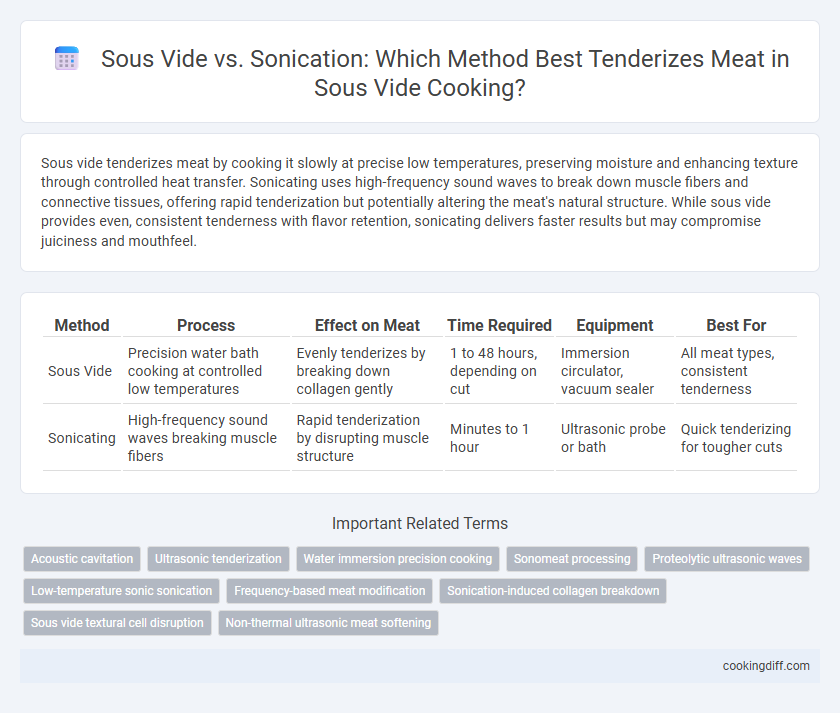
Sous vide tenderizes meat by cooking it slowly at precise low temperatures, preserving moisture and enhancing texture through controlled heat transfer. Sonicating uses high-frequency sound waves to break down muscle fibers and connective tissues, offering rapid tenderization but potentially altering the meat's natural structure. While sous vide provides even, consistent tenderness with flavor retention, sonicating delivers faster results but may compromise juiciness and mouthfeel.
Table of Comparison
| Method | Process | Effect on Meat | Time Required | Equipment | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sous Vide | Precision water bath cooking at controlled low temperatures | Evenly tenderizes by breaking down collagen gently | 1 to 48 hours, depending on cut | Immersion circulator, vacuum sealer | All meat types, consistent tenderness |
| Sonicating | High-frequency sound waves breaking muscle fibers | Rapid tenderization by disrupting muscle structure | Minutes to 1 hour | Ultrasonic probe or bath | Quick tenderizing for tougher cuts |
Introduction to Meat Tenderizing Techniques
Meat tenderizing techniques are essential for enhancing texture and flavor by breaking down muscle fibers and connective tissues. Sous vide cooking uses precise temperature control to gently tenderize meat over extended periods, preserving moisture and resulting in consistent texture.
Sonicating employs ultrasonic waves to disrupt muscle structure and accelerate tenderizing, often used in combination with marination. Both methods aim to improve tenderness, but sous vide offers superior control for uniform doneness, while sonicating is valued for reducing processing time.
How Sous Vide Works for Tenderizing Meats
Sous vide tenderizes meat by cooking it slowly at precise, low temperatures in a water bath, allowing collagen to break down into gelatin without overcooking the protein. This method ensures even cooking and retains moisture, resulting in a consistently tender texture.
- Temperature Control - Maintains a stable, low cooking temperature between 130degF and 160degF for extended periods.
- Collagen Breakdown - Converts tough connective tissues into tender gelatin through prolonged heat exposure.
- Moisture Retention - Vacuum sealing prevents moisture loss, enhancing juiciness and tenderness.
Sous vide's controlled environment allows precise collagen gelatinization, unlike sonication which physically disrupts tissue structure.
The Science Behind Sonication in Meat Preparation
Sonication uses high-frequency sound waves to create cavitation bubbles that disrupt muscle fibers and connective tissues in meat, enhancing tenderness. This process accelerates enzymatic reactions and improves marinade penetration by altering the meat's microstructure at a cellular level. Compared to sous vide, which relies on precise temperature control for protein denaturation, sonication offers a physical method to achieve tenderization more rapidly and can be combined with sous vide for optimized texture.
Texture and Tenderness: Sous Vide vs. Sonication
Sous vide cooking delivers uniformly tender and juicy meat by gently heating it at precise low temperatures over extended periods, allowing collagen to break down without drying out the protein. Sonication tenderizes meat through ultrasonic waves that disrupt muscle fibers and connective tissue, resulting in faster tenderization but potentially inconsistent texture depending on intensity and exposure. Comparing texture and tenderness, sous vide offers greater control and consistent mouthfeel, while sonication provides rapid softening but may compromise uniformity in meat quality.
Flavor Retention: Which Method Excels?
Which method preserves flavor better, sous vide or sonicating for tenderizing meats? Sous vide excels in flavor retention by cooking meat slowly at a precise, low temperature, allowing natural juices and aromas to infuse deeply. Sonicating can disrupt meat fibers more aggressively, often leading to some loss of subtle flavors and moisture.
