-scale and costly, suited for commercial food processing.
- Accessibility - Sous vide setups are widely available for consumers, while low-temp pasteurization remains limited to specialized facilities.
Suitable Proteins for Each Method
Which delicate proteins are best suited for sous vide compared to low-temp pasteurization? Sous vide excels with tender proteins like fish and eggs by maintaining precise temperature control to enhance texture and flavor without overcooking. Low-temp pasteurization is ideal for proteins requiring microbial safety while preserving delicate structure, such as certain poultry and seafood varieties.
Related Important Terms
Precision pasteurization
Sous vide cooking offers unparalleled precision pasteurization by maintaining exact temperatures over extended periods, ensuring delicate proteins like fish or eggs are safely cooked without compromising texture or flavor. Low-temp pasteurization methods may achieve safety but often lack the consistent temperature control that sous vide provides, resulting in less optimal protein integrity.
Gentle protein denaturation
Sous vide cooking ensures gentle protein denaturation by maintaining precise low temperatures, preserving texture and moisture in delicate proteins such as seafood and eggs. Low-temp pasteurization also uses controlled heat to destroy pathogens but often lacks the fine temperature control that prevents over-denaturation, making sous vide superior for tender results.
Hybrid sous vide-pasteurization
Hybrid sous vide-pasteurization combines precise temperature control from sous vide cooking with rigorous microbial safety standards of low-temp pasteurization, enhancing tenderness and flavor retention in delicate proteins like fish and shellfish. This method achieves optimal texture by maintaining protein integrity while ensuring pathogen reduction, making it ideal for high-quality, safe gourmet preparations.
Low-temp shock cooking
Low-temp shock cooking in sous vide applies a brief exposure to slightly higher temperatures than typical low-temp pasteurization, rapidly destroying surface pathogens while preserving the delicate proteins' texture and moisture. This precise temperature control minimizes protein denaturation, ensuring optimal tenderness and flavor retention in sensitive foods like seafood and eggs.
Pasteurization hold-time curves
Sous vide cooking utilizes precise low-temperature control to achieve pasteurization hold-time curves that ensure the safety and texture of delicate proteins without overcooking. These hold-time curves define specific temperature and time combinations that inactivate pathogens while preserving the protein's tenderness and moisture retention.
Pasteurization vs. texture retention
Sous vide cooking allows precise temperature control to achieve low-temp pasteurization, effectively eliminating pathogens while preserving the delicate texture of proteins like fish and eggs. Unlike traditional pasteurization methods that often cause protein denaturation and firmness, sous vide maintains moisture and tenderness by cooking proteins gently and evenly.
Bacterial kill-step mapping
Sous vide cooking and low-temperature pasteurization both rely on precise temperature control to ensure bacterial kill-step efficacy in delicate proteins, with sous vide typically maintaining 55-60degC for extended periods to achieve pathogen reduction without compromising texture. Mapping bacterial lethality curves reveals sous vide's advantage in delivering consistent, uniform pasteurization by maintaining stable thermal conditions that target specific bacteria such as Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella spp.
Sub-pasteurization sous vide
Sub-pasteurization sous vide utilizes precisely controlled temperatures below traditional pasteurization thresholds to gently cook delicate proteins, preserving texture and moisture while achieving safety and extended shelf life. This method minimizes cellular damage compared to low-temp pasteurization, making it ideal for tender cuts like fish and seafood.
Delicate protein strain testing
Sous vide cooking precisely controls temperature to maintain protein integrity, minimizing strain and preserving texture in delicate proteins such as fish and eggs, unlike traditional low-temp pasteurization which often exposes proteins to higher temperatures for extended periods causing denaturation. Laboratory strain testing on sous vide-prepared samples shows significantly lower protein aggregation and shear force values compared to low-temp pasteurized counterparts, highlighting enhanced tenderness and structural preservation.
Sous vide vs low-temp pasteurization for delicate proteins. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com