Impact on Meat Juiciness: Sous Vide Compared to Sonication
| Method | Impact on Meat Juiciness | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Sous Vide | Maintains high juiciness by cooking meat at precise low temperatures and retaining natural juices within vacuum-sealed bags. | Consistent results in texture and moisture retention; ideal for tender, succulent meats. |
| Sonication | May increase injection of moisture temporarily but can cause uneven tenderness and potential moisture loss during cooking. | Uses ultrasonic waves to disrupt muscle fibers; risk of over-processing leading to drier textures. |
Equipment and Accessibility for Home Cooks
Sous vide machines offer precise temperature control through immersion circulators, making them accessible and user-friendly for home cooks seeking consistent meat tenderizing. Sonicating devices, often used in professional kitchens, require specialized ultrasonic equipment that can be costly and less practical for everyday home use.
The sous vide method involves simple setup with affordable, widely available equipment such as water baths and vacuum sealers, which are increasingly popular among home chefs. Sonicating for tenderizing meat relies on ultrasonic waves to break down muscle fibers but necessitates advanced gadgets rarely found outside commercial kitchens. This makes sous vide a more convenient and accessible option for culinary enthusiasts aiming for tender, perfectly cooked meats at home.
Time Efficiency: Sous Vide Versus Sonication
Sous vide tenderizes meat by cooking it slowly at a precise low temperature over several hours, ensuring even texture and flavor development. Sonication uses ultrasonic waves to disrupt muscle fibers quickly, significantly reducing tenderizing time but sometimes affecting meat integrity.
- Sous vide requires extended cooking durations - Typically, tenderizing takes from 1 to 48 hours, depending on meat type and desired texture.
- Sonication offers rapid tenderizing - Ultrasound can achieve similar tenderness in minutes to an hour by mechanical disruption of meat fibers.
- Time efficiency varies by method - Sonication is faster but may alter meat quality, whereas sous vide balances tenderness with flavor preservation over longer timeframes.
Safety Considerations in Meat Tenderizing Methods
Sous vide cooking ensures precise temperature control, reducing the risk of harmful bacteria growth during the meat tenderizing process. Vacuum-sealing in sous vide also minimizes cross-contamination, enhancing food safety.
Sonicating, while effective in breaking down meat fibers, can create uneven temperature zones leading to potential bacterial hotspots. Proper calibration and monitoring are essential in sonicating to maintain safety standards comparable to sous vide.
Related Important Terms
Acoustic cavitation
Acoustic cavitation generated during sonication creates microbubbles that collapse violently, disrupting muscle fibers and connective tissue to tenderize meat more rapidly than sous vide's slow, low-temperature cooking method. While sous vide enhances meat tenderness through precise temperature control and prolonged heat exposure, sonication's acoustic cavitation offers a mechanical alternative by breaking down tissue structures without thermal degradation.
Ultrasonic tenderization
Ultrasonic tenderization uses high-frequency sound waves to break down muscle fibers and connective tissue, enhancing meat tenderness more rapidly compared to sous vide cooking. This method preserves the meat's natural juices and texture while significantly reducing the overall tenderizing time.
Water immersion precision cooking
Sous vide uses precise water immersion cooking at controlled low temperatures over extended periods, resulting in evenly tenderized meats by breaking down collagen without overcooking. Sonication, while accelerating tenderization through ultrasonic waves, lacks the temperature control and uniform cooking benefits inherent to sous vide precision, often yielding less consistent texture and flavor development.
Sonomeat processing
Sonomeat processing uses high-intensity ultrasonic waves to disrupt muscle fibers, accelerating tenderization more rapidly than traditional sous vide methods. Unlike sous vide, which relies on precise temperature control over extended cooking times, sonomeat combines ultrasonic cavitation and controlled heat to enhance meat texture while preserving juiciness and flavor.
Proteolytic ultrasonic waves
Proteolytic ultrasonic waves in sonication accelerate meat tenderization by disrupting muscle fibers and enhancing enzyme activity at a molecular level, offering a rapid alternative to the slow, precise temperature control of sous vide cooking. While sous vide maintains optimal enzymatic conditions to break down collagen gradually, sonication intensifies proteolytic effects through mechanical vibrations, significantly reducing tenderizing time without compromising moisture retention.
Low-temperature sonic sonication
Low-temperature sonic sonication enhances meat tenderization by using ultrasonic waves to disrupt muscle fibers, preserving juiciness while accelerating protein breakdown compared to traditional sous vide methods. This technique maintains precise control over temperature and texture, resulting in uniformly tender meat with shorter processing times.
Frequency-based meat modification
Sous vide uses low-temperature, long-time cooking to evenly tenderize meat by gently breaking down connective tissues, while sonicating employs high-frequency sound waves to mechanically disrupt muscle fibers for rapid tenderization. Frequency-based meat modification through sonication enhances collagen solubilization and protein denaturation without heat, complementing sous vide's precision temperature control to optimize texture and juiciness.
Sonication-induced collagen breakdown
Sonication accelerates collagen breakdown through ultrasonic waves that disrupt collagen fibers, enhancing meat tenderness more rapidly than traditional sous vide cooking. While sous vide uses precise low-temperature cooking to gradually soften connective tissues, sonication promotes immediate mechanical fragmentation of collagen, offering a complementary method for tenderizing tough cuts of meat.
Sous vide textural cell disruption
Sous vide cooking tenderizes meat by precisely controlling temperature to gently break down collagen and muscle fibers, promoting enzymatic activity that disrupts cell structure for enhanced texture. This slow, consistent heat treatment preserves moisture while softening connective tissues, resulting in a uniform, tender bite without the cellular damage caused by intense mechanical methods like sonicating.
Sous vide vs sonicating for tenderizing meats. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com